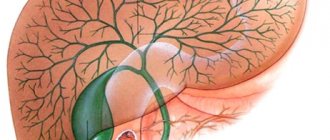
Inflammation of the gallbladder occurs at different ages. Cholecystitis in children develops gradually, often in the absence of characteristic symptoms. The inflammatory process appears against the background of infection, parasites, and in combination with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to its latent course, timely diagnosis is difficult. Treatment is conservative; surgical intervention is not performed on children.
Features of childhood cholecystitis
Detection of gallbladder inflammation in childhood is not uncommon. As in adults, pathology can be acute or chronic. But in children, cholecystitis is not always accompanied by the formation of stones; pediatricians often diagnose the calculous form.
Pathology develops slowly. The patient becomes lethargic, weakened, and complains of pain in the abdomen and head. The gallbladder is gradually deformed, the elastic tissue of its walls is replaced by dense connective tissue. As a result, the organ loses its ability to contract and becomes atonic, turning into a flaccid sac.
Unfortunately, the characteristic clinical picture may be completely absent, which greatly increases the risk of complications. Advanced forms of cholecystitis are accompanied by the formation of purulent secretion, and in the absence of timely medical care, the formation of necrotic areas with subsequent perforation and the development of peritonitis.
Intestinal dyskinesia: symptoms and signs of intestinal disorder in children
The term “intestinal dyskinesia” is used by gastroenterologists to define a complex of intestinal disorders, the mechanism of which is caused by weakness of tone and impaired motility of the tract. Deterioration in function can be observed in different parts of the organ, but most often children are diagnosed with dyskinesia of the large intestine.
Why does dyskinesia develop?
Doctors say that the condition of the digestive organ is affected by a diet in which the child consumes little fiber. Also, the primary form of dyskinesia can develop due to intestinal infection.
Secondary colitis develops in response to past and chronic diseases of the peritoneal organs (spleen, liver, pancreas). Hormonal disorders and diabetes mellitus are also among the predisposing factors.
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky calls for looking for the causes of intestinal dyskinesia in disorders of the nervous system. The pediatrician explains the neurogenic factor as the incorrect conduction of nerve impulses, which creates the preconditions for spasm or increased peristalsis. To avoid chronicity of the process, it is important to differentiate dyskinesia from other pathologies, otherwise treatment of the disease will be ineffective.
Clinical picture of dyskinesia in children
Intestinal dyskinesia, regardless of the patient’s age, occurs in two forms:
- hypomotor (atonic) pathology, characterized by constant difficulty in defecation (constipation);
- hypermotor (spastic), caused by accelerated evacuation of gastric contents into the large intestine. A sign of this form of dyskinesia is abdominal pain and diarrhea with unstructured feces.
In recent years, doctors are increasingly diagnosing functional intestinal disorders in children associated with enzymatic deficiency.
Doctors find two explanations for this condition - hidden chronic pancreatitis and stagnation in the biliary system. Bile deficiency impairs the quality of processing fatty foods.
A characteristic symptom of GIB is considered to be fatty stool with mucous inclusions.
Other symptoms signaling intestinal disorders include:
- bad feeling;
- decreased appetite;
- poor physical activity;
- pale skin tissue;
- painful sensations during physical activity.
A secondary inflammatory process that affects the thin or thick part of the tract is manifested by symptoms such as anemia, muscle dystrophy, and sudden weight loss. Stool analysis shows intestinal dysbiosis.
Flatulence, or increased gas production, helps to suspect dyskinesia in a baby. The baby's tummy becomes hard, painful, and a loud rumbling sound is heard from it.
The baby is worried, twitches its legs, and refuses to feed.
Diagnostic measures for dyskinesia
Due to its similarity with other gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal dyskinesia is diagnosed by excluding the suspected pathology. A phased examination of a child includes several activities:
- endoscopy;
- coprogram;
- irrigoscopy;
- biopsy - according to indications;
- stool occult blood test;
- exclusion of pathological neoplasms in the intestine.
Principles of disease therapy in children
Treatment of small children for intestinal dyskinesia is based on the organization of the diet and the correct distribution of hours of activity and rest. Patients are recommended to eat frequently and in small portions. In a diet that accelerates the treatment of dyskinesia, the following should prevail:
- juices;
- dried bread;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- slimy water porridges;
- products with vegetable fiber;
- fermented milk products, especially with live lactobacilli.
When treating intestinal dyskinesia in a child under one year of age, it is important to adjust the balance of food enzymes. For this purpose, very young children are prescribed special medications to compensate for the lack of enzymes. For preschoolers and adolescents, treatment is supplemented with herbal preparations with tansy, St. John's wort, and bittersweet.
If a child suffers from severe pain, non-drug assistance can be provided by applying heat to the peritoneal area. If the procedure is unsuccessful, the patient can be given No-shpu or Drotaverine, calculating the dosage according to age and weight.
