Erosive gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa, in which small defects (erosions) form on its surface. Such gastritis can be caused by various unfavorable factors, including unbalanced nutrition, stress, poor environment, long-term use of medications, as well as dysfunction of gastric juice secretion and food digestion.
This type of gastritis can also develop against the background of other chronic diseases, for example:
- problems with the thyroid gland and endocrine system;
- problems with the heart and blood vessels;
- malignant tumors.
What is erosive gastropathy
Erosive gastropathy is in second place in terms of prevalence among diseases of the digestive system after stomach ulcers.
This type of gastropathy is a pathology in which inflammation of the gastric mucosa occurs, which provokes the formation of erosions of various sizes on it. The lesions are located on the surface of the stomach walls and do not penetrate into the thickness of the walls.
Erosive gastropathy has a favorable prognosis and quite rarely leads to complications.
Erosive gastropathy is characterized by the presence of small damage to the mucous membrane - ulcers up to 1.5 cm in size. This pathology can have an acute course, forming defects (erosions) up to 1-2 mm, which can heal quite quickly - within 2-7 days after getting rid of the reasons for their occurrence. But the disease can also be chronic, in which inflammation in the damaged areas is activated due to stress or diet disorders.
Complications of the disease
Why is it so important to treat erosive gastritis? Acute erosive gastritis, dangerous with its rapid development and symptoms, is quite rare, and its occurrence is difficult to predict. The chronic form is easy to prevent with a healthy lifestyle.
It is recommended to contact a specialist at the first symptoms; the disease can provoke more severe ones. The danger of erosive gastritis is that, if not properly treated, it can develop into a stomach ulcer and provoke cancer.
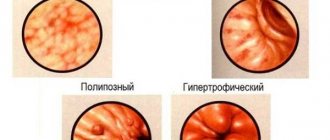
Types of pathology
Among the forms of the disease, one can distinguish primary erosions and secondary lesions that arise during the development of pathology.
According to the shape and type of erosion, they are divided into: superficial, complete and polypoid. In addition, the following classification of erosive gastropathy with erosions is given:
- Antral.
- Allergic.
- Atrophic.
- Autoimmune.
- Hypertrophic.
- Erythematous.
Depending on the stage of mucosal damage, two main forms of pathology can be distinguished: focal and widespread (diffuse).
In the focal form, inflammation appears in certain places - locally. They do not spread over the entire area of the gastric walls, but are located in one zone.
In the diffuse form, inflammation covers the entire surface of the organ. Later, erosions form in these places.
Depending on the type and strength of influence of negative factors, pathology has the following forms:
| Form | Symptoms | Peculiarities |
| Focal | Symptoms are not clearly expressed | Slight redness of the mucous membrane without damage |
| Location of ulcers in a limited area of the mucosa | ||
| Papular | A sharp increase in the synthesis of hydrochloric acid | Formation of a large number of papules with erosions |
| Decreased protective properties of mucous secretions | Gastric damage Helicobacter pylori | |
| Sour belching, heartburn | ||
| Formation of erosions with an inflammatory ridge that is raised around them | ||
| Pain syndrome is not intense | ||
| Antral erythematous | The mucous membrane of the digestive organ has redness | The appearance of small hemorrhages |
| Nausea, vomiting | ||
| Decreased or even loss of appetite | The antral region of the stomach is most often affected | |
| Congestive gastropathy in the antrum | The appearance of multiple wall defects in the area of gastric narrowing | Erosive and ulcerative defects of the gastroduodenal mucosa |
| Decreased protective functions of mucous secretion | Secondary damage to the gastric wall due to a more active abnormal process in another organ |
Causes of pathology
Most often, the development of erosive gastropathy is facilitated by the activation of the Helicobacter pylori bacterium in the patient’s body. Once in the organ cavity, the bacterium secretes special enzymes that weaken the protective environment of the stomach. This microorganism, actively multiplying, provokes chronic inflammation.
