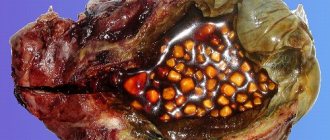
The human body is a mechanism in which every detail is in its place and each performs a vital function. At the same time, the parts do not work separately: they are connected into a single system, so as soon as one element “falls out of life,” all the others are at risk. It's the closest neighbors who have the hardest time. This explains the statistics according to which 70% of patients with cholelithiasis (GSD) have problems with the pancreas. The most common complication of cholelithiasis is pancreatitis.
Which UDCA drug is more effective for cholelithiasis: a study. Candidate of Medical Sciences, hepatologist Sergei Vyalov, in his new study, compared the effectiveness of three UDCA-based drugs in patients with cholelithiasis and biliary sludge.
Features of the diet for combined pathologies: pancreatitis and cholelithiasis
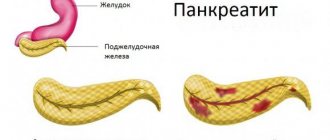
Pancreatitis and cholelithiasis often go hand in hand.
As a rule, gallstones begin to form first, followed by inflammation of the pancreas a little later. Through their combined efforts, these two pathologies seriously complicate a person’s life. After all, their treatment requires not only long-term medication, but also a lifelong diet for pancreatitis and gallstone disease. To understand the relationship between these pathologies, you should familiarize yourself with some anatomical features of the digestive tract. Everything is simple here! The gallbladder (vesica biliaris) and pancreas (pancreas) have a similar functional load - participation in the digestion of food. In addition, they are connected by a common bile duct, through which secretions are discharged into the lumen of the duodenum. And if this pathway is blocked by a gallstone, the removal of enzymes from the pancreas is disrupted, which can lead to inflammation of this organ.
Since one of the etiological bases for the development of combined pathology is an incorrect approach to nutrition, complete treatment requires, on the contrary, to organize an adequate selection of products and methods of processing them, as well as to create an optimal menu.
Is it possible to take Pancreatin for cholecystitis?
Comments:
: 66
[hide]
- What causes cholecystitis and pancreatitis?
- Features of the appointment of Pancreatin
The inflammatory process of the gallbladder can cause dysfunction of other organs. How justified is taking Pancreatin for cholecystitis is far from an idle question for a patient with a chronic form of the disease. The accumulation and release of bile into the digestive system, which is produced by the liver, is the main function of the gallbladder.
The pathological process is provoked by a number of negative factors:
- Eating fatty foods.
- Physical inactivity.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Formation of stones with stagnation of bile.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Toxic damage.
- A constant source of bacterial infection.
- Cholesterol balance disorder.
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
Pancreatitis can provoke disruption of metabolic processes and functions of the digestive system, causing cholecystitis. On the other hand, 2/3 of cases of acute pancreatitis are caused by inflammatory pathology of the gallbladder. Sometimes both disorders appear simultaneously, requiring qualified treatment.
What causes cholecystitis and pancreatitis?
In more than 80% of people, the duct that provides the exit of bile into the digestive system has a common opening with the exit duct of the pancreas.
The common orifice, located near the nipple of Vater, communicates with the cavity of the duodenum. If the bile duct is located 2–5 cm below the pancreatic one, we are talking about anatomically independent formations.
Once in the bladder, the secretion of the pancreas irritates the mucous membrane, causing cholecystitis.
Both inflammations have common causes:
- metabolic disorders;
- bacterial infections;
- obesity;
- physical inactivity;
- binge eating;
- toxic lesions.
Typically, the gallbladder and pancreas perform 1 task, helping the intestines process food. Occurring in 1 organ, inflammation leads to pathology of the 2nd organ. If the diseases accompany each other, doctors diagnose cholecystopancreatitis. Treatment of the gallbladder and pancreas is carried out by a gastroenterologist.
Inflammation of interconnected organs leads to insufficient production of enzymes necessary for normal digestion. Pathology can lead to diseases of the stomach, liver, and diabetes.
In chronic cholecystitis, the formation of stones can prevent the normal flow of bile through the ostium, causing inflammation of the pancreas.
The symptoms of the diseases coincide and complement the picture of cholecystopancreatitis:
- Cholecystitis gives pain in the right hypochondrium. Pancreatitis adds pain on the left, radiating to the back.
- The bitter taste in the mouth is aggravated by dryness.
- Bloating, diarrhea and intestinal colic are common signs of 2 inflammatory processes.
Both diseases cause autonomic disorders - pallor or redness of the skin, fever, chills. If cholecystitis is accompanied by pancreatitis, the doctor may prescribe Pancreatin as part of a comprehensive treatment. The decision about whether an enzyme preparation can be taken should only be made by a specialist based on a complete examination of the patient.
Pancreatitis may be accompanied by excessive or insufficient enzymatic activity of the gland. If increased secretion occurs, drugs are prescribed to stabilize the pancreas.
If the gland is sluggish and has low activity, the doctor prescribes Pancreatin to compensate for the lack of enzymes. Pancreatin is an extract of the pancreas of cattle. The drug comes in the form of tablets. If the organ is functioning normally, no medicine is prescribed.
Treatment is usually limited to drugs against cholecystitis.
If chronic cholecystitis is accompanied by pancreatitis, an enzyme preparation is prescribed to relieve the pancreas. Sometimes cholecystitis causes the need to remove the diseased gallbladder. After surgery, the digestion process becomes difficult. In this case, Pancreatin is prescribed, which significantly alleviates the patient’s condition.
Like any medicine, Pancreatin has contraindications. You can take the enzyme preparation as prescribed by your doctor, following all the instructions.
When treating pancreatitis, the drug Panzinorm Forte or Pancreatin combined can be used. The medicine contains cholic acids.
The drug can be prescribed by a doctor at a medical institution. Self-administration can lead to exacerbation of liver pathology associated with insufficient bile formation.
The use of Pancreatin is excluded for a number of diseases:
- Acute inflammatory processes in the bile ducts or ducts, cholelithiasis.
- Hepatitis.
- Liver failure.
- Blockage of the bile ducts by a cyst or tumor.
- Functional liver disorders.
You should take the medicine as prescribed by your doctor. The patient is prescribed laboratory tests, ultrasound, tomography. Based on the data obtained, the specialist makes a conclusion about the condition of the pancreas, bile ducts and liver. A gastroenterologist has the necessary knowledge about the structure of internal organs and the relationship between the 2 diseases.
Source: https://ozheludke.ru/drugoe/pankreatin-protiv-holetsistita.html
Principles of diet for joint illness
The combination of cholelithiasis and pancreatitis requires adherence to fairly strict nutritional principles:
- exclusions from the menu of foods containing high amounts of cholesterol;
- minimizing bile concentration;
- selection of products containing a fairly large amount of magnesium salts and unsaturated fatty acids in order to remove excess cholesterol;
- increasing the share of fresh vegetables in the menu;
- replacing all methods of heat treatment of food with one - steaming.
Meals should become fractional - food should be taken up to 6 times a day, but in small portions. Fluid intake should be increased to at least 2 liters per day.
What products should be included in the diet?
The recommended diet for a combination of cholelithiasis and pancreatitis should include foods containing plant fiber, vitamin complexes, and magnesium salts. In this case, the food must be pureed and the drink heated. This diet provides:
- stimulation of intestinal peristalsis;
- reduction of inflammatory phenomena;
- weakening of spasms.
