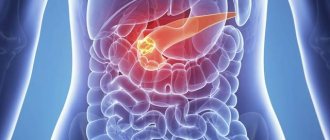
Acute edematous pancreatitis is familiar to a considerable number of people. Pathology occurs as a result of the inflammatory process. Patients themselves contribute to its occurrence. By eating improperly and abusing alcohol, people create favorable conditions for the development of the disease. Often the cause is problems in the duodenum. Gastritis provokes the disease.
Patient's gastritis
With proper treatment, the disease is curable. A frivolous attitude towards lifestyle and nutrition becomes the cause of pancreatic necrosis, during which the pancreas becomes inflamed, enlarges, and edema appears. Edematous pancreatitis is a mild form of inflammation. The structure of the gland has a lobular appearance; foci of necrosis and exudate may occur in the abdominal cavity.
Causes:
- Fried or fatty foods;
- A sharp transition from lean foods to fatty foods;
- Failure to comply with the gradual transition to the usual regimen after dietary nutrition;
- Toxic drugs;
- Change of basic food products (to spicy unusual foods);
- Alcohol consumption;
- Ingestion of toxic substances into the body.
Doctors say that edematous pancreatitis often occurs due to problems in the digestive system, due to improper food intake, a sudden diet break, or alcohol consumption. Some patients mistakenly talk about the relationship between microbes and the appearance of edema, but the cause of the inflammatory process and swelling is spasm and disturbances in digestive secretion.
Pancreatic enzymes are very aggressive and long-term exposure causes destructive processes in the body. It is necessary to identify swelling in time and begin treatment, avoiding necrosis. Edematous pancreatitis also affects other areas responsible for the endocrine system. For this reason, the secretion of enzymes decreases, and impaired synthesizing processes of glucagon and insulin lead to diabetes mellitus.
What complications can there be?
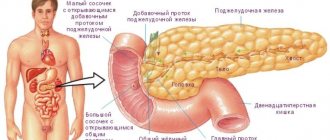
The pancreas produces enzymes necessary to digest food. These are amylase, lipase and protease. They enter the duodenum through ducts, where they are activated and break down proteins, fats and carbohydrates of food into smaller structures. In addition, some of its cells are needed to produce hormones, primarily insulin. It is necessary for the normal absorption of glucose and its transport to tissues. Due to the inflammatory process, gland cells die and are replaced by fibrous tissue, therefore the number of enzymes and hormones decreases.
Pancreatitis can occur in acute or chronic form. Acute inflammation is severe, with fever, severe pain and digestive disorders. The earlier treatment for this disease is started, the better the prognosis.
But even if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, after recovery the patient will feel the consequences of pancreatitis all his life. In most cases, the disease becomes chronic. After all, destroyed pancreatic cells are not restored, so its functions are reduced.
At the same time, women are less likely to develop complications, since they are more responsible about their health, follow a diet and follow doctor’s recommendations. In men, exacerbations occur more often, which leads to faster destruction of pancreatic tissue. The risk of developing serious complications is especially high in those who abuse alcohol.
There are several most common complications that often accompany pancreatitis:
- purulent processes - abscess, phlegmon, sepsis, peritonitis;
- internal bleeding due to destruction of the walls of blood vessels;
- vein thrombosis;
- blockage of the bile ducts and bile stagnation;
- the appearance of cysts and other tumors;
- sclerosis or fibrosis of the pancreas;
- diabetes;
- intestinal obstruction;
- kidney dysfunction;
- pathologies of other organs.
Conclusion
For those people who have overcome pancreatitis, recovery is an important part of life's journey. To prevent an exacerbation from happening, to prevent the disease from becoming chronic if you follow advice, diets and a healthy lifestyle is, in fact, quite simple. Quitting alcohol and cigarettes and introducing proper nutrition into your life is not at all difficult. The ease of life without illness is much more important than the temporary pleasure (and bad habits are actually a rather dubious way to get pleasant sensations) from taking poison in the form of fatty foods and red wine.
Consequences of acute pancreatitis
In acute pancreatitis, inflammation develops quickly and without timely treatment can cause serious complications. This form of the disease affects the functioning of all organs. After all, digestive enzymes enter the blood, which causes symptoms of intoxication. Emerging toxins can penetrate the brain, resulting in toxic encephalopathy.
