Author's rating
Author of the article
Green Elena Stanislavovna
Otolaryngologist of the second category
Articles written
665
about the author
A cough, in most cases, indicates a cold or viral infection in the body. Heartburn is one of the symptoms of indigestion. And few people know that cough and heartburn in combination indicate pathology in the digestive organs. This could be functional dyspepsia, GERD or another disease.
What is stomach cough
A stomach cough is different from a regular cold. It is not accompanied by symptoms typical of viral infections: runny nose or sore throat. Also, during attacks, sputum does not leave the respiratory tract. The most common cause of reflux and cough at the same time is reflux disease. It also manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- belching;
- feeling of “heaviness” in the stomach.
Stomach cough is caused by poor diet. At risk are people from 35 to 50 years old who abuse alcohol, smokers and overweight people. It is difficult to confuse a stomach cough with a cold, as it has distinctive features:
- This is a dry, lingering cough;
- bothered by stomach cramps;
- frequent stomach upsets;
- there is a sour taste in the mouth;
- I'm worried about a sore throat.
The nature of this symptom is determined by gastrointestinal diseases. It will not be possible to eliminate cough and heartburn with medications. It is necessary to eliminate the root cause of their occurrence.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of the disease or avoid relapse, it is recommended to follow a number of rules:
- Nutrition should be complete. The basis should be vegetables, fruits, lean meat and fish, and cereals. It is important to eat foods rich in fiber.
- Meals should be taken at regular intervals, at least 5-6 times a day.
- Dishes should be consumed only fresh.
- Products should be processed carefully.
- You can cook food by steaming or boiling.
- After eating, you must be in an upright position for an hour.
- It is necessary to remove fast foods, soda and fatty foods from your diet.
- Monitor the state of the immune system.
By following simple recommendations, you can easily get rid of the disease or prevent the development of stomach cough. In childhood, it is important to show the baby to the doctor at the first symptoms, since independent selection of treatment can harm the child.
If it is known that the pathology is associated with gastrointestinal diseases, then before visiting a specialist it is necessary to organize proper nutrition, and in case of poisoning, rinse the stomach and drink sorbent.
Mechanism of occurrence
If the appearance of a cough is caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease, then this is fraught with serious consequences. With GERD, nerve endings are irritated, which causes symptoms. Also, with esophagitis, the walls of the esophagus increase in size, which can cause swelling. Then the trachea is compressed and a cough appears.
Heartburn is caused by acid, which causes stomach contents to reflux into the esophagus. The esophagus becomes irritated and this becomes the cause of this unpleasant symptom. Almost every fourth person who suffers from heartburn also experiences a cough. Heartburn bothers a person mainly after eating. It can also be caused by overeating. Almost 25% of chronic coughs are caused by GERD. How is the mechanism of its occurrence explained:
- The content of hydrochloric acid increases and this causes a reflex action;
- Acid droplets enter the throat or vocal cords. In this case, coughing manifests itself as a protective mechanism.
Diagnostics
To determine whether a person’s cough is due to a sick stomach or caused by a cold, various diagnostic procedures are prescribed. A comprehensive examination is prescribed only if, based on existing complaints, it is not possible to determine the cause of the cough.
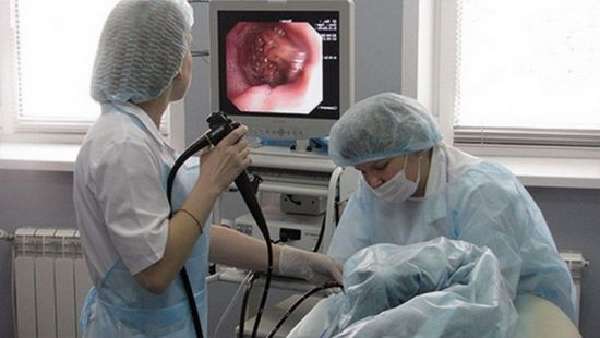
Fibrogastroscopy is one of the methods for diagnosing diseases of the stomach and duodenum.
The patient is prescribed:
- Fibrogastroscopy is an examination of the walls of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum using a special device. FGS helps to diagnose the presence of an inflammatory process and accompanying changes.
- Examination of urine, blood and feces.
- X-rays of light. The technique helps confirm/refute respiratory diseases.
If necessary, the patient may be prescribed consultations with highly specialized specialists.