The table below indicates which products and in what form are acceptable for people diagnosed with gallstone disease in combination with pancreatitis:
How to eat properly with pancreatitis and cholelithiasis?

Pancreatitis and cholelithiasis (GSD) are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in which the pancreas and gallbladder are involved in the inflammatory process. Treatment requires an integrated approach. At the same time, therapeutic nutrition and drug therapy are prescribed. The diet and menu for cholelithiasis and pancreatitis are similar, since the organs have a close functional connection. Therapeutic nutrition speeds up recovery with proper menu planning. Failure to adhere to the diet leads to exacerbation of inflammation and deterioration of well-being.
Treatment of cholecystitis and pancreatitis with drugs: joint therapy
Simultaneous inflammation of the secretory digestive organs, pancreas and gallbladder, is diagnosed very often.
The combined occurrence of pancreatitis and cholecystitis in medical circles is often called the same common name cholecystopancreatitis, and the same treatment is used to eliminate pathological conditions.
Due to the fact that this disease, considered very serious by practicing gastroenterologists, until recently often ended in death, it should be treated only in a hospital setting, under the direct supervision of a specialist.
What are diseases?
Pancreatitis and cholecystitis are diseases of the digestive system, characterized by damage and inflammation of its secretory organs responsible for the production of special enzymes that are necessary for the breakdown of food.
The joint development of diseases most often has a chronic course and is due to the fact that the bile produced by the liver stagnates in the gallbladder, and at the same time the outflow of pancreatic secretions worsens. The latter, due to its aggressiveness, begins to “eat” the gland from the inside.
Gastroenterologists associate the occurrence of such a pathological condition with the direct influence of the following factors:
- unbalanced diet, frequent dry snacks and excessive content of easily digestible carbohydrates and animal fats in the daily menu,
- serious gastrointestinal diseases that disrupt the functioning of the digestive system,
- frequent stress, causing nervous tension and provoking the development of dangerous diseases,
- alcohol dependence, which contributes to toxic damage to secretory organs,
- obesity, increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
These are the main provoking factors due to which the pancreas and gallbladder are simultaneously destroyed, which impairs their functioning. Less common is the medicinal type of pathology associated with uncontrolled use of certain medications. This cause of the disease is detected mainly in people who constantly self-medicate.
Gallstones can also cause the disease. They completely block its duct, which is combined at the outlet with the pancreatic one, which provokes a delay in the secretory digestive organs of aggressive secretions. This leads to their simultaneous inflammation and destruction. The patient's diagnosis in this case indicates the gallstone type of disease.
The most dangerous is the simultaneous influence on the human body of several negative factors that provoke the development of cholecystopancreatitis. In this case, the risk of developing a complicated form of diseases of the secretory organs, which is quite easily susceptible to malignancy, increases significantly.
Features of the course of cholelithiasis and pancreatitis
Most often in clinical practice, biliary type of pancreatitis and acalculous cholecystitis occur simultaneously.
The symptoms accompanying them are very similar, so only an experienced gastroenterologist can make the correct diagnosis, or rather, identify the inflammation of which organ was the root cause of the pathological condition.
But any person should know the warning signs indicating the development of a dangerous combined disease, as this will help identify it in a timely manner and significantly increase the patient’s chances of a full recovery. Among the most common signs of cholecystopancreatitis, practicing doctors highlight the following:
- heaviness and acute pain localized in the right hypochondrium and radiating to the left side or back,
- dyspeptic intestinal disorders (diarrhea followed by prolonged constipation),
- constant nausea, interspersed with attacks of breakthrough vomiting,
- feeling of dryness and bitterness in the mouth.
These are general signs indicating that an inflammatory process begins in the pancreas and gall bladder.
But in these manifestations there are also specific differences that indicate to the specialist which of the secretory organs has suffered more, for example, with cholecystitis, the pain is stronger on the right, and if the pancreas is inflamed, on the left. They help the attending physician in prescribing and adjusting the correct medication treatment.
In the event that a person has at least one such symptom, or even worse, several, it is necessary to immediately seek advice from a practicing gastroenterologist.
A doctor of this qualification will help make the correct diagnosis, on the basis of which an adequate course and treatment regimen will be selected, allowing the patient to be relieved of the pathology in a short time and prevent its aggravation.
Drug treatment of diseases
All therapeutic measures that help relieve negative signs of cholecystopancreatitis should be prescribed only by a gastroenterologist. Any medicine taken without his knowledge can not only aggravate the situation, but also lead to the development of irreversible changes in the secretory organs. Drug treatment used for this disease has the following goals:
- removal of intoxication caused by the inflammatory process,
- normalization of the functional activity of damaged organs,
- reduction in the production of aggressive digestive secretions,
- relief of pain syndrome,
- elimination of tissue swelling.
For any of these therapeutic stages, the attending physician selects a specific medication for each specific patient, depending on individual diagnostic indicators and the general condition of the person.
It is necessary to take prescribed medications with strict adherence to the treatment regimen so as not to provoke the development of complications of the disease.
And also during the treatment of the disease, the attending physicians set an indispensable condition for patients to adhere to a special diet that facilitates the functioning of the damaged organs.
Important! All medications for cholecystitis and pancreatitis should be prescribed only by a gastroenterologist who, based on the results of a diagnostic study, thoroughly knows what pathological changes have occurred in the pancreas and choleretic secretory organs. Self-medication for these diseases is strictly prohibited, as it can easily provoke serious, often irreversible consequences.
What medications should I take if pancreatitis and cholecystitis develop simultaneously?
Treatment of cholecystopancreatitis with medications pursues such goals as eliminating infection, stopping congestion in the gallbladder and pancreas, relieving pain, and relieving inflammation.
Therapeutic measures can give a fairly effective result only if they are carried out comprehensively and with strict adherence by the patient to all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Simultaneous treatment of cholecystitis and pancreatitis with drugs involves the use of the drugs indicated in the table.
An approximate list of drugs prescribed for the combined treatment of pancreatitis and cholecystitis, and their effect:
| Medicinal groups. | Effect on the body | Drugs of choice |
| Painkillers. | Relaxation of compressed ducts of secretory organs by relieving spasms from them and reducing the pain effect. | Papaverine, Ketorolac, Motilium, Meteospasmil, No-shpa. |
| Antacids. | Reducing acidity and improving the digestive process. | Almagel. |
| Enzyme preparations. | Normalization of the digestive and absorption functions of the digestive system. | Creon, Festal, Mezim, Pancreatin. |
| Vitamins. | Improving the process of absorption of useful substances by the secretory organs of the digestive system, restoring their damaged tissue structures. | Vitamin preparations of groups A, C, E. |
Each drug on this list is capable of simultaneously affecting the gall and pancreas, so a sick person in a short time begins to experience significant relief of symptoms.
As numerous clinical studies show, in the joint treatment of pancreatitis and cholecystitis, these drugs provide the greatest help.
But it should be remembered that all therapeutic measures are carried out exclusively in a hospital, and the home method of drug therapy for cholecystopancreatitis is categorically unacceptable.
Any pill, if taken without the knowledge of a specialist, can lead to serious consequences.