If the outflow of pancreatic juice is disrupted due to the inflammatory process, it accumulates in the gland. At the same time, enzymes continue to be produced, and the inflammatory process causes their activation. They begin to digest the tissues of the gland itself - pancreatic necrosis develops. As a result, the vessels are damaged, which causes bleeding, or the walls of the gland. Because of this, its contents enter the abdominal cavity and peritonitis develops. Liver abscesses, retroperitoneal phlegmon, and gastrointestinal bleeding may occur.
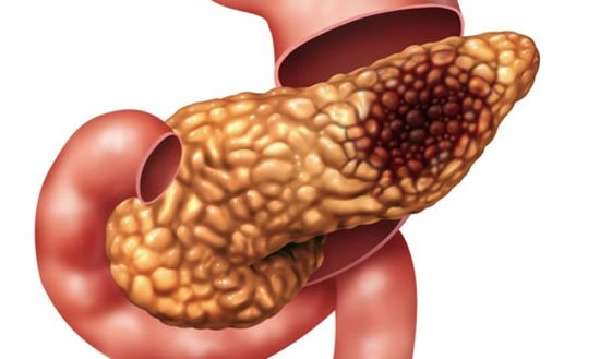
A severe inflammatory process can lead to necrosis of pancreatic tissue.
Shock is also a serious consequence of acute pancreatitis. In the presence of infection, infectious-toxic shock develops; after bleeding, hypovolemic shock develops. But the most common is pain shock, since pain during acute inflammation can be very severe.
Attention: all these conditions require immediate hospitalization of the patient. Without timely medical care, multiple organ failure may develop.
The reason for this is an enlargement of the liver and a violation of its detoxification functions. As a result, a large load falls on the kidneys. Without timely medical care, the patient will fall into a coma. The consequence of this can be death. Most often, the cause of death is a late visit to the doctor, resulting in the development of renal or cardiovascular failure, purulent inflammation or bleeding. The risk of death increases with age, alcohol intoxication or poor diet.
Causes of the disease
The formation of pancreatic dysfunction of the pancreas in an acute form of manifestation may be preceded by the presence of the following factors:
- excessive consumption of alcohol-containing products,
- regular consumption of fried and fatty foods, as well as smoked and salty foods,
- a large number of extra pounds,
- development of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, hepatitis,
- penetration of viral infections into the body, in the form of mumps or hepatitis B,
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum and stomach, as well as gastritis and the progressive stage of tumor pathology,
- presence of hyperparathyroidism,
- infestation by helminth representatives,
- abnormal narrowing of the passage in the pancreatic ducts,
- disruption at the hormonal level,
- blunt trauma to the abdominal cavity, as well as surgical interventions,
- development of severe food allergies,
- progression of cystic fibrosis,
- smoking,
- hereditary predisposition.
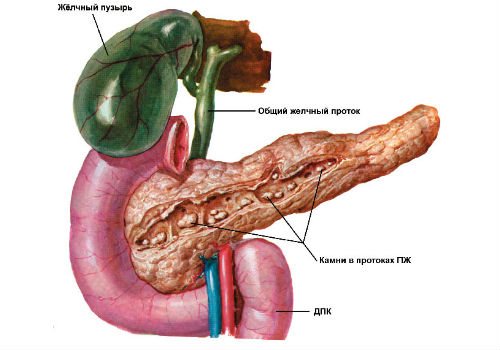
Consequences of the chronic form
Not all patients know the dangers of chronic pancreatitis. Many people believe that if there is no pain, then treatment is not necessary. But non-compliance with the diet leads to the gradual death of pancreatic cells. This negatively affects the work of all organs. Pancreatitis especially affects the digestive system. After all, due to a disruption in the production of enzymes, food enters the intestines undigested. Nutrients are less well absorbed, so the patient may develop anemia, weakness, drowsiness, and decreased performance. He is losing weight and losing his appetite.
Patients with chronic pancreatitis experience increased fatigue and decreased blood pressure. If insulin production is not impaired, blood sugar levels will drop. As a result, oxygen starvation develops, which primarily affects brain cells.