To relax the nervous system, treatment includes antidepressants or antipsychotics. Additionally, with intestinal dyskinesia, children can be prescribed autogenic training, exercise therapy, hypnosis, and acupuncture.
Folk remedies for intestinal dyskinesia
Harmless treatment of spastic and atonic colitis is carried out using folk remedies. Mint leaves, chamomile flowers, and valerian roots contribute to the restoration of normal peristalsis of the tract. The components take 1 tsp. each, pour a glass of boiling water over the phyto mixture and leave covered for 20 minutes. The napar is filtered and given to the child 3 times. 100 ml per day half an hour before meals.
Another remedy is obtained from sage and yarrow herbs, oak bark, St. John's wort flowers, and motherwort raw materials. The amount of each ingredient is 2 tbsp. l. The collection is doused with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for a couple of hours. Then the drug is filtered and the child is given 4 rubles. per day, measuring 100 ml of drink each time.
Our specialist comments
- Organize bowel movements in a timely manner if your baby suffers from constipation.
Difficulties with the excretion of feces entail not only dyskinesia - their danger lies in general intoxication of the body, loss of appetite and decreased performance. Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract contributes to stagnation and rotting of food masses, which can subsequently cause the child to develop allergies. - If dyskinesia causes a frequent urge to defecate, give your baby a decoction of chamomile and calendula flowers, thick jelly or a hard-boiled egg.
Specific treatment for intestinal disorder will be prescribed by your pediatrician. - To relieve spastic colic, use compresses.
Apply a bandage soaked in vinegar solution to the intestinal area. The ratio of acidic product and water is ½ cup to 3 liters. If you have the opportunity to give your child a pine bath, be sure to take advantage of it. Treat yourself with paraffin applications.
Prevention of intestinal dyskinesia for children is to create a favorable atmosphere in the family, avoid stress, and eat high-quality foods without dyes, preservatives and flavoring additives. If you have constipation, it is important to limit your intake of rice in your diet.
Intestinal dyskinesia in a child
Source: https://LechenieDetok.ru/gastroenterolog/diskineziya-kishechnika-u-detej.html
Types and stages of the disease
In pediatrics, cholecystitis is classified according to the course of the disease. Sudden and rapidly developing inflammation is called acute cholecystitis, a sluggish pathological process is called chronic. Often in children the disease occurs with alternating exacerbation and remission; this form is recorded as recurrent.
According to the nature of the inflammatory reaction:
- catarrhal is accompanied by aseptic inflammation (without infection);
- phlegmonous - with the formation of purulent exudate;
- gangrenous is characterized by the death of sections of the bladder wall.
If a child has a history of cholelithiasis, he develops calculous cholecystitis. If there are no stones - calculous (stoneless).
Considering the phase of the disease:
- exacerbation;
- remission.
In children, incomplete remission of the disease occurs, the so-called subacute stage.
Intestinal dyskinesia in children: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
Intestinal diseases are quite common in children. Young children are especially susceptible to this pathology. At the same time, intestinal dyskinesia occupies a special place among the complex of intestinal disorders.
Gastroenterologists use this term to designate disorders caused by impaired motility of the intestinal tract and weakness of its tone.
In young children, in most cases, dyskinesia of the large intestine is diagnosed, although the duodenum and other parts of the digestive tract may be affected by pathological effects.
Both adults and children suffer from intestinal dysfunction
Reasons for development
All pathologies of the digestive system in childhood develop mainly due to poor nutrition. Insufficient fiber content in food negatively affects intestinal motility. But there are a number of factors that can trigger the pathological process:
- intestinal infections;
- chronic diseases of the abdominal organs;
- hormonal disorders;
- diabetes.
Another cause of dyskinesia in children, which doctors do not exclude, is nervous disorders. It is very important to recognize the disease in time and prevent it from becoming chronic.
Symptoms and manifestations
Often in children, dyskinesia is asymptomatic against the background of a normally functioning intestine. The absence or dullness of symptoms may lead to an incorrect diagnosis. Therefore, it is worth knowing about the peculiarities of the course of this pathology in children.
Intestinal dyskinesia in a child is divided into two types:
- Atonic – when intestinal motility is reduced, as evidenced by constant constipation.
- The spastic form, on the contrary, is characterized by a tendency to diarrhea, the presence of undigested food residues in the stool, and abdominal pain.
The following symptoms signal an intestinal disorder in a baby:
- weakness and lethargy;
- lack of appetite;
- refusal to play, decreased activity;
- pale skin;
- low-grade fever (up to 37.5), but sometimes it rises to higher numbers.
Lack of appetite may indicate bowel dysfunction
Increasingly, pediatricians are having to diagnose disorders associated with enzymatic dysfunction in young children. This is explained by two factors:
- dysfunction of the biliary tract;
- chronic pancreatitis in a latent form.