Antibacterial therapy for these diseases
Recently, due to the fact that statistical data increasingly confirm the infectious nature of the development of the inflammatory process in the secretory digestive organs, gastroenterologists are beginning to be inclined to prescribe antibacterial therapy for the joint occurrence of cholecystitis and pancreatitis. But taking medications that inhibit bacterial microflora is recommended only for those patients who have been diagnosed with an acute, severe form of cholecystopancreatitis.
Due to the fact that any antibacterial agent has a negative effect not only on pathogenic, but also on bacteria beneficial to the human body, the selection of such drugs is carried out very carefully.
Before prescribing any antibiotic to a sick person, the attending physician will necessarily check the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora to it, and also recommend probiotics that help restore beneficial intestinal microflora.
The following antibacterial drugs are mainly recommended for the treatment of the pancreas and gallbladder:
- Third generation cephalosporins. Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone are usually prescribed, which are administered parenterally (intravenously or intramuscularly). The optimal course of treatment with them is a week. In some cases, it can be extended by the attending physician up to 10 days.
- Drugs from the penicillin group, Ampiox and Amoxicillin, which are taken orally for a rather short period, no more than 7 days.
- Aminoglycosides (Gentamicin). This drug is administered exclusively intramuscularly and is prescribed only when pathogenic bacteria resistant to penicillin are detected in a person.
Antibacterial drugs provide invaluable benefits in the treatment of cholecystopancreatitis, since thanks to them the patient’s general condition significantly improves already on the second day of treatment.
This is expressed in a sharp decrease in temperature and normalization of the physiological state.
But they also have a significant disadvantage - a high likelihood of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract, such as constipation or diarrhea.
To restore the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, patients should take a probiotic, which normalizes the intestinal microflora, simultaneously with the antibacterial tablet.
Features of joint treatment of pancreatitis and cholecystitis
Cholecystopancreatitis is a very serious and difficult to cure disease, so its treatment should be approached very responsibly. If an acute phase of the disease occurs, the sick person must be immediately admitted to a hospital, where he will be monitored around the clock with medication.
The question of what is best to take for pancreatitis and cholecystitis is the exclusive prerogative of a specialist who, based on the results of a diagnostic study, is aware of the true state of the secretory organs of the patient’s digestive system.
The principles of drug therapy for this disease are based on solving certain problems using the following measures:
- normalization of the production of digestive enzymes by secretory organs,
- elimination of the infectious focus that served as the root cause of the disease,
- relieving the patient of painful symptoms,
- restoration of human activity and performance.
Medicines play a major role in prescribing a therapeutic course. But just taking them is not enough. Cholecystopancreatitis can only be overcome with complex treatment.
In addition to the use of traditional medications, it should include mandatory dietary nutrition and the use of healing decoctions prepared according to centuries-old traditional medicine recipes.
And also to effectively cleanse the body of toxic substances accumulated in it, patients are recommended to regularly drink certain types of mineral waters, which are selected by the attending physician depending on the general condition of the body.
Bibliography
- Kostyuchenko A.L., Filin V.I. Emergency pancreatology: a reference book for doctors, 2nd edition, revised and expanded. St. Petersburg Dean Publishing House, 2000
- Lopatkina T.N. Chronic pancreatitis: diagnostic problems, the role of biliary disorders and approaches to treatment. Wedge. Pharmacol. ter. 2004 No. 1, pp. 9–11.
- Ilchenko A.A., Bystrovskaya E.V. Experience with the use of duspatalin for functional disorders of the sphincter of Oddi in patients who underwent cholecystectomy. Minushkin O.N., Maslovsky L.V. Diagnosis and treatment of functional disorders of the biliary tract. RMJ. Section “Gastroenterology” 2010, volume 18, no. 4.
- Kryzhanovsky, S.A. Modern medicines: More than 10,000 items / S.A. Kryzhanovsky, M.B. Vititnova. M. Ripol-Classic 2009
Source: https://mfarma.ru/pankreatin/lekarstva-dlya-lecheniya-pankreatita-i-holestitsita
General rules of nutrition for a combination of two diseases
Nutrition for cholelithiasis and pancreatitis has a number of restrictions. Table 5A or 5P according to Pevzner is assigned. The choice between the two options depends on the nature of the disease. When an acute process is localized in the bile duct, “A” is prescribed, in the pancreas – “P”.
- stimulation of bile secretion;
- restoration of liver functions;
- normalization of the pancreas;
- gentle operating mode for the gastrointestinal tract;
- relieving spasms from the gallbladder;
- prevention of fatty hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis.
The basic principle of proper nutrition for pancreatitis and cholelithiasis is rationality. This principle provides:
- meals should be frequent, but small in volume;
- proper culinary processing: boiling, steaming, stewing, baking;
- exclusion of cholesterol products to prevent the formation of gallstones;
- serving temperature - 37-40°C;
- products with an abundance of “healthy” fatty acids and coarse fiber;
- water regime - 1.5-2 liters per day.
Treatment of pancreatitis after cholecystectomy
After removal of the gallbladder, the patient is prescribed treatment with a minimum amount of medications:
- Antibiotics. Prescribed immediately after surgery to prevent inflammation of the bladder bed, the organs near which it was located, and its main excretory duct. Taking antibacterial drugs lasts 3-5 days.
- Painkiller. To relieve pain and spasms that may appear after removal of the gallbladder, analgesics (Baralgin, Pentalgin) and antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Buscopan) are prescribed.
- Suspension or tablets Ursofalk - prevent the formation of stones in the bile duct.
- Pancreatin tablets - to improve digestion.
On an individual basis, some patients are prescribed choleretic agents and enzymes to prevent pancreatitis, which normalize the intestinal microflora and improve the functioning of the entire digestive system.
When the gallbladder is removed, exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis become more frequent. To relieve pain, doctors prescribe such patients to take analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs (Paracetamol, Ketanov, Diclofenac). In severe cases, the patient is hospitalized and intravenous painkillers are administered to relieve pain.
Complications after gallbladder removal are rare and most often due to poor diet. Therefore, it is very important for the first year after surgery to follow all the instructions of the attending physician.
Menu design principles
The daily menu depends on the stage of the disease. In the acute period, the patient is prescribed several days of fasting with a smooth transition to natural nutrition. During the period of remission, the goal of the diet is to prevent exacerbations and activate restoration processes in the organs.
What products are allowed
Food products with a combination of pancreatitis and cholelithiasis should contain coarse fiber, vitamins, and a lot of magnesium.

A decoction with rosehip has a stone-dissolving effect. If you have cholelithiasis, you need to drink this decoction every day.
Food should be mechanically gentle: pureed, ground in a meat grinder, chopped in a blender. The drink should be warm, unsweetened. This food will provide:
- normalization of digestion;
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- antispasmodic effect.
Foods allowed for pancreatitis and cholelithiasis:
- lean meats: chicken (skinless fillet), rabbit, lean beef, veal;
- fish: hake, pollock, halibut;
- eggs in the form of a white omelet;
- vegetable fats: olive, coconut, flaxseed, sunflower oils;
- butter for stable remission;
- cereals: buckwheat, oatmeal, rice;
- wheat bread crackers;
- baked fruits and vegetables;
- vegetable soups, weak meat broths;
- dietary cottage cheese casseroles;
- soft pasta.
