Constipation criteria
In babies under one year of age, stool has a mushy consistency.
According to the criteria adopted this year in Rome at the European Gastroenterology Week, chronic constipation in childhood is considered to be a rare rhythm of bowel movements that lasts for more than three months.
For children under 3 years of age, a deviation is considered to be stool occurring less than 6 times a week, and for older children - less than three times a week. In this case, chronic stool retention should be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- stool is firmer than usual and there is too much (or too little) of it
- the child has to push very hard,
- Older children claim that they have not completely emptied their bowels.
In babies under one year of age, stool should have a soft, mushy consistency. Before the introduction of the first complementary foods, stool in most cases coincides with the number of feedings, provided that the child is fed only breast milk.
Children who receive artificial or mixed nutrition from the first days of life have rare bowel movements - no more than twice a day. With the start of complementary feeding, stool becomes less frequent even in children who are breastfed (up to 2 times a day).
Children older than one year should ideally have bowel movements every day. In babies under one year of age, pseudoconstipation can be diagnosed, when rare stools are caused by a lack of milk from the mother, or the child sucks sluggishly and often burps.
Constipation in young children can occur temporarily during hyperthermia, when due to elevated temperature the stool becomes severely dehydrated. The same situation can arise if there is an excess of calcium in the child’s diet or with hypervitaminosis of vitamin D.
When does constipation require treatment?
The phenomenon of a baby's lack of stool is not always considered a pathology. To determine the spectrum of the problem, you need to focus on the child’s condition. For example, if a baby does not have a bowel movement for several days, but at the same time he feels great (he is active, eats constantly and in sufficient quantities) and the act of defecation occurs without any signs of anxiety, there is no reason to carry out treatment.
Another thing is pronounced constipation. In this case, the child shows anxiety, cries during bowel movements and kicks his legs. You need to pay attention to the consistency and frequency of stool. In newborns, stool should be mushy and soft. After the introduction of the first vegetable complementary foods, it becomes a little thicker. When cereals, soups, and meat are added to the diet, the stool becomes more formed and soft. Any deviation from the norm requires taking urgent measures to eliminate the problem.
Why functional constipation occurs in infants and preschoolers
A lack of digestive enzymes can cause constipation.
The causes of functional constipation at an early age differ from the causes of constipation in children of older preschool age or in younger schoolchildren. Reasons for stool retention in infants:
- The mechanisms of peristalsis and excretion of feces are disrupted in the colon.
- Condition after hypoxia and damage to the central nervous system, its dysfunction.
- Prematurity, immaturity of the child and, as a consequence, delayed production of intestinal enzymes.
- Muscle hypotonia after rickets and perinatal hypoxia.
- L-carnitine deficiency in food, leading to decreased sphincter tone.
- Lack of digestive enzymes due to early introduction of complementary foods.
Read: Choosing the right constipation remedies for newborns
In children of senior preschool and primary school age, the causes of functional constipation may be:
- Suppression or absence of the reflex (so-called psychogenic constipation) occurs during the period of adaptation of the child to kindergarten or school.
- Neurosis due to separation from mother. Lack of habit of regular bowel movements.
- Suppression of urges.
- Rectal fissure and fear of pain during bowel movements.
Long-term use of medications: muscle relaxants, diuretics, anticonvulsants and psychotropic drugs, anticholinergics. They inhibit the work of the subcortical center that controls defecation, lead to a blockade of the nerve pathways that control intestinal motility, and lead to the loss of potassium, which stabilizes the movement of feces through the intestines.
Constipation in a two month old baby
You should not confuse constipation with ordinary bowel retention and panic. The pathological condition can be recognized by some characteristic signs:
- The stool becomes hard and resembles peas.
- Child's crying and restlessness.
- The baby constantly twists his legs or tucks them in.
- Constipation prevents the passage of gas.
- The abdomen feels hard and tense.
- Daytime and nighttime sleep is disrupted.
- Appetite worsens.
If it is difficult for a child to have a bowel movement, then the question arises of what to do in this case. For formula-fed infants, constipation is a common problem. These babies need to be given water constantly. Insufficient fluid intake can cause the formation of hard stool.
The main reason why a child may suffer from constipation is the improper diet of a nursing woman. If she eats too much dry food, then the disease will not take long to appear.
In this case, a revision of the mother’s diet is indicated. If the child is not yet 3 months old, then you should approach nutrition very responsibly. First of all, before feeding the baby, lay him on his stomach for 5 minutes. This will help stimulate peristalsis and improve digestion. In addition, gases will not be retained in the intestines.

Clinical manifestations of functional stool retention
A characteristic clinical symptom of constipation is the absence of gas discharge.
In most cases, functional constipation develops sequentially, with stool disturbances observed for three or more months.
Sudden, prolonged retention of stool for more than three days is considered an acute manifestation of constipation.
Each such case requires careful attention so as not to miss a life-threatening pathology for the child - intestinal obstruction that occurs due to inflammation, possible accumulation of helminths or a tumor.
A characteristic clinical symptom of obstruction is the absence of gas discharge. To differentiate this pathology from organic constipation, anomalies of the large intestine should be immediately excluded during examination.