For high-quality food processing, a sufficient amount of bile is required. If it is not enough, mucus inclusions will be present in the stool.
Intestinal dyskinesia is especially pronounced in infants. Small children experience bloating and intense gas formation. During this period, the baby becomes restless, writhes his legs, is capricious, sleeps poorly and refuses to eat.
Source: https://LechiGemor.ru/drugie-zabolevaniya/kishechnik/765-diskinezii-kishechnika-u-detey.html
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation of the gallbladder in young patients can be caused by various factors. According to pediatricians, the most common reasons are:
- parasitic and helminthic infestations: giardiasis, opisthorchiasis, ascariasis;
- congenital deformation of the gallbladder: bending, doubling, change in the size of the organ;
- Gastrointestinal pathologies: colitis, Crohn's disease, gastritis, duodenitis;
- dyskinesia of the gallbladder and ducts;
- cholelithiasis;
- hereditary predisposition.
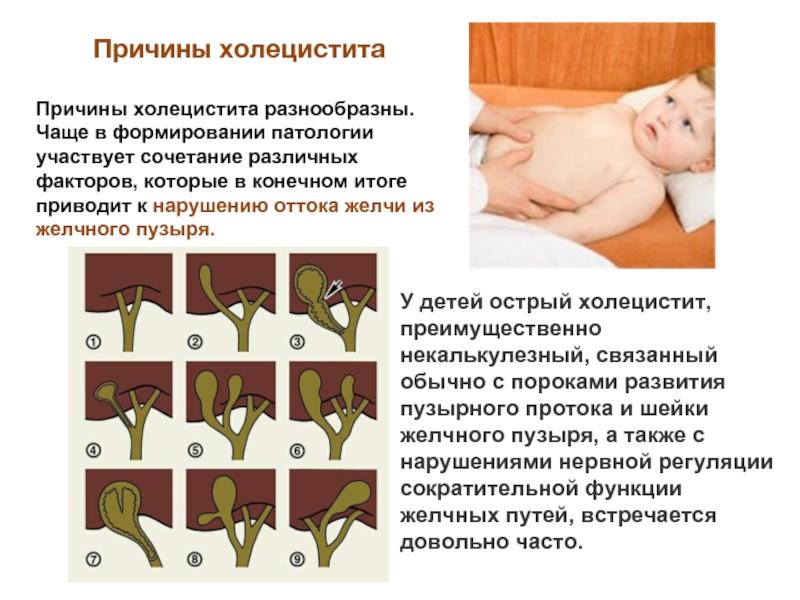
Good blood supply is of great importance for the health of the organ; the occurrence of ischemia leads to damage to the gallbladder. One of the main reasons is infection. Bacteria can enter the cavity of the biliary tract through ascending pathways from the intestine or with the blood from distant infectious foci:
- carious teeth;
- chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis;
- inflammation of the bladder - cystitis;
- pyelonephritis - inflammatory damage to the kidneys;
- intestinal infections: dysentery, salmonellosis.
In adolescents and children of primary school age, the pathology develops against the background of stress, increased workload at school, poisoning, and abdominal injuries. Chronic cholecystitis affects young patients prone to allergies and with weakened immune systems.
Cholecystitis is provoked by poor diet and sedentary lifestyle. Abuse of fast food, overeating, large gaps between meals cause functional disorders with the further development of inflammation.
Treatment
After a diagnostic examination (ultrasound of the gallbladder, X-ray examination, etc.), the gastroenterologist will prescribe appropriate treatment for the child. Thus, medications and time-tested folk remedies are used as therapy.
Drug therapy
To relieve discomfort and pain, children are prescribed the following medications:
- Papaverine - reduces smooth muscle tone and has a vasodilator and antispasmodic effect. The product is available in the form of tablets and ampoules for injection.
- No-shpu has a powerful antispasmodic effect and is available in the form of tablets and solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration.
- Allochol - enhances the production of bile, and also enhances the secretory and motor functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Release form: tablets.
- Cholenzym is a combined drug of animal origin that has a choleretic effect and normalizes digestive processes. The product is available in the form of tablets.
You can use medications as therapy only after prior consultation with your doctor. The doctor will select a dosage that is safe for the child and prescribe a course of treatment.
Treatment with folk remedies
The following recipes are most effective:
- Olive oil and lemon juice - for hypomotor form of pathology, it is recommended to take 1 tbsp orally daily. l. olive oil and immediately wash it down with freshly squeezed lemon juice with added sugar. Course of application: until the condition normalizes. Course of application: 7-10 days.
- Oatmeal - they need to be infused for 15-20 minutes in hot water, cooled and taken twice a day (half an hour before breakfast and dinner).
- Rose hips - dried rose hips are ground in a coffee grinder and in the amount of 3 tbsp. l. pour 2 glasses of hot water, then boil for three minutes, filter, add honey to taste and give children half a glass 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks.