You can drink compote, weak tea, chicory drink, warm mineral water, diluted berry juice.
Fully or partially limited products
For gastrointestinal diseases, the following products should be completely avoided:
- fatty meats;
- salo;
- coffee;
- sausages;
- alcohol;
- margarine, spread;
- smoked meats;
- meat by-products (liver, kidneys, brain);
- fatty dairy products (cottage cheese, cheese, sour cream, cream, whole milk);
- greenery;
- sour fruits and berries;
- carbonated sweet drinks;
- durum wheat pasta;
- canning, even homemade;
- flour.
If Diet 5 is prescribed, then you should not overuse herbs and spices. Various sauces with seasonings and vinegar are an additional burden on the pancreas.

All products used in cooking must be fresh.
Honey and other bee products can be eaten in limited quantities.
Example of a weekly diet
- Breakfast: biscuits with a piece of low-fat cheese, weak green tea.
- Lunch: protein omelet, 50 g of white crackers, a teaspoon of honey, a decoction of dried fruits.
- Lunch: slimy rice porridge seasoned with olive oil, steamed chicken cutlet, baked apple, chicory coffee.
- Afternoon snack: low-fat cottage cheese.
- Dinner: oat bran porridge, carrot and apple salad, berry compote.
- Breakfast: buckwheat porridge with lactose-free milk with honey, green tea.
- Lunch: baked apple.
- Lunch: vegetable puree from zucchini and broccoli, boiled veal.
- Afternoon snack: a glass of low-fat kefir.
- Dinner: vegetable broth, a glass of Greek yogurt, bread.
- Breakfast: oatmeal with diluted milk (1:1), a spoonful of honey, biscuits, green tea.
- Lunch: a glass of kefir and some bread.
- Lunch: weak chicken broth, bread, rosehip broth.
- Afternoon snack: a glass of low-fat soft cottage cheese.
- Dinner: steamed fish with baked vegetables, dried fruit compote.
- Breakfast: steamed protein omelet, biscuits, green tea.
- Lunch: cottage cheese with tea.
- Lunch: chicken fillet baked with vegetables.
- Afternoon snack: creamy vegetable soup.
- Dinner: baked apple, tea with honey.
- Breakfast: cottage cheese casserole with tea.
- Lunch: bread and rosehip broth.
- Lunch: a bowl of vegetable soup with white croutons, a little butter or sour cream can be added to the soup if remission is stable.
- Afternoon snack: Greek yogurt, dried fruit compote.
- Dinner: chicken dumplings, carrot salad, green tea.
- Breakfast: oatmeal, honey, tea.
- Lunch: bread and rosehip broth.
- Lunch: fish soup, a portion of white bread crackers, compote.
- Afternoon snack: a glass of low-fat fermented baked milk.
- Dinner: stewed vegetables, a piece of boiled veal, green tea.
- Breakfast: fruit jellies, biscuits, chicory coffee.
- Lunch: fish dumplings, carrot salad.
- Lunch: meat soufflé, bread, compote.
- Afternoon snack: baked apple.
- Dinner: fish casserole, a handful of raisins, green tea.
This diet is suitable for gallstone disease and pancreatitis. Dishes can be changed depending on taste preferences and the stage of the disease.
Functions of the pancreas and gallbladder in the body
The functions performed by the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract are aimed at maximizing the digestion of incoming food. The role of these organs in the digestive process is different, but their general activity involves the breakdown of food components and providing the body with necessary substances and energy.
The pancreas, due to its structure, is intended for the synthesis of pancreatic juice, which contains 20 enzymes, combined into 3 groups:
- lipase - breaks down fats;
- protease - proteins;
- amylase - carbohydrates.
These enzymes are produced in an inactive form. Their structure changes under the influence of the duodenal enzyme, enterokinase. It is released when a bolus of food enters the stomach and becomes active, in turn, in the presence of bile, converting trypsinogen (protease) into trypsin. With its participation, other pancreatic enzymes are activated, which enter the intestinal lumen when food enters there.
Bile is a catalyst for pancreatic and duodenal enzymes. The qualitative composition and quantity of enzymes released depend on the food consumed.
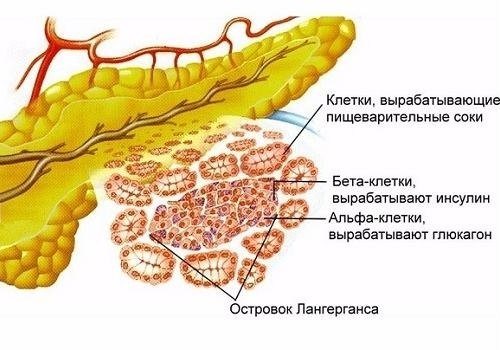
The pancreas produces 1.5−2 liters of pancreatic juice per day. Through the small ducts of the acini (islands consisting of glandular cells that have their own ducts and vessels), the secretion enters the larger excretory canals, through which it flows into the main - Wirsung - duct. Through it it is poured into the small intestine in small portions. The required amount of pancreatic secretion is regulated by the sphincter of Oddi.
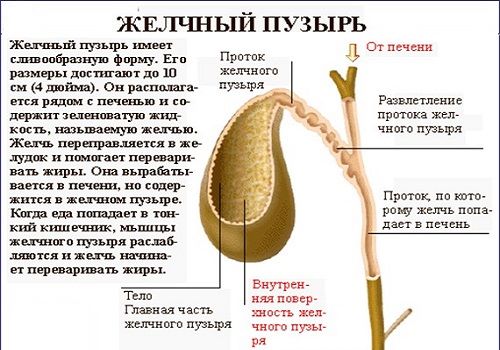
Main functions of the ZhP:
- accumulation of bile produced by the liver;
- implementation and control of its receipt in the KDP.
Bile is produced by the liver constantly. It also continuously enters the hepatic duct and gallbladder. Up to 50 ml of bile can accumulate in the bladder (this is its volume), which, if necessary, thanks to the contraction of the muscle walls, enters through the excretory and common bile canal into the duodenum. A functional feature of the gallbladder is the ability to concentrate bile in such a way that in its space of 50 ml it accumulates in a highly concentrated form corresponding to a volume of 1 liter or more.
Bile and bile pigments are involved in the breakdown and absorption of lipids. The release of the contents of the gallbladder is associated with the digestion process and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system: the organ receives a signal that a food bolus (chyme) has entered the duodenum and contracts, releasing the secretion into the duct. This occurs in response to fatty foods. Otherwise, with continuous entry into the intestines (in the absence of food and intestinal contents), the organ mucosa would be damaged under the aggressive influence of acids.
The gallbladder is not an irreplaceable organ: after its resection, the function of storing bile is performed by the duodenum.
How is the gallbladder connected to the pancreas?
The gallbladder is connected to the pancreas anatomically and functionally.
Anatomically, the ducts of the pancreas (the Wirsung duct and the accessory duct, the Santorini duct, which is located in the head of the pancreas and can be connected to the main duct or be independent) and the common bile duct (gallbladder duct) flow into the lumen of the duodenum. There are several options for their final location:
- Type 1 - 55%: Wirsung and common gall are combined into a common ampoule;
- Type 2 - 33%: the ducts merge into one near the duodenum without forming an ampoule;
- Type 3 - 4%: channels are not combined;
- Type 4 - 8%: merge at a great distance from the nipple of Vater.