Cough with reflux esophagitis
With esophagitis, the cough can be either temporary or prolonged. It all depends on the degree of irritation of the nerve endings. Chronic cough may be one of the symptoms of GERD. This can be detected by the following signs:
- paroxysmal cough bothers you at night and after meals;
- attacks occur more often when the patient is in a supine position.
If attacks have been bothering you for a long time, then you can suspect reflux disease if you:
- not a smoker;
- have not taken medications for a long time;
- did not suffer from asthma or colds;
- you are not overweight;
- tests did not reveal any pathologies.
Also, a cough with GERD is always unproductive, the throat does not hurt, and breathing through the nose is free. In some cases, this symptom may be accompanied by:
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- loss of consciousness.
Often these signs are confused with symptoms of asthma or allergies. For an accurate diagnosis, you need to undergo an examination.
Heartburn is closely related to cough due to GERD. Mostly it occurs during the daytime. But for many people, heartburn cough occurs after eating spicy or fatty foods just before bed. This attack is characterized by a sour taste in the mouth. However, these symptoms are not the same for all people. Sometimes the disease is completely asymptomatic. But the disease continues to progress and can become chronic. To treat it, you need to completely change your diet and lifestyle. But only under the guidance of a doctor. Endoscopy is used to diagnose GERD.
Symptoms of GERD in children are:
- frequent regurgitation;
- vomit;
- wheezing in the chest;
- loss of appetite
- nervousness;
- weight loss.

Characteristic symptoms
Regardless of the form of the pathology, cough will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- impaired breathing (the symptom intensifies when the person lies down);
- symptoms of impaired intestinal motility: heartburn, sour belching, attacks of nausea;
- cough with gastritis of the stomach does not always occur, but only after eating;
- soreness and burning sensation in the throat;
- change in odor from the mouth, unpleasant taste;
- change in stool—prolonged constipation or diarrhea;
- deterioration of general condition, constant feeling of fatigue, drowsiness.
Cough from an ulcer that occurs against the background of gastritis is accompanied by a gag reflex.
Clinical picture
With gastrointestinal problems, in addition to coughing, patients begin to notice a change in their voice, problems with swallowing and a sore throat. If gastritis or an ulcer develops, you may experience discomfort in the chest and throat. Heartburn and cough can appear due to dysbacteriosis and the presence of helminths in the body. Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, symptoms may vary. For example, in diabetics, the disease may occur without any symptoms. Increased intra-abdominal pressure is another cause of unpleasant symptoms. It occurs due to:
- uncomfortable and tight clothing;
- pregnancy;
- diseases of internal organs;
- overeating.
In this case, you need to monitor your liver function. Diagnostic method is ultrasound. This problem is treated with surgery.

Features of cough in connection with the cause of the lesion
With gastritis and ulcers, the cough does not appear immediately after eating, but after 40-55 minutes. With reflux, the cough occurs after eating and is non-productive. Due to the large accumulation of air, the patient may feel a sense of sputum discharge, although in fact there is none.

In acute cases, relief does not occur for a long time. If the process is chronic, then a cough due to the stomach appears only after eating fatty, spicy or sour foods and quickly disappears.
If there are parasites or dysbacteriosis in the body, the cough is dry. Cough can be separated from sputum only with a viral etiology. Secretion with pink mucus indicates damage to the capillaries of the bronchial tree due to adenovirus.
How to deal with a cough due to heartburn
To cure the symptoms, it will be enough to change your lifestyle. What is needed for this:
- wear loose clothing made from natural fabrics;
- if you are overweight, you need to lead a more active lifestyle and eat according to the developed diet;
- avoid foods that irritate the stomach;
- within 2 and a half hours after eating you should either stand or sit;
- sleep on a high pillow.
You should also exclude from your diet:
- alcohol;
- chocolate;
- caffeine;
- citrus;
- spices;
- onion and garlic;
- fried and spicy foods.
Cough and heartburn should be treated with drugs that reduce the level of acidity in the stomach. These could also be:
- antacid drugs;
- medications that eliminate the source of irritation;
- H2 blockers.
For dysbiosis, medications are prescribed that improve intestinal microflora. Self-treatment and taking the wrong medications can cause complications. Therefore, for diagnosis you need to visit a specialist. The doctor can also recommend traditional recipes for treatment. These can be herbal decoctions that effectively fight heartburn. For example, a quick method to eliminate it is water with baking soda. But the effect is temporary; after an hour, heartburn may worsen even more. You can also use:
- Milk. A few sips will quickly neutralize the acid.
- 1-2 spoons of raw potato juice helps relieve heartburn. You need to take it 2 times a day half an hour before meals.