We recommend: Cough in a child
But in order not to harm the child, it is also advisable to coordinate the use of traditional recipes with the attending physician.
Clinical manifestations
The main symptom of cholecystitis in a child is pain. It occurs in the right hypochondrium and is dull in nature. In most cases, pain is accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms:
- nausea, belching;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- vomiting, bloating.
Children with cholecystitis often complain of headaches, sleep disturbances, weakness, and fatigue. In young patients, appetite worsens, constipation occurs, and unstable stools occur. Manifestations of dermatitis appear on the skin - rashes, weeping eczema.
Gross dietary errors, strong emotions, long-term drug therapy can provoke an exacerbation, during which the intensity of pain increases sharply. Patients develop biliary colic. In children with a history of gallstone disease, acute cholecystitis can be caused by migration of stones.
Causes and symptoms
Gastrointestinal diseases (gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis, pathologies of the biliary tract) are the main causes of dyskinesia. Other factors predisposing to the development of dysfunction of the duodenum are:
- previous operations on the stomach;
- disruption of the endocrine glands;
- poor nutrition;
- infectious processes;
- genetic reasons;
- gynecological diseases;
- physical inactivity.
There are 2 types of dyskinesia: spastic and atonic. The first option develops with stomach colic, constipation, hypertension, and spastic contractions of the intestines. In the second case, the symptoms include constipation against the background of weakened intestinal tone and motility, abdominal pain, and a feeling of fullness. The condition is dangerous with the risk of intestinal obstruction.
Dyskinesia occurs with periods of remission and exacerbation. The latter is characterized by a complex of specific features:
- constant pain in the epigastric region;
- nausea, vomiting interspersed with bile;
- feeling of heaviness;
- loss of appetite;
- belching;
- bloating;
- bowel dysfunction;
- increased fatigue;
- excessive irritability.
Over time, the manifestations of dyskinesia fade into the background, and the person begins to be bothered by the symptoms of the disease that caused the pathological disorder of the duodenum.
Periods of remission usually occur with mild or absent symptoms.
Possible complications
It is often difficult to notice the disease in a child at an early stage. Children cannot always explain their feelings, and for many, the disease can progress without obvious external manifestations. Delayed diagnosis leads to neglect of the disease, which is fraught with dangerous consequences:
- empyema of the gallbladder - filling the organ cavity with purulent contents;
- wall perforation due to gangrenous tissue damage, gallstone breakthrough;
- biliary-dependent pancreatitis;
- effusion of bile into the abdominal cavity and the development of peritonitis.

When the duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, the patient's skin and sclera turn yellow, urine becomes dark and feces light, and body temperature rises. The appearance of such signs signals the development of obstructive jaundice. This is a common complication of calculous cholecystitis.
The development of complications in childhood is rare. In case of emergency, doctors decide to remove the affected organ (cholecystectomy).
Diagnostics
If you detect at least one of the above symptoms in a child, you must immediately consult a doctor so that he can conduct all the necessary studies and prescribe the correct treatment, since the sooner it is started, the better the effect will be achieved.
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will have to perform several procedures:
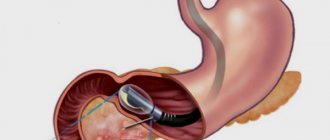
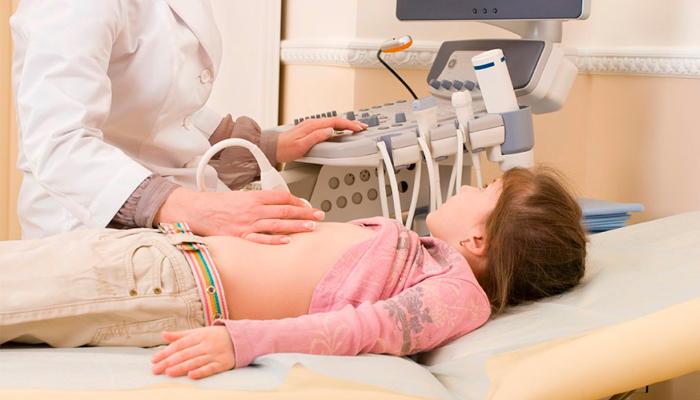
- Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder. During this procedure, the doctor completely studies the structure of the bladder, its ducts, records the dimensions, considers whether there are any congenital defects that can cause pain, etc. All results are recorded and sent directly to the attending physician
- Ultrasound examination before and after breakfast. If any abnormalities were noticed on the initial ultrasound, the doctor will have to conduct the following study: the child is given an ultrasound before he has breakfast. Then, the child is given something to eat, fatty food at that, and after half an hour or forty minutes another ultrasound examination is performed. During it, you will see how much the bladder will shrink, and what form of the disease is present in the baby
- Duodenal sounding. To conduct this study, you need to prepare the child well, as it takes quite a long time, and the procedure is very unpleasant. So, a probe is inserted into the duodenum, with the help of which bile is examined. For this, several samples are taken. True, this method is used very rarely today, since it is rare that a child will be able to withstand this procedure
- X-ray. This study is not done for all children, but only for those who, based on the results of an ultrasound examination, were found to have congenital malformations of the gallbladder and its ducts
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. This study is very serious and is carried out very rarely, only on special instructions from a specialist.