How to prepare healthy diet meals
It is easier for patients to stick to a diet if the dishes in it are varied and tasty. It is important to follow the rules of cooking and serving food.
The following recipes are suitable for feeding patients on the 5P and 5A diets:
- Steamed turkey cutlets. Ingredients: 200 g turkey fillet, 30 g white bread, 50 ml milk, 3 teaspoons vegetable oil, salt to taste. Soak the bread pulp in milk for half an hour. Prepare minced meat, add butter, salt, bread and milk. Mix well and form into cutlets. Place on a steamer rack and cook for 30-40 minutes.
- Fish in Bechamel milk sauce. Bake any lean fish fillet in foil. For the sauce you need 150 ml of milk (fat content up to 3.2%), a teaspoon of butter, a teaspoon of flour, a pinch of sugar, salt to taste. Melt butter in a frying pan, add flour using a sieve. Fry the flour for 2 minutes. Pour in the milk (should be hot) in a thin stream. After boiling, cook for another 10 minutes. Add sugar and salt. Pour the prepared sauce over the fish.
- Diet Olivier. To prepare, you will need one medium-sized carrot, two potatoes, two eggs, 300 g of boiled chicken fillet, fresh cucumber, and a spoonful of low-fat sour cream. Peel potatoes and carrots, boil in salted water. Hard boil the eggs. Peel the cucumber. Cut all ingredients into cubes, mix, add salt and season with sour cream.
- Fruit cake without baking. Ingredients: 1 ripe banana, can of canned peaches (you can take 2 fresh), 300 ml of unsweetened yogurt, biscuits, 200 ml of water, sachet of gelatin. Pour gelatin with warm water and let it dissolve. Add yogurt and stir. Cover the bottom of the vessel with parchment. Break the cookies into crumbs. Layer the ingredients. Place the finished cake in the refrigerator overnight. In the morning, dessert is ready.
Nutrition for cholelithiasis and pancreatitis
Gallstone disease (GSD) is a pathological condition in which a solid deposit forms in the gallbladder. The main cause of the disorder is poor, improperly adjusted nutrition, genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders, and infections.
According to statistics, women are more susceptible to the disease than men, but their gallstone disease is much milder. The most common stones are: cholesterol, pigment, calcareous and combined types.
For a long time, the disease proceeds without symptoms, when formations in the gallbladder reach a certain size, they make themselves felt with discomfort and pain.
Pathology is almost always accompanied by serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, this can be:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- nausea;
- stool disorder.
The inflammatory process occurs against the background of increased body temperature. Large stones cause severe pain under the right rib. The disease is characterized by the appearance of yellowness of the sclera of the eyes and skin.
The cause of the attack may be physical exertion, stress or hypothermia. Often, specific symptoms worsen soon after consuming smoked, fried and fatty foods, spices and hot seasonings.
Complications of cholelithiasis include hepatic colic, biliary peritonitis, acute or chronic pancreatitis, and gangrene of the gallbladder. To improve well-being, take pancreatin for gallstone disease.
Treatment of pancreatic diseases with medications
The pancreas in the human body performs the functions of producing enzymes for breaking down and digesting food, as well as producing some hormones. If you do not pay proper attention to caring for your iron, this will lead to a deterioration in your health and provoke a number of diseases, the treatment for which will take a long and painful time.
Pancreatic diseases
A person’s lifestyle has a strong influence on the functioning of the digestive system. Poor nutrition (fatty, spicy and salty foods, food additives and carbonated drinks), lack of exercise, alcohol, various infections, medications taken without the necessary indications, along with some diseases, negatively affect the functioning of the pancreas. Often the organ suffers from an inflammatory process called pancreatitis. As a rule, other diseases of the pancreas (pancreatic necrosis, diabetes mellitus, cysts, fistulas, abscesses, cancer) are the result of advanced inflammation.
The pancreas produces pancreatic juice, consisting of enzymes and bicarbonates, which normally enters the duodenum along with bile and starts the digestion process. If the common duct is blocked, enzymes will not be able to leave the pancreas and will begin to destroy the organ, causing inflammation. The cause of the phenomenon is often cholelithiasis. When a gallstone blocks the common duct, the pancreas is primarily affected. We will discuss the symptoms of the disease, treatment with medications and principles of prevention in the article.
Acute pancreatitis poses a threat to the patient's life and often leads to dangerous complications and disability. Accurate diagnosis and timely treatment are extremely important. Signs of acute pancreatitis include:
- painful sensations in the upper abdomen, spreading to the back or encircling;
- heat;
- nausea and vomiting;
- frequent light-colored loose stools;
- dry mouth.
Treatment of the pancreas begins with relieving the load on the affected organ. The patient is prescribed fasting and rest for the first days. You are allowed to drink non-carbonated mineral water and lightly concentrated tea without sugar. On the third or fourth day, a gentle diet is prescribed, developed by the attending physician, based on the severity of the disease and the degree of the inflammatory process.
Treatment with medications for diseases of the pancreas is carried out in order. Initially, enzymatic (Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon, Enzistal, Festal, etc.) and antisecretory drugs (Pirenzepine, Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, etc.) are prescribed, which allow the diseased organ to “rest” and recover. Remember, taking this type of medication for too long will lead to decreased production of pancreatic juice in the future. Patients must take medications in the prescribed dosage and strictly adhere to the duration of the course.
Periodically, attacks of acute pancreatitis are accompanied by severe pain that can provoke painful shock. To combat the phenomenon, antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-Shpa) and analgesics (Pentazocine, Baralgin) are prescribed. In severe cases, narcotic drugs (Promedol, Tramal) are used. The main sign of positive dynamics of treatment is a noticeable reduction or absence of pain. If a bacterial infection is added to the inflammation, a course of antibiotics is prescribed (Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Vancocin). Often pancreatitis is accompanied by increased stomach acidity, which can provoke stomach and duodenal ulcers; it is recommended to take antacids (Maalox, Almagel).
The above treatment methods will lead to positive results if the root cause of inflammation is eliminated. The article will focus on cholelithiasis (GSD), as a likely culprit in the development of pancreatitis.
Cholelithiasis
Gallstone disease is the formation of stones in the gallbladder or bile ducts. The pathology has become widespread, mainly in prosperous countries, which is associated with changes in the composition and norms of nutrition. According to statistics, middle-aged and older women are more often affected by the disease. At risk are people who are overweight and lead a sedentary lifestyle. Therapy for gallstone disease is carried out by a gastroenterologist and takes several years.
General information about housing and communal services
Gallstones are divided into 3 types:
- cholesterol;
- bilirubin;
- calcareous.
If the patient has stones of the last two types or cholesterol stones, but of a large diameter, the pills will no longer help, surgeons get to work.
The leading causes of cholelithiasis include:
- excessive consumption of fatty and refined foods;
- insufficient amount of fiber in the diet;
- lack of physical activity;
- hormonal disorders;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- long-term use of drugs to thicken bile.
Methods for preventing cholelithiasis are simple and quite obvious.
- pain in the right side of varying nature and intensity;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- diarrhea and flatulence.