It is important to diagnose intestinal obstruction in time so as not to miss time for rational therapy or surgical intervention.
Clinical symptoms of functional constipation depend on the cause of its occurrence, how long and severe it lasts, and how impaired intestinal functions are. Symptoms of functional constipation resulting from hypomotor dyskinesia:
- large fecal cylinder;
- violation of the frequency of bowel movements;
- anorexia;
- pale skin, appearance of pustules on it;
- abdominal pain in the form of attacks, stops after defecation;
- discomfort when examining the colon;
- coated tongue.
Read: Chronic constipation in a 6 month old baby - what to do at home
Symptoms of functional constipation with loss of the reflex to defecate:
- one bowel movement is separated from another by up to 5-7 days; expansion of the distal intestine, the appearance of megacolon;
- overflow of the rectum with feces (a symptom detected during a rectal examination);
- relief of the condition and disappearance of pain after a cleansing enema;
- proctosigmoiditis as a complication of the process.
Symptoms of spastic functional constipation:
- “sheep feces” in the form of fragments;
- intense intestinal colic in infants;
- attacks of pain in older children; under stress they intensify and disappear after defecation;
- the child is irritated, the act of defecation causes him anxiety;
- bloating often occurs, accompanied by increased gas formation;
- pallor of the skin appears, a tendency to the appearance of pustules.
Symptoms of constipation in irritable bowel syndrome:
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- sensitivity to stress, consumption of coarse fiber;
- the child feels that the intestines have not emptied completely;
- the appearance of a streak of blood in the stool;
- children noticeably lose weight;
- low hemoglobin content.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of constipation, it is necessary to carry out light prevention. Actions that seem simple at first glance will save your baby from big problems. To prevent your baby from having problems with bowel movements, it is recommended to follow the following recommendations:
- Place the baby on his tummy several times a day, at least for 1-2 minutes;
- Pay special attention to the amount of fluid the child consumes;
- Mothers who are breastfeeding are advised to consume foods rich in potassium;
- It is not recommended to allow the child’s body to overheat;
Performing these simple steps, along with careful adherence to the diet, will prevent problems with bowel movements in infants.
Note! Nowadays, the Internet is simply teeming with various videos on how to cure constipation in a baby. Remember that using traditional and modern methods to treat a child without the advice of an experienced specialist is strictly not recommended. They can negatively affect the baby's health. If you notice that your child is acting differently than usual, try to take him to the doctor as soon as possible.
01 Mar 2020 admin 1681
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Why does a baby spit up like a fountain?
- Water for babies. The need for supplementation, how much and when to give.
- White plaque in the baby’s mouth – causes and treatment
- Signs of dysbiosis in infants
Child examination
For constipation, a specialist prescribes a comprehensive examination.
When parents with a child suffering from chronic constipation consult a doctor, the specialist will prescribe a comprehensive examination.
First, a family gastroenterological history is collected from the parents and the child himself.
The doctor is interested in the developmental history of the little patient, possible behavioral disorders, stress factors of family upbringing, the child’s diet, and previous treatment.
Then an examination is carried out to identify clinical symptoms of constipation: determining the color and elasticity of the skin, the size of the abdomen, and the condition of the tongue. On palpation, the presence of feces in the colon and its soreness are noted.
Examination of the area near the anus allows you to see skin irritation, the presence or absence of a crack. Laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out:
- Scatology of feces - for the presence of mucus, blood, red blood cells, white blood cells;
- X-ray of the large intestine with a barium suspension - to determine the violation of its passage, lengthening, change in location;
- Irigoscopy - to determine intestinal abnormalities, type of constipation.
- Sigmoidoscopy – to determine the tone and parameters of the colon;
- Colonoscopy - to exclude oncological lesions or inflammatory processes.
- Blood test for hemoglobin;
- Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis.
Read: A 7-month-old baby has constipation, what to do, how to help his little belly?
Massage for constipation in children
A 2 month old baby's digestive system is very weak. To reduce the risk of recurrent constipation, it is recommended to massage the abdomen daily before each feeding. To do this, you need to use two types of movements. First of all, you should move your palm clockwise over the baby's belly. It is not recommended to apply pressure. A couple of minutes is enough to activate the digestive system.
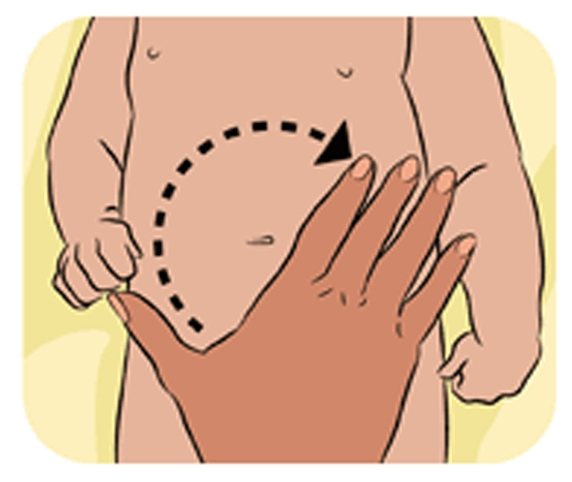
Another effective way of massage is to pull the baby's legs towards his abdomen. This must be done smoothly and carefully so as not to cause harm. In this case, you need to talk with the child. Many children readily accept massage. It gives them pleasure and helps them communicate with their mother.