The danger of chronic pancreatitis is that due to a lack of nutrients and constant intoxication, susceptibility to infections increases. Inflammation of the pancreas can be complicated by a purulent process, sometimes abscesses, ulcers or fistulas appear. Because of this, blood poisoning is possible. In addition, the patient becomes vulnerable to viral diseases. And against the background of constant poor health, he develops depression, possibly even psychosis.
Attention: if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations and deviates from the diet, the process of destruction of pancreatic cells occurs faster.
Its cells are replaced by fibrous ones, fibrosis develops. In addition, tumors begin to form. Most often these are cysts or pseudocysts, but oncology can become a complication of chronic pancreatitis.
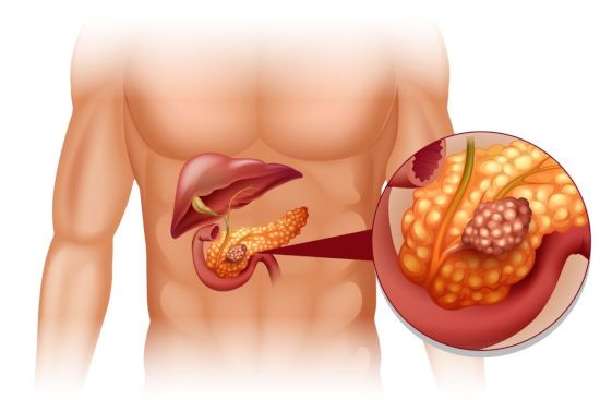
One of the most serious consequences of pancreatitis is the appearance of tumors.
Another serious consequence of pancreatic inflammation is diabetes. It occurs when inflammation leads to the destruction of cells responsible for producing insulin.
Prevention of the disease and its relapses
It is difficult to cure chronic pancreatitis, so it is worth remembering that it is easier to avoid this disease by adhering to simple rules:
- Eat right - forget about fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, fast food.
- Maintain drinking regime.
- Do not self-medicate or uncontrolledly take medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- Do not overeat, eat in small portions.
- Do not abuse strong alcoholic drinks.
- Stop smoking.
- Do not drink strong tea and coffee.
- The diet should not be dominated by fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods.
- In order to prevent pancreatitis and other dangerous diseases, systematically undergo examinations by medical specialists.
- Do an ultrasound at least once every six months.
- Lead an active lifestyle.
Treatment for pancreatitis is complex and combines proper nutrition and replacement therapy. The internal organs and systems of the human body are closely interconnected, so monitor the condition of the liver, gall bladder and stomach. Traditional methods will tell you how to treat pancreatitis using folk remedies, as well as support the body during remission.
Effect on the digestive system
The most common complication of pancreatitis is disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Decreased production of basic digestive enzymes leads to poor digestion of food. Because of this, there is a deficiency of many vitamins and minerals. In addition, intestinal function is disrupted, and ulcers or erosions often develop on its walls. The patient constantly experiences discomfort, he often experiences diarrhea, constipation, and flatulence. In the most severe cases, this condition leads to intestinal obstruction.
A prolonged inflammatory process can provoke diseases of neighboring organs. The gallbladder is most often affected. The bile ducts exit into the duodenum along with the pancreatic ducts, so they are the first to be affected by the inflammatory process. Cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, and cholelithiasis develop. And if the enlarged gland blocks the ducts, stagnation of bile may occur and obstructive jaundice develops. In this case, only surgery can save the patient.
Gastritis, peptic ulcers, esophageal erosions, and gastroduodenal reflux are also frequent companions of pancreatitis. Sometimes degeneration of liver cells and the development of lipomatosis may begin.
Cardiovascular and respiratory systems
When pancreatic enzymes enter the bloodstream, this negatively affects the functioning of all organs. An inflammatory process in the pancreas can disrupt the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This is due to insufficient liver function, lack of essential microelements and an increase in the size of the gland. As a result, the heart rhythm is disrupted and blood clotting decreases. The consequence of this may be tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and frequent bleeding. Vascular spasms also occur, and blood pressure may decrease.
Intoxication and lack of certain trace elements in the blood leads to a decrease in the amount of oxygen. This negatively affects the state of the respiratory system. Hypoxia develops, and fluid can accumulate in the lungs. Any cold leads to severe pneumonia.