Cholelithiasis is diagnosed based on patient complaints and as a result of a biochemical blood test. To confirm the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is performed. Simplicity, safety, high information content and low cost have made ultrasound the main method for diagnosing cholelithiasis. The study allows you to determine the presence or absence of stones in the gall bladder and ducts, determine the exact location of formations, number, size and shape.
Treatment methods for cholelithiasis
Based on the results of the examination, a decision is made on treatment methods. There are 3 options:
- surgical;
- shock wave lithotripsy (method of crushing stones using a sound wave);
- use of special drugs.
Before starting treatment, the doctor is obliged to convey to the patient a simple truth - without normalizing lifestyle and changing eating habits, there is no point in talking about recovery. Treatment methods will not bring tangible results if the patient does not begin to take care of his own body.
A common method used for treatment is removal of the gallbladder. It is performed in two ways: cholecystectomy (classical abdominal surgery) and laparoscopic cholecystectomy (performed with a special device through a small incision). Shock wave lithotripsy, a non-invasive method of crushing stones, has proven itself positively.
Drug treatment of gallstones is carried out if the stones are small (up to 2 cm), located in the gallbladder and occupy half of the volume. Drug treatment is used solely to get rid of cholesterol stones. It is possible to determine the composition by probing the duodenum to collect a portion of bile for further study in the laboratory or using radiography with a contrast agent.
Shock wave lithotripsy
The method is considered innovative in the treatment of cholelithiasis and avoids surgical intervention. Its effectiveness with proper selection of patients is 65-70%. To crush stones, special devices are used that generate acoustic waves. The effectiveness of treatment is assessed after three months to a year and a half. During this period, the gallbladder is freed from stone fragments. Often the patient needs to undergo several sessions of the technique. According to statistics, the probability of re-formation of stones is 50%.
It is permissible to use shock wave lithotripsy if:
- diameter of stones less than 2 cm;
- the gallbladder is not inflamed;
- gallbladder motility and duct patency were preserved.
In addition to the above conditions, contraindications are taken into account:
- ulcer history (presence of stomach or duodenal ulcer);
- calcined stones;
- pregnancy.
When using the method, large stones break up into small fragments or turn into sand. The crushing effect is achieved by the directed action of shock waves. After the procedure, the remaining stones are transported by a current of bile into the duodenum and are excreted from the body with feces. At the exit, the particles must be less than 0.5 cm in diameter, otherwise the pieces risk getting stuck in the bile ducts and causing complications.
Even after curing the disease using the mentioned method, medications are prescribed for the next 3-6 months to dissolve gallstones for prophylactic purposes; there remains a high probability of recurrence.
Treatment of cholelithiasis with drugs
Medicines for gallstone disease work on:
- dissolving stones;
- stimulation of gallbladder motility;
- increased bile production.
The second point can be achieved through the use of medications, consumption of a sufficient volume of fluid in combination with physical activity.
Drug treatment of cholelithiasis is carried out with bile acid preparations, choleretic agents and the drug Ziflan.
Bile acid preparations
This group of drugs has been used for decades and has proven effectiveness. The work of the products is aimed at bringing bile acids and cholesterol to a balanced ratio. The drugs Ursosan, Ursofalk and Ursohol are based on ursodeoxycholic acid. Reaching bile, the acid forms a composition in the liver secretion that dissolves cholesterol stones. Henodeoxycholic acid (Henochol, Henofalk, Henosan) converts cholesterol from a solid state to a liquid crystal state through chemical reactions. These two types of medications are used together to achieve the best effect. The course of treatment lasts on average 6 months – 2 years. To monitor treatment, an abdominal ultrasound is prescribed twice a year.
When treating gallstone disease with a group of drugs, it is necessary to take into account their incompatibility with Cholestyramine and the hormone estrogen. The simultaneous use of antacids with bile acid preparations significantly reduces the effectiveness of the latter. There are a number of known contraindications:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- stone cholecystitis;
- peptic ulcer;
- liver diseases.
Choleretic drugs
Medicines that enhance the motility of the gallbladder and ducts include Zixorin, Allohol, Berberine, Flamin. For productive treatment, contraindications to the use of drugs are taken into account in order to avoid negative consequences.
Medicines of the described type are not prescribed if the patient is diagnosed with: erosion of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, pancreatitis or diarrhea.
Ziflan
Ziflan is produced on the basis of immortelle extract. Thanks to its natural composition, there are virtually no side effects. Contraindications to the drug include obstructive jaundice and intolerance to the components. The drug is not recommended for pregnant and nursing mothers. The possibility of allergic reactions has been described. Ziflan stimulates liver cells to produce bile with the correct composition, which does not precipitate. The drug normalizes the outflow of bile, increases tone and stimulates the motility of the gallbladder. Ziflan is an excellent tool for the treatment of gallstone disease. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to periodically repeat the course of treatment.
Despite technological progress and the capabilities of medicine, humanity has not yet invented a “golden pill” that can finally cure people of various diseases and restore health. You will have to try and change your usual lifestyle.
Sources used: gastrotract.ru
Treatment options
A diet for pancreatitis and cholelithiasis helps to achieve excellent positive results; a proper balanced diet avoids surgical intervention and removal of the affected organ. The diet is also indispensable during medical and surgical treatment.
To eliminate the problem, antispasmodics (to eliminate pain), antibiotics (to eliminate infection), hepatoprotectors (to protect the liver from bile stagnation and damage) are recommended.
When conservative treatment does not bring the expected result, an acute attack of the disease occurs, and surgery to remove the gallbladder is indicated. After the intervention, the patient must adhere to dietary table No. 5 according to Pevzner for a long time.
It is nutrition and diet that become the main factors in recovery, regardless of:
- severity of the disease;
- characteristics of the patient’s body;
- stages of the disease.
To minimize the risk of a recurrent attack, you should completely exclude prohibited foods and follow the recommendations of a nutritionist regarding the correct methods of heat treatment of food.
What influence do organs have on each other?
Since the organs of the digestive system are closely interconnected, the pathology of any of them cannot occur in isolation. This is especially true for gallstone disease - cholelithiasis, which in its prevalence in recent years is not inferior to heart disease. When the common duct is obstructed by a stone, a large amount of pancreatic secretion and bile accumulates not only in the common ducts, but also in the small canals of the pancreas. The pressure in them rises sharply as the liver and pancreas continue to function and produce pancreatic juice and bile. Small and fragile ducts of the pancreas rupture, their contents enter the parenchyma of the organ. At the same time, tissue cells and nearby vessels are damaged. In case of injury (rupture of the ducts), the enzymes are activated, the process of self-digestion of the gland begins in the parenchyma - pancreatitis develops, which can be complicated by massive pancreatic necrosis. At the same time, the walls of the gallbladder become inflamed, leading to cholecystitis, bile stagnation, hypersplenism, and ascites.
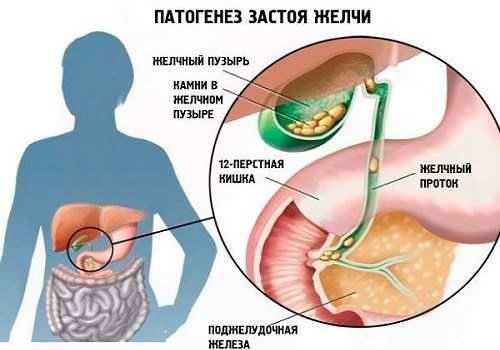
Therefore, at the first symptoms, even unexpressed and seemingly insignificant, you cannot self-medicate and use traditional methods. You must immediately contact a specialist.