- Grind a tablespoon of fennel, dill and anise and pour boiling water (1 cup). Leave for a quarter of an hour. Drink the resulting drink 1-2 glasses daily.

Treatment
How to treat stomach cough? Therapy in this case involves an integrated approach and is aimed at eliminating the provoking disease. Treatment of stomach cough is carried out by the following groups of drugs:
How to check stomach acidity?
- Prokinetics. Increases the tone of the digestive organs.
- Antacids. Necessary for neutralizing high acidity. They form a protective film on the surface of the mucosa.
- Antisecretory agents. The production of digestive juice by the stomach receptors is temporarily stopped.
- Antimicrobial drugs. They are used to identify pathogenic microorganisms in order to stop their vital activity.
- Foaming medications. Neutralizes acid and relieves heartburn.
- Antitussives. Necessary to eliminate sore and dry throat.
When dysbiosis develops, prokinetics are prescribed - medications that help restore normal gastrointestinal microflora.
Review of the most commonly prescribed drugs
There are several medications that are especially frequently prescribed.
Amoxicillin
The drug belongs to the group of penicillins. Used in diagnosing the bacterial origin of stomach cough. The drug is contraindicated in the following cases: intolerance to penicillin, allergy to beta-lactam antibiotics, allergic diathesis, asthma, infectious mononucleosis, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, problems with the liver and kidneys.
Amoxicillin is prescribed with caution during pregnancy, breastfeeding, newborns and premature babies.
Phosphalugel
Included in the group of antacids, it normalizes the acidity of gastric juice. Envelops the mucous membranes of the stomach, forms a dense protective layer. Indications for use are heartburn and stomach cough, provoked by the development of gastritis, peptic ulcer, reflux esophagitis. In case of severe impairment of kidney and liver function, it is not prescribed.
Motilak
Motilak is prescribed for disorders of gastrointestinal motility. Activates the contractility of the stomach and duodenum. Contraindications are:
- Intolerance to the components of the product.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Perforation or intestinal obstruction.
- Prolactinoma.
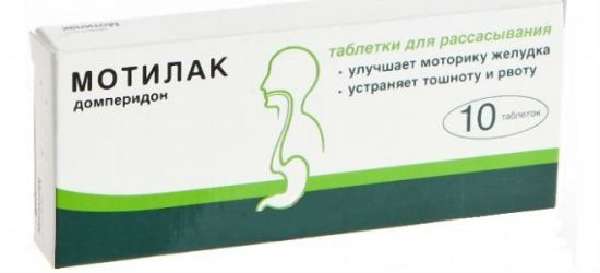
The product is not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The use of the drug must be agreed with the attending physician. Side effects while taking Motilak develop in rare cases.
Domperidone
Domperidone is a drug with antiemetic action. It is quickly absorbed and has an almost instant effect. Indicated for use for nausea and hiccups. Contraindications: internal bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal obstruction, prolactinoma, gestation and breastfeeding, hypersensitivity to the active component. Intestinal upset and allergic reactions are possible.
Treatment with folk remedies
In the process of treating stomach cough, folk remedies can be used. The compositions should include anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antiseptic components.
- The following mixture will help in treating cough caused by existing gastritis. It is necessary to combine a little olive (250 ml), honey (100 ml), lemon juice (2 tbsp.). Store the composition in the refrigerator. Take 1 tsp daily. before meals.
- Stir 0.5 grams of mumiyo in a glass of warm milk. Divide the resulting volume into 2 parts and take twice a day before meals. The product soothes and softens the gastric mucosa.
- Increased stomach acidity is neutralized by freshly squeezed potato juice. In the morning you need to take ½ cup of the product on an empty stomach.
Decoctions of chamomile, sage, plantain and licorice have soothing properties. They protect the gastric mucosa, soothing coughing attacks. To prepare a medicinal drink you need 1 tbsp. l. Brew the herbs with boiling water (250 ml) and leave for two hours. Filter.
Important! Before starting treatment, you should consult with your doctor.
Nutritional Features
Most of the diseases associated with dysfunction of the intestines and the development of inflammation in the mucosal tissues are associated with poor nutrition. Harmful foods - fatty, spicy, fried - cause serious damage to the gastric mucosa, which subsequently becomes the cause of the development of acute gastritis and its transition to a chronic form.
In the process of treating stomach cough, it is recommended to follow the principles of dietary nutrition. If there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, food intake should be fractional. The weight of a serving should not exceed 300 grams. This is quite enough to fill you up.