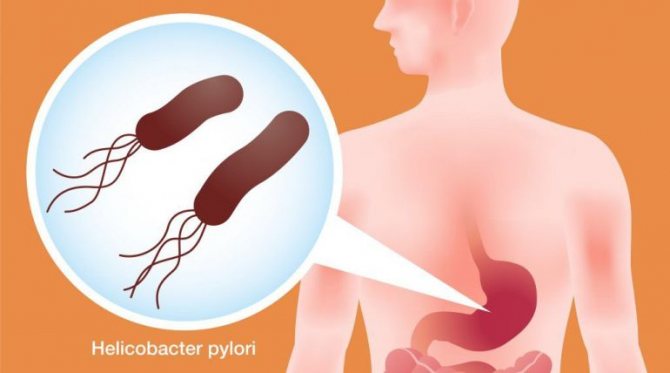
In addition to the activity of Helicobacter pylori, the following factors contribute to the appearance of erosive gastropathy:
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- stress and extreme anxiety. This increases the level of acidity in the stomach, which can contribute to the development of pathology;
- consumption of harmful foods (fatty, spicy, smoked);
- the presence of chronic diseases of the digestive system. That is, in the presence of an ulcer, hepatitis, pancreatitis or other pathologies, the patient’s risk of developing this disease is much higher;
- drinking coffee on an empty stomach;
- violation of diet, fasting, strict diets;
- treatment with certain potent medications. Hormonal drugs and NSAIDs are considered the most dangerous for the stomach;
- diabetes;
- bad dream. Lack of sleep also has a detrimental effect on the body; the risk increases due to the weakening of the body’s defenses, which does not have time to fully recover;
- metabolic disorder;
- injuries, burns;
- oncological neoplasms;
- hereditary predisposition;
- intoxication.
Why does gastropathy develop?
The main symptom of this disease is the formation of ulcerations on the gastric mucosa in the absence of an inflammatory process. Such erosive lesions are small areas of superficial necrosis that do not extend beyond the muscular layer of the digestive organ and heal without scars.
Damage to the internal lining of the stomach is the result of insufficient mucus production and impaired blood microcirculation in the gastric arteries.
The main causes of erosive gastropathy include:
- severe stress;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle;
- poor nutrition;
- long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- diabetes;
- oncological neoplasms;
- bacterial infection;
- hereditary predisposition;
- intoxication.
Symptoms of the disease
In addition to the specific symptoms that are inherent in certain types of erosive gastropathy, patients may complain of the following manifestations of pathology:
- Heartburn.
- Unpleasant sour belching.
- Vomiting with black matter.
- Increased gas formation.
- Pain in the stomach area.
As erosive gastropathy develops, the patient may begin to lose a lot of weight, lose his appetite, and experience nausea after eating.

Additional common features include;
- weakness;
- shortness of breath;
- decreased endurance;
- tachycardia.
Stomach bleeding may also occur.
Treatment with medications
Classic drug therapy for erosive gastropathy involves the use of the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics to get rid of the bacteria Helicobacter pylori (“Clarithromycin”);
- proton pump inhibitors;
- histamine receptor blockers (“Famotidine”);
- cytoprotective agents;
- antacid drugs that restore the gastric mucosa.
In some cases, gastropathy can go away on its own. It can go away without the use of medications if it was triggered by an improper diet or alcohol abuse. This is true only if there is slight redness and a mild degree of pathology. Defects will quickly heal, provided that they were caused by an endoscope, since the tube could accidentally touch the walls of the organ.

When the primary disease is not determined, then no further treatment is required, and the gastric walls themselves will return to normal in a few days.
But often erosive gastropathy appears against the background of other pathologies. In this case, the drug treatment regimen is selected based on the primary disease.
Therapy for erosive gastropathy will be successful when the patient, along with taking medications, strictly follows a diet and follows a nutritional regimen.
General recommendations for curing pathology are as follows:
- compliance with the rules of proper nutrition;
- avoiding stress;
- control of the course of chronic diseases;
- full sleep - 7-10 hours;
- moderate mode of work activity.
Treatment of erosive gastritis
Therapy for erosive lesions is carried out comprehensively. This is taking medications to eliminate the cause, restore microflora, normalize the acidity of gastric juice, relieve symptoms and prevent the development of complications.
The second stage is diet therapy and folk remedies.