How will the organs work if one of them is resected?
The gallbladder is an auxiliary organ, therefore, in case of pathological formations or severe inflammatory process (phlegmonous or gangrenous cholecystitis), which is accompanied by pancreatitis, cholecystectomy is indicated. Otherwise, this will cause the development of pancreatic necrosis, a life-threatening condition with an unfavorable prognosis. The earlier the operation is performed, the lower the risk of developing pancreatitis. The functions of the gallbladder are performed by the duodenum: bile produced by the liver enters its lumen. This happens constantly, as bile is produced, and not at the time of eating. Therefore, the mucous membrane of the duodenum is affected, a disorder of the microflora in the large intestine occurs, which leads to stool disorders (constipation or diarrhea), and pancreatitis may develop.
When the pancreas or its affected part is removed, replacement therapy is prescribed: the patient takes glucose-lowering drugs for existing diabetes mellitus or enzymes. The dosage is determined by an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist individually in each case. Taking these medications is necessary for a long time (months, years, sometimes a lifetime). In addition to drug therapy, a person must follow a strict diet: table No. 9 for diabetes, table No. 5 for pancreatitis.
To avoid serious consequences and lifelong use of drugs with a strict diet, you need to take care of your health, give up bad habits and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
How to eat with gallstone disease
Nutrition for gallstone disease and pancreatitis may change as the patient recovers.
During the period of exacerbation, it is necessary to avoid a number of dishes that can be eaten during stable remission. It is important to know that dishes are steamed or boiled with a minimum amount of salt. Fried and smoked foods are completely removed. During an exacerbation, all food must be ground and eaten in small portions at least 5-6 times a day. It is harmful to eat before bed, to rush and chew food poorly.
It is allowed to eat chicken, rabbit, beef, and skinny fish, including river fish. Pork, smoked meats and sausage were banned. As for chicken and quail eggs, they are eaten only boiled; it is also allowed to cook a protein steamed omelet.
Can I have honey or coffee?
For pancreatitis and gallstones, sweets are allowed, but in strictly limited quantities. Natural honey will benefit the body; it is rich in valuable substances and is indispensable in the human diet. However, we must not forget that there is an increased risk of developing allergic reactions to this beekeeping product.
Reviews from patients say that there are even a number of recipes for the treatment of gallstone disease. You can consume honey 2-3 times a day, diluted with a glass of warm boiled water.
To combat stagnation of bile, take a herbal infusion with honey; the remedy is prepared from hops, valerian root, and clover. If you mix black radish juice with honey, you will get a therapeutic and preventive remedy against pancreatitis, cholecystitis and other disorders. Mix a glass of radish juice and the same amount of honey, drink a tablespoon a couple of times a day.
Before using the proposed recipes, you need to check for the presence of individual intolerance to honey.
Diet for duodenitis and pancreatitis excludes coffee consumption:
- soluble;
- custard;
- caffeinated drinks.
Instant coffee and energy drinks, which contain record amounts of caffeine, are especially harmful.
When a patient suffers from a whole “bouquet” of diseases at once, coffee is completely excluded from the menu. If the habit of invigorating oneself with such a drink does not leave a person, they drink coffee with skim milk and only in the morning.
Treatment of cholecystitis and pancreatitis with drugs - a detailed list of drugs
Cholecystitis is a pathological process in the gallbladder. In almost all cases, it occurs at the same time as pancreatitis, which is an inflammation of the pancreas. The symptoms of both diseases are surprisingly similar. Because of this, the disease has to be treated at the same time and with almost the same medications.
Treatment of cholecystitis and pancreatitis with medications
Causes of diseases
The disease can develop for several reasons, including the following:
- constant presence of infection in the nose, throat and larynx;
- problems with metabolism, which can be caused by errors in nutrition and the presence of gastrointestinal diseases;
- development of diabetes mellitus;
- slight mobility of the patient;
- constant constipation and disorders;
- overweight and obesity;
- slight tone of internal organs;
- unhealthy diet, which can be rich in flour, fried and salty foods;
- insufficient caloric nutrition, which can even lead to anorexia;
- consumption of large amounts of spicy foods;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- frequent food poisoning or intoxication of the body with other harmful substances.
Attention!
It is very dangerous when a person accumulates several factors at once, which can lead to the development of cholecystitis and pancreatitis. In such cases, there is a possibility of developing a complicated form of the disease, which can even lead to cancer.
Pancreatitis Cholecystitis
Medicines against cholecystitis
For conservative drug treatment of cholecystitis, the following drugs are used:
Ursofalk
Ursofalk is available in the form of capsules and suspensions
Belongs to the group of drugs containing ursodeoxycholic acid). This group of medications helps reduce cholesterol stones and increases fat emulsification. Limited effectiveness - in 10 percent of patients.
Buscopan
Buscopan is one of the most effective antispasmodics in the treatment of gallbladder diseases.
The drug belongs to the class of antispasmodics and relieves colic. It has a selective effect, it relaxes the walls of the gastrointestinal tract without affecting cells that are in a physiological state. The pain goes away in about half an hour, the effect lasts for six hours.
Duspatalin
Duspatalin (mebeverine hydrochloride) relieves spasms in the intestines
Another antispasmodic. It is used specifically for pain in the abdomen or intestines (it works best on the colon). It acts in about a quarter of an hour, eliminating or reducing pain without affecting the rest of the gastrointestinal tract.
Motilium
Motilium relieves attacks of nausea, vomiting and intoxication of the body
The drug relieves attacks of nausea, vomiting and intoxication of the body. It quickly removes waste from organs and tissues, easing the course of diseases and eliminating pain. The drug can only be taken from the age of five and when the patient’s body weight has reached 20 kg.
The classic dosage of the medicine is 10 mg of the active substance, which is taken two to three times a day. You must take the tablets strictly half an hour before meals. In this case, it is necessary to adjust the dosage if the patient suffers from liver and kidney diseases.
The duration of therapy can only be determined by a gastroenterologist.
Holosas
Holosas helps with problems with the gallbladder and intoxication of the body
The drug is available in the form of syrup. It perfectly helps with problems with the gallbladder and intoxication of the body. Holosas can also be used for liver diseases, which are a complication of pancreatitis and cholecystitis. The medicine can be used not only by adults, but also by children. Dosages and course of therapy are calculated individually in each case.
The classic dosage for children is 2.5 ml of syrup two to three times a day, half an hour before meals. Adults also take 5 ml of the active substance two to three times a day 30 minutes before eating.
Sometimes during treatment, patients experienced severe heartburn, which required systematic treatment.
During pregnancy, the use of Holosas can only be initiated by a gastroenterologist if there are real reasons for this.
Hymecromone
Odeston is used to eliminate exclusively biliary pain
It is used exclusively to eliminate bile pain and restores the movement of bile. Taken 30 minutes before meals, the course lasts two to three weeks. Cannot be used for renal, liver failure, duodenal ulcer, hemophilia and obstruction of the bile ducts.
Alverin
Meteospasmil - an analogue of alverine
Antispasmodic, contains two active ingredients: the analgesic alverine and the defoamer simethicone. Thanks to the combination of substances, the medication quickly eliminates flatulence, which is common in patients with biliary tract diseases. Take one tablet as needed.