In addition, very often the child’s blood is taken for analysis, where deviations in some values will be visible. After all the basic studies have been carried out on the patient, the doctor makes a conclusion and makes a final diagnosis.
Examination methods
The treatment and detection of cholecystitis is carried out by a pediatrician together with a gastroenterologist. A presumptive diagnosis is established based on the patient’s complaints and physical examination: the appearance of pain upon palpation of the area where the gallbladder is located, tension in the abdominal muscles.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following is prescribed:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- duodenal intubation to assess the composition of bile and the functioning of the biliary tract and sphincters;
- blood chemistry;
- coprogram - stool examination;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- endoscopic examination of the upper digestive tract;
- cholangiocholecystography - x-ray examination of the biliary tract using a contrast agent.
Additionally, the patient is referred for consultation with a specialist – an otolaryngologist and a dentist.
The clinical picture of cholecystitis in children is similar to other diseases, which are important to recognize in time. Main differences:
- in chronic pancreatitis, the pain is girdling in nature or concentrated slightly above the navel;
- in chronic gastroduodenitis, pain is localized in the stomach and is accompanied by severe dyspepsia;
- with enterocolitis, abdominal pain is accompanied by increased gas formation in the intestines, unstable stools, and the pain decreases immediately after bowel movement;
- If a child has an ulcerative lesion of the gastric mucosa, pain occurs a couple of hours after eating.
The final diagnosis is established based on the results of a complete examination of the child.
Dyskinesia of the gastrointestinal tract in children: causes, symptoms and treatment of the intestines
Intestinal dyskinesia in children is a pathological disorder in the body. The child has dysfunction in the development of motor motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
The baby may regularly suffer from colic as a result of irritable stomach syndrome. It is important to promptly diagnose a disease such as intestinal dyskinesia in children.
Symptoms and treatment may vary, depending on the form and severity of the pathology.
Forms of the disease
Intestinal dyskinesia can be hypermotor and hypomotor . In medical practice, there are several stages - primary and secondary. With the development of hypermotor dyskinesia, symptoms of mild intestinal irritation occur. The activity of the colon begins to gradually fade away.
At the primary stage of the disease, clinical manifestations occur after suffering stress. It is necessary to monitor the diet and not give children heavy foods. The secondary stage of the disease progresses against the background of other diseases of the digestive system.
Hypomotor dyskinesia of the stomach is characterized by regular spasms in the intestines and increased tone. Food lingers in the body and does not have time to be digested. Because of this, constipation occurs along with pain.
If diagnosis is delayed, there is a risk of developing intestinal obstruction. Intoxication of the body occurs as a result of excessive accumulation of feces. This condition provokes intestinal hypertonicity.
The patient may feel nausea and dizziness, and vomiting often occurs..
Causes of intestinal dyskinesia
If parents do not care about the baby’s health and do not monitor his diet, dyskinesia may develop. Unhealthy diet affects body weight, often leading to obesity at a young age. Diabetes mellitus is considered a provoking factor.
Scientists have not identified the exact reasons, because the disease manifests itself in combination with other pathologies or independently. It is almost impossible to detect the disease in a timely manner and begin treatment. Gastroenterologists recommend not overloading the stomach, eating right and leading a healthy lifestyle.
Reasons for the development of gastrointestinal dyskinesia in children:
- nervous overstrain, stress, fear;
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle;
- the sleep and rest schedule is not observed;
- penetration of infection into the digestive system;
- genetic predisposition;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- obesity and overweight.
Enzyme deficiency often leads to the development of dyskinesia. The pathology occurs as a result of impaired functioning of the pancreas, chronic stagnation of bile in the ducts. These are the main factors that contribute to the development of dyskinesia.
Depending on the reasons that led to the onset of the disease, spastic and atonic forms of the pathology are distinguished. As the spastic form progresses, food quickly passes through the intestines in the child’s body.
The little patient begins to suffer from profuse diarrhea and severe pain in the abdomen.
Atonic dyskinesia is characterized by slow movement of food, so the intestine begins to become clogged with feces. The baby experiences pain, bloating, flatulence, and frequent constipation .
Clinical manifestations
The main symptoms of gastrointestinal dyskinesia:
- gradual weakening of the intestinal muscles;
- the child is rapidly losing weight;
- the skin becomes pale and too thin;
- when taking a blood test, the level of red blood cells is quite low;
- clinical manifestations of dysbacteriosis appear.