Drugs
Drug therapy is prescribed based on the diagnostic results obtained. The choice of drugs is based on the etiology of the disease, the characteristics of the patient’s body, the presence of complications and concomitant pathological disorders. What can be prescribed:
- Painkillers: Analgin, No-shpa, Papaverine, Platiphylline.
- If erosions have formed due to infection with Helicobacter pylori or other microorganisms, antibacterial therapy must be prescribed. Drugs based on tetracycline, amoxicillin, clarithromycin and levofloxacin are used.
- To reduce the level of hydrochloric acid, antacids are needed: Phosphalugel, Almagel, Rennie, Venter, Maalox. Additionally, the substances contained in them contribute to the formation of a protective film and regeneration.
- Antacid medications dull the functionality of the gastric remedy, so along with them it is necessary to take enzymes that enhance digestion: Digestal, Pancreatin, Mezim, Creon, Festal.
- To improve motor skills, contraction activators of the gastrointestinal tract are used: Reglan, Motilium, Cerucal.
- To eliminate inflammation, the doctor prescribes De-nol, Ranitidine or Omez.
- For tissue and mucosal restoration: Iberogast, ascorbic acid, vitamin therapy (mostly group B), Trental.
- For erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis, hemostatic drugs must be prescribed: Dicinone, Etamzilat, Vikasol, thioctic acid.
Complex treatment should include a visit to a sanatorium or physiotherapy based on the intake of alkaline mineral waters. The same therapy is indicated for prophylaxis in chronic cases.
Nutrition
Diet therapy is an important part of the treatment and recovery period. This applies to both acute and chronic forms. When erosive gastritis is in the active stage of exacerbation, it is recommended to adhere to diet No. 1. In some cases, with a chronic course, the diet changes to diet 2. Next, there is a smooth transition to table No. 5.

Basic principles of dietary nutrition:
- With increased acidity, acid-based foods are excluded.
- Fatty foods, smoked foods, seasonings and spices, and fried foods are strictly prohibited.
- All dishes must be cooked in a steam bath or boiled.
- The daily norm should be divided into 5-6 doses, portions should be small.
- Food should have a mushy texture.
- The temperature of the food is warm (not too hot or too cold).
The diet may contain stale bread, mashed potatoes, light mashed soups, liquid porridges, dietary meat and fish, vegetable oil and butter (minimal doses), and fermented milk products.
But rich pastries, freshly baked bread, sweets (especially chocolate), sausages, lard and pork should be excluded.
Sample menu for the day:
- breakfast No. 1 – cottage cheese casserole, milk cocoa;
- breakfast No. 2 – sweetened tea (not strong), yesterday’s bad bun or bread with butter;
- lunch - soup with light meat broth, steamed vegetables with meat or fish, compote;
- afternoon snack – jelly, crackers;
- dinner No. 1 – rosehip decoction, baked meat with vegetables (no oil);
- dinner No. 2 – fermented milk drinks (yogurt, fermented baked milk, kefir).
To properly plan your diet, you need to consult a qualified nutritionist. The diet is based on the course of the disease.
You can learn about nutrition for erosive gastritis, as well as other ways to treat the disease at home, from the video presented:
Folk remedies
“Grandma’s” recipes allow you to accelerate the positive dynamics of treatment and improve the general condition of the patient, since they are all based on components of natural origin.
Before using them, you should consult with your treating gastroenterologist, since the level of acidity plays an important role - the same remedy cannot be used for different people.
Best recipes:
- Grind the peeled raw potatoes and squeeze out the juice. Take 100 ml on an empty stomach once a day.
- Flax tincture. Pour one and a half tablespoons of flax seeds into a cup and pour a glass of warm water. Leave to brew overnight. Eat half a glass of the mixture on an empty stomach.
- If you have high acidity, it is useful to drink carrot juice 30-40 minutes before eating. The daily norm is half a liter.
- Cut off an aloe leaf and put it in the freezer for 6-8 hours. Next, peel and squeeze out the juice. For 50 ml of water you need 1-2 tsp. juice Drink at this dosage 3-4 times a day.