Trimebutine
Trimedat - a drug for relieving pain due to cholecystitis
Normalizes gastrointestinal motility, relieving abdominal pain within 1 hour, eliminating dyspepsia. Reception is carried out three times a day. Usually well tolerated by patients.
If conservative treatment fails, surgical treatment is used. Its main method remains cholecystectomy. it prevents not only complications during the acute course of the disease, but also gallbladder cancer in the distant future. Removal of the organ now occurs laparoscopically; it is not contraindicated for pregnant women or the elderly.
Pregabalin
Pregabalin - a drug to reduce pain due to pancreatitis
The anticonvulsant medication shows good results in eliminating persistent pancreatic pain. It is also used in the treatment of neuropathic pain syndrome. In addition, the drug has no anti-anxiety effect, which can further improve the well-being of patients.
Enzyme preparations
Medicines used for replacement therapy in case of enzyme deficiency are Festal, Mezim, Creon. Each of these drugs contains varying amounts of lipase, protease and amylase.
The dosage and medicine must be chosen by the doctor, taking into account the fact that a person needs to receive at least 25 thousand and no more than 40 thousand units for the main meal. Most effective when taken during or immediately after meals.
The dosage is calculated individually for each patient.
Pancreatin
Pancreatin is taken to facilitate the digestive process and normalize enzyme production
The drug is taken to facilitate the digestive process and normalize the production of enzymes. Even small children under one year old can take the drug. The dosage is determined solely by the attending physician. The duration of treatment also depends on the patient's health and his response to the drug. Therapy can last several months.
The classic dosage of the drug is 400 thousand units/day for significant problems with the pancreas.
Children from one and a half years to 16 years old take a maximum of 100 thousand units/day, small children under one and a half years old can take up to 50 thousand units/day. For liver and kidney problems, minor dosage adjustments may be necessary.
If the pancreas has relative problems and has just shown symptoms of the disease, lower dosages can be prescribed.
Attention!
This instruction does not consider the individual course of the disease. That is why you should check your dosage with your doctor.
Cost of medicines
DrugImagePurposePrice
| Motilium | Antispasmodic | 600 rubles |
| Buscopan | Antispasmodic | 300 rubles |
| Holosas | For the production of bile | 100 rubles |
| Festal | To improve digestion and reduce the load on the gallbladder and pancreas | 150-600 rubles |
| Mezim | To improve digestion and reduce the load on the gallbladder and pancreas | 85-290 rubles |
| Pancreatin | To improve digestion and reduce the load on the gallbladder and pancreas | 50 rubles |
Attention!
The cost of the medicine may vary depending on the country of origin. Foreign analogues are many times more expensive, but they often show much faster and noticeable results.
Additional treatments
To support treatment when using medications, additional therapies are prescribed.
- For cholecystitis, ultrasound heating and electrophoresis on the liver are prescribed; usually 10 procedures are sufficient. After such sessions, bile production will significantly improve, blood circulation in the organ will improve, and discomfort and pain will gradually disappear.
- The same procedures are prescribed for the development of pancreatitis. But the device is installed on the stomach. Typically, several areas are heated to reduce inflammation and protect nearby organs.
- Mineral baths. For the procedure, it is better to choose a procedure with carbon dioxide and sodium chloride solution. The water in the bathroom should be no more than +37 degrees and no less than +35 degrees.
- Drinking 150 ml of Essentuki and Borjomi mineral water, you can take any medicinal water, significantly facilitates digestion and reduces the load on the gallbladder and pancreas.
- After the disease enters the stage of remission and the exacerbation is relieved, you can take mud baths and use special applications for gluing them to the area of the liver and pancreas.
- You should definitely follow a diet, excluding from your diet everything fried, floury, spicy, sweet and salty.
The use of Borjomi and Essentuka facilitates digestion and reduces the load on the gallbladder
Attention!
Physiotherapy can be used to treat diseases that are not in the acute stage. Otherwise, the problem may worsen significantly and lead to the need for urgent surgery.
Complications of cholecystitis and pancreatitis
If the disease is not treated, a number of serious complications can occur. However, sometimes some of them develop even with adequate therapy. Among them the following stand out:
- development of liver diseases, including hepatitis;
- development of gastritis and ulcers, including their complicated forms;
- manifestation of symptoms of diabetes mellitus;
- poor digestion of foods, which can lead to increased constipation and diarrhea;
- insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals;
- development of peritonitis, which can lead to death;
- development of cancer.
Attention!
The first signs of the disease force you to urgently visit a gastroenterologist to undergo a full examination to identify all problems with the gallbladder and pancreas.
Before starting therapy, you should first consult with your doctor, as you should carefully select the dosage of the drugs. They sometimes differ significantly from the classic ones, which are prescribed in the instructions. This may be due to complications, problems with the liver, heart and kidneys. The duration of therapy in many cases also depends on the patient and his condition.
Healthy and unhealthy vegetables and fruits
Gallstone disease, gastroduodenitis and chronic pancreatitis require the patient to consume many fruits and vegetables, some of which will even become medicinal.
Traditional medicine suggests drinking a few tablespoons of strawberry juice on an empty stomach; the recipe helps fight gallstones and inflammation in the pancreas. In addition, strawberries will help normalize low-density blood cholesterol levels. Nutritionists do not prohibit eating melon, watermelon, bananas, apples, avocados, cherries, pears and various berries. The exception will be sour varieties of apples and berries, for example, cranberries.
The diet includes the consumption of beets, ripe tomatoes, potatoes, carrots, pumpkins and zucchini. Eat any types of cabbage with caution, especially white and savoy. Cabbage can be consumed only during the period of remission, exclusively in boiled or stewed form.
The consumption of tomatoes causes a lot of controversy; doctors agree that tomatoes must be ripe, not sour, and their color can be any color. To ensure normal tolerance of the product, it does not hurt to peel the vegetables and eat only the pulp.
An expert will tell you how to eat with cholelithiasis and pancreatitis in the video in this article.
Gallbladder diseases
Gastrointestinal diseases include the following pathologies:
- inflammatory process – cholecystitis;
- formation of stones in the lumen of the bladder - cholelithiasis;
- violation of ductal motility - dyskinesia;
- polyps;
- malignant neoplasms;
- parasitic diseases (giardiasis, opisthorchiasis, fasciliasis).
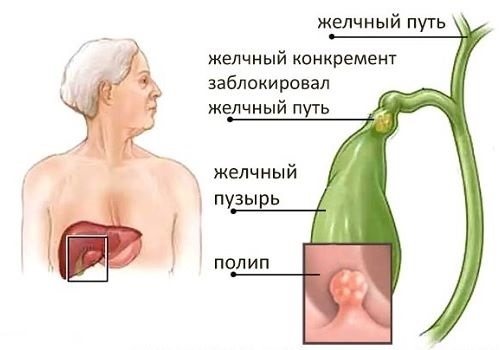
Any pathological process in the gallbladder is accompanied by inflammation - cholecystitis.
The stones that form in the lumen of the gallbladder consist of cholesterol and calcium salts bound together by bilirubin. A stone, polyp or tumor can block the cystic duct, which will not only lead to the development of biliary colic, but can also cause acute pancreatitis.