It is impossible to single out one symptom because several of them can occur at the same time. The child’s general health sharply deteriorates, there is a loss of strength, and there is no appetite. Babies are constantly capricious and restless, crying and screaming. The abdomen becomes hard and bloated. Rumbling is heard in the intestines, children refuse food .
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of dyskinesia is a complex and multi-stage process. The child undergoes the following tests:
- examination and palpation of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- internal examination of the intestine using an endoscope;
- taking stool for analysis;
- irrigoscopy and biopsy (to clarify the form and severity of the disease);
- collection and analysis of medical history (questioning parents to determine the child’s diet and daily routine).
During diagnosis, the doctor carefully examines the symptoms. It is important for him to consistently exclude the development of concomitant diseases in order to accurately determine the cause and make a diagnosis.
How to treat correctly
Treatment of gastric dyskinesia in an infant begins with adjusting the level of enzymes that contribute to the functioning of the digestive system.
For this purpose, medications are prescribed that contain protein elements. For children over five years old, it is important to add infusions based on medicinal herbs to their diet.
The most effective plants are St. John's wort, bittersweet, and tansy.
To normalize intestinal motility, the child is prescribed Metoclopromide . If acute abdominal pain causes discomfort to your baby, you need to take No-shpu or Drotaverine. These are two drugs that have the same effect. Drotaverine is an analogue of No-shpa. Medicines belong to the group of myotropic antispasmodics.
Action of No-shpa
The active component is drotaverine hydrochloride, which is included in the drug in an amount of 40 mg. The product is produced in the form of yellow tablets or solution for injection. The action of the drug is aimed at instantly eliminating spasms in the body. No-spa helps to dilate blood vessels and reduce muscle tone in internal organs.
The components contained in the composition do not affect the child’s central nervous system. Young children are not given No-shpa in tablet form, but are administered intramuscularly. The dosage is set individually, depending on age. The drug is not prescribed to children under six years of age.
Drotaverine for children
Drotaverine contains drotaverine hydrochloride in an amount of 40 mg. The drug helps children eliminate spasms in the smooth muscles of the intestines and internal organs. This occurs by reducing muscle tone and reducing the supply of calcium ions.
Drotaverine is an effective and efficient drug that has virtually no contraindications for use. The drug, like No-shpa, is not prescribed to children under six years of age. Dosage and method of application are prescribed individually.
It is strictly forbidden to buy antispasmodics for children on your own. If intestinal colic does not manifest itself intensely, you can try applying a warm compress to the stomach. Treatment is recommended using a rubber heating pad filled with hot water.
Traditional medicine
Treatment of children with traditional medicine is recommended only after consultation with a pediatrician. This therapy is most effective when combined with medications. Traditional medicine recipes:
- To improve the functioning of intestinal motility, the child is given a tincture based on valerian roots, chamomile flowers and mint leaves. The medicine is easy to prepare at home. You can buy plants at the pharmacy. To make an infusion, you need to take valerian root, chamomile flowers and mint leaves one tablespoon each. The dry mixture is poured with two glasses of boiling water. Infusion time is 20-25 minutes. You need to strain the broth and give the child 100 ml 3 times a day before meals.
- Recipe for the second decoction: take a tablespoon of oak bark, sage, St. John's wort and motherwort. Pour everything over with two glasses of boiling water. You need to drink 100 ml 4 times a day. This medicine will help quickly eliminate the negative symptoms of dyskinesia.
All traditional medicine can be used if the child does not have an allergic reaction to medicinal herbs. You need to take the decoction at regular intervals.
Proper nutrition
It is important to additionally follow a few basic nutritional rules:
- products should not contain preservatives, dyes, flavors and other additives of artificial origin;
- the diet should consist of cereals (porridges are prepared not too dry, so that their consistency is more liquid);
- It is recommended to stop eating rice cereals;
- the daily menu should contain fiber (apples, cabbage, carrots, beets);
- carrot and apple juice, rosehip decoction;
- food is boiled by steam or in water;
- salt restriction;
- Be sure to include dairy products (kefir, cottage cheese, sour cream) in your daily diet;
- refusal of fatty and fried foods, meat, fish.
The child should be given dairy products because they contain lactobacilli, which are good for the gastrointestinal tract and strengthening bones. Children should not be given smoked foods, spicy foods, flour, sweets, or cakes.
This is the best prevention to prevent intestinal dyskinesia from developing. Symptoms and treatment depend on the severity of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the body. You need to eat food in small portions so as not to overload your stomach.
It is important for your baby to follow the correct daily routine, sleep at least 9 hours at night and go to bed at lunchtime.
Parents must provide their child with the correct diet and daily routine to prevent the development of many diseases associated with the gastrointestinal tract.