- You will need herbs: marsh cudweed, dill seeds, knotweed, aloe (30 grams each), mint (40 g), hop cones, valerian, chamomile (50 grams each). Fill the collection with two liters of water and place in the oven on the lowest heat. The mixture should simmer for at least 8-9 hours. After cooling, strain. Directions for use: drink 200 ml on an empty stomach, then take half a glass every 2-3 hours. Duration of therapy is 2 weeks.
- Combine honey (preferably linden) and aloe juice in equal proportions. Drink 1 tbsp. l. at night for 30 days.
- In the evening, brew calendula (1 tablespoon of herb per glass of boiling water) in a thermos. Strain in the morning and drink the resulting solution in small portions throughout the day.
- Aloe mixture. You need 10 large leaves of the plant, which are crushed with a knife and placed in a steam bath container. Simmer for 10 minutes, then add 1 tbsp. l. honey, bring to a boil. Take a spoonful twice a day.
- The juice of 4 parts carrots and 1 part celery root helps a lot. Drink 2 times daily. Dosage per dose: 100 ml.
- Carrot-spinach juice is taken in the same proportions.
- Cabbage juice deserves special attention, which should be drunk according to the following scheme:
- the first 7 days - a glass of water and the same amount of juice (drink 3-6 times before meals, 100 ml each);
- next week – juice (400 ml), water (glass), drink 200 ml;
- week three – water (200 ml), juice (2 glasses), drink a glass before meals and 60 minutes after eating throughout the day;
- week four, final - the ratio of juice and water is identical to the previous one, take 200 ml 4 times a day, regardless of meals.
Diet for erosive gastropathy
For erosive gastropathy, it is recommended to follow the “Table No. 1” diet.
The following products are prohibited:
- borsch;
- legumes;
- high-fat dairy products;
- strong alcoholic drinks;
- mushrooms;
- strong tea and coffee;
- fresh bread;
- sour fruits and berries;
- various marinades;
- sweets;
- spicy and fatty foods.
The list of permitted products includes:
- dried bread;
- boiled vegetables;
- milk soups with cereals;
- cottage cheese;
- boiled fish and meat;
- honey;
- porridge from: semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat and rice;
- sweet fruits and berries in grated form.
The intervals between meals can be about 3 hours. Portions of food consumed should be small, and food should be consumed not hot.
Therapy with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can only be used in conjunction with the main treatment, but not replace it completely.
It is effective to use propolis for this pathology. Having previously frozen it in the refrigerator, grind a piece of propolis into powder and pour a glass of milk, drink the mixture in the morning before meals.

The following remedy has proven itself well: a mixture of nut oil and propolis. Boil this mixture in 0.5 liters of milk and drink it twice a day.
You can drink aloe juice mixed with honey an hour before eating.
It is good to use decoctions of oak bark, chamomile flowers, and flaxseed. You can use them alternately.
Freshly squeezed cabbage juice helps with this disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
The disease requires mandatory medical intervention. It is impossible to diagnose it only on the basis of complaints and an initial examination. For help, turn to a specialized doctor - a gastroenterologist. He prescribes standard examinations: general and biochemical analysis of blood, feces, bacteriological examination of vomit and feces. When the disease occurs, the surface of the gastric mucosa suffers, and superficial gastritis develops.
Thus, a visual examination of the gastric mucosa is mandatory. This can be done using a special fibrogastroscopy (FGS) procedure. During FGS, a person with suspected gastritis swallows a flexible tube with a camera at the end that passes directly through the esophagus and allows the nature of erosions to be assessed. The gastroenterologist provides a referral for an x-ray of the stomach.
The disease requires regular monitoring by a gastroenterologist. FGS should be done at least once a year.
Disease prevention
Erosive gastropathy is much easier to prevent than to deal with long-term treatment. To prevent the disease, follow these tips:
- treat gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner;
- watch their diet and avoid starvation;
- stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- do not eat fatty or spicy foods.
List of references: https://med88.ru/vidy-gastrita/jerozivnaja-gastropatija/ https://professor.perm.ru/klinika/novosti-i-aktsii/201-gastropatiya-prichiny-vidy-simptomy.html https: //empendium.com/ru/chapter/B33.II.4.5.1. https://ilive.com.ua/health/erozivnaya-gastropatiya-antralnogo-otdela-ochagovaya-atroficheskaya_121906i15938.html Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/17/2020