Oncology
During the inflammatory process, pancreatic cells die. The consequence of this is often necrosis, which can lead to malignant degeneration of cells. Most often, this organ is affected by adenocarcinoma.
Attention: the main cause of malignant tumors is calculous pancreatitis, in which stones form in the ducts of the gland and block them.
Pancreatic cancer is a very serious disease that is often fatal. Only at the initial stage can the part of the gland damaged by the tumor be removed. Even complete resection of an organ in the absence of metastases to other organs can save the patient’s life.
Rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after acute pancreatitis is a rather long and painstaking process, during which unquestioning adherence to all instructions of the treating specialist is necessary. Moreover, regular examination procedures and treatment in a sanatorium-resort are prescribed every six months. It is recommended to visit balneological resorts, where the main attraction is hydrocarbonate waters with medium and low levels of mineralization. Among the most popular resorts of this type are:
- Borjomi,
- Essentuki,
- Morshyn,
- Truskavets.

Carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures is possible only during a period of stable remission, when for a long period of time there are simply no symptomatic manifestations of pancreatic pathology.
The entire rehabilitation period is divided into three main stages, which we will consider below.
Among other things, the patient, together with his attending physician, draws up an individual diet menu with all his (the patient’s) culinary preferences.
Elimination of pancreatic pathology at the first stage of rehabilitation is based on abstaining from eating fried and fatty foods, as well as sweet and salty foods to ensure maximum rest of the parenchymal organ.
During the rehabilitation period, medications can be administered either intramuscularly or intravenously.
After 2-3 months of following a strict dietary diet, the patient, depending on the condition of his pancreas, may be allowed to eat lean varieties of meat and fish, fresh fruit crops, etc.
The next stage of the rehabilitation period after acute pancreatic disease is adherence to a simplified dietary diet, which may already include an impressive amount of protein foods and fats.
Drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking tobacco, even in small doses, is strictly prohibited during the rehabilitation period.
The last stage of rehabilitation is a complete transition to proper nutrition, eating only healthy foods in combination with an annual visit to the gastroenterologist’s office and undergoing a detailed examination.
Remember that acute pancreatitis can cause a prolonged period of disability. And after the patient’s general condition has normalized, employment should be carried out in conditions where the following will be excluded:
- physical stress,
- trauma to the abdominal area,
- various body concussions,
- contact with toxic substances.
A protracted type of acute form of pancreatic disease without prompt and timely treatment can lead to long-term disability and disability of groups II and III.
How to avoid complications
A favorable outcome of the disease is possible only with timely medical care. The patient must be kept at rest, completely avoid eating, and apply a cold compress to the pancreas area. Medicines to relieve pain and inflammation should be prescribed by a doctor.
But even after recovery, such a disease does not go away without leaving a trace. In most cases, pancreatitis becomes chronic. And this forces the patient to follow certain rules and take certain medications for the rest of his life. Only this and a special diet will help preserve the functions of the pancreas and avoid complications.
Sequence of treatment
Treatment of acute pancreatitis consists of completely abstaining from drinking alcohol-containing beverages and following a dietary diet that consists of consuming foods with a low concentration of animal fats. It is also necessary to exclude all medications that can irritate an already affected gland.
The main objective of therapeutic measures is to eliminate pain, corrective procedures to restore its functionality, as well as to prevent and treat possible complications.
In order to eliminate pain, analgesic drugs are prescribed, and the dosage is determined only by an experienced specialist. For these purposes, the following drugs are most often used:
- No-Shpa, or domestic Drotaverine,
- Spasmalgon,
- Mebeverine.
If conservative treatment methods do not provide the desired effect, then the question of surgical intervention is raised. Surgical treatment of the disease can maximize the life cycle of patients, improving the quality of their life.
It is important to remember that during an attack of acute pancreatic disease, you should never take enzymatic spectrum drugs such as Festal or Mezim. They can increase the intensity of intestinal motility and cause the development of diarrhea, which will contribute to a significant deterioration of the patient’s condition.
Moreover, it is not recommended to use choleretic drugs, as well as various herbs and decoctions of traditional healers, without consulting an experienced, qualified gastroenterologist.
After acute pancreatitis, the patient's treatment should consist of further rehabilitation measures.