It is important to instill these habits from childhood. Children who eat properly and follow a daily routine have strong immunity.
They do not experience such unpleasant symptoms as constipation and diarrhea. Children are less likely to suffer from viral diseases.
Source: https://chebo.pro/zdorove/simptomy-i-lechenie-diskinezii-kishechnika-u-rebyonka.html
Treatment of childhood cholecystitis
The list of therapeutic measures determines the degree of damage to the child’s gallbladder. For minor disorders, therapy can be successfully carried out at home. The indication for treatment of cholecystitis in a hospital is severe pain, frequent exacerbations - more than 3 times a year. They are urgently hospitalized for surgery with pain, the intensity of which does not decrease after taking analgesics.
Main goals of treatment:
- elimination of the acute phase of inflammation;
- correction of functional disorders of the biliary system;
- elimination of symptoms: pain, dyspeptic symptoms;
- elimination of the disease.
To achieve the assigned tasks, an integrated approach is required.
Drug therapy
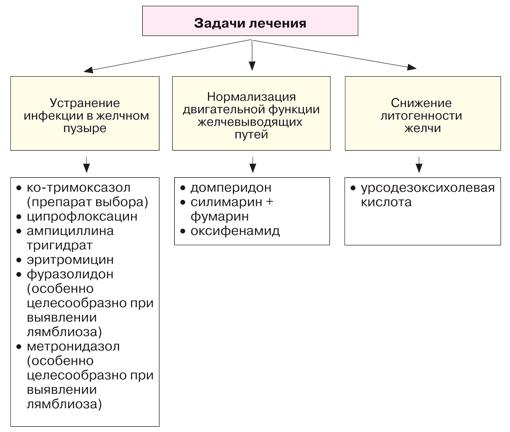
Conservative methods of treating gallbladder inflammation in children necessarily include taking medications. The attending physician selects them, prescribes the dosage, duration and duration of the course. For cholecystitis in pediatrics the following is used:
- antibiotic to destroy pathogenic microflora - Amoxicillin, Azithromycin;
- antifungal drugs, if the disease is caused by a fungus - Itraconazole;
- antiulcer agents to protect the gastrointestinal mucosa - Lansoprazole;
- antispasmodics to improve the motor function of the bladder and ducts - Drotaverine, Platyfillin;
- choleretic drugs to normalize the formation of bile and its flow into the intestines - Silymarin;
- antidiarrheal agent for unstable stool - Loperamide;
- multivitamins to improve immunity;
- enzyme preparations for good digestion - Pancreatin;
- anthelmintic drug if the test result is positive for worms - Pirantel;
- for bloating, medications that reduce flatulence - Simethicone;
- hepatoprotectors to improve liver function – milk thistle.
For each specific case, the pediatrician selects an individual list of medications. For children with elevated body temperature, antipyretics may be needed, and for allergies, antihistamines.
Non-drug treatment
If a child is diagnosed with cholecystitis, he is transferred to dietary nutrition. The treatment table is based on diet No. 5 with a limitation of animal fat and a slight increase in the amount of easily digestible protein. Children are fed low-fat fermented milk products, dietary meat, fish, non-acidic fruits, and vegetables.
Diet is of great importance. The patient should eat at least 5 times a day at regular intervals. Products are boiled, baked, steamed. Exclude from the diet foods high in fat, smoked and canned foods, sweet carbonated water, chocolate, and fast food.

To improve the composition of bile and prevent lithogenicity of the secretion, parents are advised to give their child mineral waters. Borjomi and Essentuki No. 4.17 are well suited for drinking therapy. The optimal daily dosage of water is determined by weight - 3 ml per 1 kg of body weight. Drink mineral water in small sips 1 hour before meals. The duration of one course is no more than 2 weeks, re-appointment - after 3-6 months.
To improve the outflow of bile, young patients are prescribed physical therapy, massage and physiotherapy. Weakened children with a long course of chronic cholecystitis are advised to undergo regular sanatorium-resort treatment.
Symptoms of intestinal dyskinesia in children, causes of development, treatment methods
Intestinal diseases are quite common in children. Young children are especially susceptible to this pathology. At the same time, intestinal dyskinesia occupies a special place among the complex of intestinal disorders.
Gastroenterologists use this term to designate disorders caused by impaired motility of the intestinal tract and weakness of its tone.
In young children, in most cases, dyskinesia of the large intestine is diagnosed, although the duodenum and other parts of the digestive tract may be affected by pathological effects.
Both adults and children suffer from intestinal dysfunction
Diagnosis of intestinal problems
All diagnostic measures for intestinal dyskinesia in children are aimed at excluding other pathologies. A step-by-step examination is carried out, including the following diagnostic methods:
- endoscopic examination of the intestine,
- coprogram - a laboratory analysis of stool that allows you to assess how the stomach and other digestive organs function,
- checking stool for occult blood,
- if necessary, the patient is referred for irrigoscopy - one of the types of x-ray examination of the large intestine using a contrast agent,
- in rare cases, a biopsy is performed to exclude oncological pathology.