Exceeding the recommended amount of food can create additional stress on the organs of the digestive system, which leads to increased symptoms and worsening of the condition. The break between two meals should not be more than four hours. This must be taken into account when creating a menu.
It is important to remember that fast carbohydrates are completely absorbed in one to two hours. For this reason, meals should be prepared from protein foods and contain complex carbohydrates. Thoroughly boiled porridge should be included in the menu. They will envelop the walls of the stomach, eliminating irritation of the mucous membrane. Rice, buckwheat and oatmeal are allowed.
You can add boiled vegetables and mild seasoning to the dish. To prepare, you can use a double boiler, bake them in the oven in foil, boil, or stew. Frying is completely prohibited. For the entire period of treatment, it is necessary to completely exclude fast food. This is the so-called fast food. It is important to keep your diet balanced. This will not only speed up your recovery, but also help improve your overall well-being.

The diet should include as many healthy foods as possible
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
The appearance of regurgitation of gastric contents into the esophageal cavity can cause heartburn. Acid refluxate, entering the esophageal lumen, acts on the cells of its mucous membrane, causing chronic inflammation. Heartburn is a clinical syndrome that is manifested by a burning sensation in the epigastric or xiphoid process. In this case, the patient experiences an unpleasant sour taste in the mouth. This is due to the propagation of a reflex antiperistaltic wave.
Heartburn can cause an obsessive, persistent cough. It is caused by the action of the same refluxate. The contents of the stomach, and then the esophagus, can immediately enter the oral cavity with an antiperistaltic wave. It “burns” the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks, and oropharynx. That is, one of the pathogenetic factors is the direct effect of acidic contents. The second causal factor is reflex.
A cough is a reflex contraction of muscle fibers, which is aimed at clearing the mucous membrane of the oropharynx from dust, mucus and other irritants and substances.
Therapists and general practitioners have encountered the problem of chronic cough. When examining the bronchopulmonary system, no significant data were revealed for bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, pneumonia and other pathological conditions of the respiratory tract. Doctors are trying to use antitussives and expectorants. Obviously, their approach is unsuccessful. This makes diagnosis difficult and confuses the patient and the treating doctor. When identifying a medical history, it is very important to determine the presence of heartburn. If these symptoms exist in parallel, then one should think about the presence of reflux gastritis or esophagitis, diagnose and treat these conditions.
Cough may be one of the symptoms of reflux esophagitis
Combination of GERD and bronchial asthma
Not so long ago, another important mechanism of bronchospasm became known, not associated with allergic reactions to food products, household allergens, and environmental pollutants. This is the backflow of gastric juice into the esophagus. It is noted that with heartburn and cough, the relationship between these two diseases is obvious.
Statistics provide the following data: in 35-70% of cases of diagnosed bronchial asthma, reflux disease (gastroesophageal reflux) occurs. These two conditions mutually support each other's progression. Not all patients with asthma may experience heartburn and other manifestations of reflux esophagitis; more often, the latter pathology is asymptomatic.
Refluctate is an aggressive environment in relation not only to the mucous membrane of the esophagus, but also to the epithelial lining of the oropharynx, as well as the upper and lower respiratory tract, including the bronchi. It causes bronchospasm if it enters the lumen of the bronchial tree. This usually occurs at night, when the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, in particular the vagus nerve, is maximum.
Therefore, the course of bronchial asthma is aggravated if anti-reflux recommendations for food intake, diet and other aspects of life are not followed. Exacerbations of the disease occur more often, as they are provoked by the reflux of acidic contents into the esophagus, and then into the cavity of the oropharynx with aspiration into the bronchial tree.
Episodes of daytime cough are preceded by heartburn. But in the case of nocturnal attacks, there are no warning signs, since the person does not wake up due to a burning sensation in the area of the xiphoid process. Therefore, the attending physician may be disoriented.
A man uses an aerosol for bronchial asthma
In addition to cough and heartburn, when these symptoms are combined, the following clinical manifestations occur:
- Dyspnea.
- Impaired exercise tolerance.
- Losing weight.
- Pain in the epigastric region in the presence of type C gastritis, accompanying reflux disease;
- Flatulence.
- Nausea, sometimes vomiting.
- The “wet pillow” symptom is due to the reflux of esophageal contents into the oropharyngeal cavity, accompanied by hypersalivation (excessive salivation at night due to increased tone of the vagus nerve).
Which specialists should you contact if you have a cough and heartburn, and what tests are recommended?