Constipation, which a 2-month-old child suffers from very often, can also be cured with a relaxing warm bath. To do this, you need to add a decoction of the string to the water. It will also calm the baby. Relaxing baths will help speed up peristalsis and stimulate digestion. In addition, this procedure will relieve abdominal pain.
Constipation is always difficult for a 2 month old baby. To alleviate the baby's condition, you can use a warm diaper. This simple method will reduce pain and relax the intestinal muscles.

Another way to relieve constipation in a baby is mechanical stimulation of peristalsis. This must be done extremely carefully. You will need a small cotton swab. It should be dipped in Vaseline or baby cream and carefully inserted literally 0.5 cm into the anus. Then remove it and place the baby on the tummy.
How to help your baby
Enema should not be used on infants.
Rational treatment of functional constipation depends on what caused it, the child’s concomitant diseases and the presence of complications.
The goal of treatment is to normalize the speed of stool passage through the colon and soften its consistency.
In infants, enemas should not be used to treat constipation. This can only be a means for emergency relief, since enemas cause intestinal spasms and the appearance of secondary and habitual constipation.
Children who are breastfed and receiving complementary foods should drink enough water (about 100 mg per day). The introduction of vegetables and cereals into complementary foods enhances peristalsis. The diet of a nursing mother should not contain foods that stimulate gas formation in the baby.
Dysbacteriosis is stopped by the introduction of pre- and probiotics; in case of dense stools, a drug containing lactose is prescribed. Additional therapeutic measures for children of the first year of life:
- massage of the tummy, back and skin area around the anus,
- physiotherapy,
- the use of glycerin suppositories,
- dill water or fennel tea for increased gas formation,
- with artificial feeding - mixtures with lactulose and oligosaccharides.
In preschool children, special attention should be paid to developing a reflex to defecation. To do this, use a step-by-step method:
- Cold drink on an empty stomach.
- Taking a laxative.
- Breakfast.
- Using a cold glycerin suppository to stimulate bowel movements.
- Defecation.
For spastic constipation, antispasmodics, warm baths, and pain-relieving suppositories with papaverine are used.
For constipation caused by hypomotor dyskinesia, prokinetics and B vitamins are prescribed.
Children should have opportunities to be physically active. Their diet should be rich in foods rich in plant fiber and contain enough liquid. The amount of easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, white bread, baked goods), on the contrary, should be reduced.
A specially selected diet is of great importance for eliminating functional constipation. It contains rye bread, vegetable soups, cereals, eggs, olive oil, and dairy products. Eating fresh fruits is encouraged: cherries, apples, melons, watermelons, prunes. Recommended vegetables: cucumbers, radishes, turnips, carrots, beets.
Functional constipation in children has many symptoms. Only a specialist - a pediatrician, a pediatric gastroenterologist - can determine the cause of their occurrence, the type of constipation, conduct a competent examination and prescribe treatment. By following the doctor’s recommendations and following the diet recommended for the child, you can get rid of this pathology in the shortest possible time.
Read along with this article:
- If a baby cannot go to the toilet - how to help him
- The child has constant constipation: psychological and organic causes
- Chronic constipation in a 6 month old baby - what to do...
- Note to mothers: normal stool in a newborn
- Will an enema help children with constipation?
- Green poop in a baby: causes, methods...
- Why fecal incontinence occurs in a child and how to deal with...
- Why does a child poop often and how to help him in this case?
- A 7 month old baby has constipation, what should I do, how can I help my little belly?
Treatment with medications

If the above methods do not bring results, it is recommended to use special means:
- Glycerin suppositories. The safest suppository, ideal for a fragile child's body. They are used for emergency purposes; they are not advisable to use constantly.
- Lactose products. An effective laxative, which is a nutrient medium for normalizing intestinal microflora. It has no contraindications and is suitable for children of any age.
- Enemas. Used exclusively in special cases; prior to use, consultation with a pediatrician is required.
It is worth noting that before giving any medicine to the baby, you should consult a doctor. He will find out the cause of constipation, advise on nutritional rules and prescribe the optimal treatment.
Today, the pharmacological market offers many effective drugs that are prescribed to infants. One of the most popular is Duphalac. The medicine can be given to a baby from the first year of his life. Children over 6 years old can be given Forlax. This remedy is identical to Duphalac in principle and effectiveness; it can be taken for a long period, as it is not addictive.
If constipation is caused by bloating and colic (usually observed at 2-3 months), treatment of stool retention should be carried out using “carminative” drugs. The most popular today: Espumisan, Plantex, Bebicalm. When choosing a drug, you should take into account the contraindications specified in the instructions.
Before using a laxative, you should consult your pediatrician. It is better to determine the cause of constipation and successfully eliminate it than to regularly take laxatives. Otherwise, the pathology can take on a protracted, chronic form and cause many problems.