Endoscopic examination of the intestine is a necessary measure in making an accurate diagnosis
The entire range of measures when diagnosing intestinal disorders in newborns and children of the first year of life comes down to identifying dysbiosis and disturbances in the production of enzymes.
What is therapy?
If symptoms characteristic of this pathology indicate dyskinesia in an infant , then the doctor begins treatment by eliminating the main causes.
First of all, the balance of food enzymes is corrected. For this purpose, the child is prescribed special medications that can compensate for enzyme deficiency.
Drug treatment is aimed at relieving pain and other symptoms that negatively affect the general condition of the child.
When treating older children, the therapeutic complex is based on creating an adequate nutritional regimen for a particular child.
In this case, a dietary diet implies adherence to a strict meal schedule. Often the treatment complex is supplemented by physiotherapeutic procedures and therapeutic exercises.
When developing a treatment program, doctors attach great importance to organizing the child’s active leisure time and sleep patterns.
Nutrition for intestinal dysfunction
The basis of therapy for any intestinal problems in children is a balanced diet. It is useless to try to treat dyskinesia with medications alone, because without following a special nutrition program it is impossible to achieve a positive result. When forming a diet for a sick child, factors such as the quality of food and cooking methods must be taken into account.
It is important to follow the following recommendations:
- The presence of preservatives, flavors, and food colorings in children's menus is unacceptable.
- Food should be varied, with a predominance of foods rich in fiber. In this regard, vegetables and fruits are indispensable, especially green apples.
- The daily diet for intestinal dyskinesia in children should include fresh juices, preferably with pulp. In addition to natural drinks, you can prepare unsweetened decoctions for your child. We must not forget about the benefits of ordinary drinking water; it is best to take it from natural sources.
- All fatty, fried and smoked foods will have to be removed from the diet. Baby food should be steamed or boiled.
- Fermented milk products must be included in the menu of a child with dyskinesia. Priority is given to products that contain live lactobacilli: sour cream, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir.
- Slimy porridges cooked in water and dried bread can speed up the normalization of all intestinal functions.
- And lastly : meals for children of any age should be fractional, up to 6 times a day. Eating small portions to your child will help the food be better absorbed in the intestines and prevent overeating.
- chamomile,
- senna,
- mint leaves,
- oak bark,
- valerian root,
- buckthorn bark and other natural ingredients.
In addition to drug treatment for intestinal problems, you need to focus on proper nutrition
Drug treatment
After the diagnosis, the doctor decides to prescribe drug therapy. Usually, children with dyskinesia are given enzymatic agents, vitamins, sedatives and choleretic drugs.
If a child complains that his stomach hurts a lot , parents can give him some of the antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine) in a dosage appropriate for his age.
It is not recommended to give other medications to children on their own.
Gymnastics
A special set of exercises helps improve intestinal motility of a sick child. For atonic type dyskinesia, therapeutic exercises are aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles.
The complex includes walking and breathing warm-up - the emphasis is on mastering diaphragmatic breathing techniques.
Imitation of cycling and exercises to change body position help well with intestinal atony.
In spastic forms of the disease, the emphasis of the therapeutic gymnastics complex is on relieving spasms. Therefore, all exercises are performed at a slow pace with limited range of motion. A specialist from the exercise therapy department should draw up a training program and select exercises that are appropriate for the age of the sick child.
Traditional methods of treatment
Medicinal herbs are widely used to treat dyskinesia in children. The natural medicine is completely harmless to the child’s body and quickly normalizes intestinal activity. From herbs you can prepare decoctions, infusions, and medicinal teas. The list of useful herbs includes:
Any traditional recipe must be agreed with your doctor. The specialist will advise which composition is most suitable for the sick child.
It is worth remembering that different ingredients are used for spastic and atonic forms. The dosage and regimen for taking medicinal formulations should also be determined by a medical professional.
But if the main symptom of dyskinesia suddenly manifests itself at home - spastic colic, parents can do the following:
Chamomile, familiar to everyone, can relieve a child of intestinal problems. The main thing is to know how to prepare the decoction
Conclusion
It is easier to prevent any intestinal problems than to treat them. Therefore, competent prevention plays a key role in this matter.
It is recommended that the child create favorable conditions at home for rest and activities; he must carefully monitor his diet, avoid “dry snacks” and exclude harmful additives from the diet. You need to be especially careful when choosing a menu for kids.
If the slightest intestinal disorder occurs, parents should immediately contact a medical facility.
Loading…
Source: https://MedBoli.ru/gemorroj/drugie-zabolevaniya/simptomy-diskinezii-kishechnika-u-detej-prichiny-razvitiya-metody-lecheniya