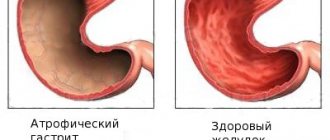
Lymphocytic gastritis is one of the forms of this disease. Very rare. Elderly people are at risk; it rarely occurs in young children. It is worth noting that women often experience this type of gastritis than men.
Characteristics of the disease
The chronic form is dangerous. Against the background of its development, exhaustion of the body occurs, cells of the mucous membrane grow against the background of slow and prolonged inflammation. If you do not consult a doctor in time and start treatment, the manifestations can threaten a person’s life. Gastritis is divided into the following forms:
- atrophic;
- non-atrophic;
- rare and special forms - lymphocytic, eosinophilic, chemical, radiation.
Forms that occur rarely require special monitoring. This also applies to lymphocytic gastritis.
Lymphoid gastritis
This is a rare and insidious disease: the symptoms are mild, and serious pathological changes occur in the stomach that do not allow it to function fully. The exact cause of the development of this particular pathology is unknown. One thing is clear - lymphoid gastritis occurs against a background of chronic gastritis.
A rare form of gastritis has distinctive features in the form of accumulations of lymphocytes that unite into follicles in the area of irritation and degeneration of the epithelium. Lymphatic vesicles formed in large quantities, necessary for the restoration of areas affected by Helicobacter, are often confused with hypertrophied gastritis or tissue atrophy - this is the difficulty of diagnosis.
- What is the danger of hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach and its treatment methods?
Another name for the disease - follicular gastritis - was given to it due to the appearance of formations - follicles, which can grow to significant sizes and form a dense layer, thereby complicating not only the digestion process, but also the diagnosis of the pathology itself.
A rare form of gastritis has distinctive features in the form of an accumulation of lymphocytes uniting into follicles in the area of irritation and degeneration of the epithelium
The development of a rare form of the disease is facilitated by inflammation of the mucous membrane, which was ignored for a long period of time, and there was no necessary treatment and prevention.
Diagnosis of gastritis is often difficult due to the lack of specific manifestations of lymphoid pathology, and at the initial stage – very disturbing symptoms. Follicular gastritis is easily confused with the hypertrophic or atrophic form. Advanced lymphoid gastritis can lead to a disease of the lymphatic tissues of the stomach, which at the initial stage of examination is sometimes confused with cancer, but with timely treatment, the chances of recovery are much greater.
The duration and effectiveness of treatment for gastritis depends on how long the sick person decided to seek help from a doctor, on a full examination, and on following all prescribed therapeutic recommendations. Traditional medicine reference books have a huge number of recipes to help overcome this unpleasant disease. Whether it is worth resorting to unconventional methods is something everyone has the right to decide for themselves, but this issue must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Follicular gastritis, which appears against a background of chronic gastritis, requires the use of various medications that relieve inflammation of the gastric mucosa, eliminate pain, have an enveloping effect, the ability to reduce and regulate the production of hydrochloric acid, and help break down food with the help of enzymes. If Helicobacter is detected in the gastric environment, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to suppress pathogenic microorganisms.
Causes of pathology
To date, doctors have not yet been able to establish the true cause of this form of the disease. Possible factors include:
- Helicobacter pylori infection. Affects the gastric mucosa. In the case of lymphocytic gastritis, changes are observed that are characteristic of the bacterial form of the disease.
- Gluten intolerance. This is a protein found in cereals. The immune system perceives it as a harmful component. This is accompanied by damage to the mucous membranes and organs of the digestive system.
This form is mainly detected during endoscopic examination. Occurs in 4% of patients.
Development mechanism
This form has no specific manifestations. The following manifestations are noted against the background of endoscopic examination:
- the mucous membrane is covered with granular accumulations;
- severe swelling and thickening of the mucous membrane is visible;
- small erosions.
During fibrogastroduodenoscopy, the mucous membrane is collected for histological and cystological examination. During the development of lymphocytic gastritis, there is an accumulation of lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing harmful substances.
What is lymphocytic gastritis and how to treat it?
The term “lymphocytic gastritis” refers to a special form of pathology, the distinctive feature of which is a pronounced infiltration of the gastric epithelium.
The disease affects mainly elderly women, but also occurs in children in the first year of life.
What exactly causes its development and why it threatens men to a lesser extent is not currently known to medicine.
Lymphocytic gastritis is a rare chronic disease. It is characterized by nonspecific clinical and endoscopic signs.
This is a special type of gastritis of pathogenetic origin, in which an increased number of lymphocytes is observed on the epithelium of the gastric mucosa.
If there is no correction in the form of adequate treatment, cells of the immune system continue to grow randomly, provoking autoimmune reactions.
The task of the lymphocytes located inside the epithelium of the stomach is to collect and transmit to immune cells information about food entering the digestive organs. However, due to “system breakdowns” of unknown etiology, lymphocytes make mistakes and the organ’s own cells are recognized as dangerous. The consequence of this recognition is the attack of healthy tissues by immune cells and their subsequent destruction.
Gastritis of the lymphocytic (lymphofollicular) form is an inflammation in which unusual particles penetrate into the stomach tissue, causing foci of irritation, erosion and ulcers. The disease is dangerous and can cause the development of malignant neoplasms.
People who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract need to take it as a rule:
- constantly adhere to a therapeutic diet;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid troubles, learn to take care of your peace of mind;
- eat small meals and only foods that combine with each other;
- do not self-medicate.
Reasons for development
It is impossible to determine the exact causes of the disease. Today, most gastroenterologists believe that the disease develops against the background of individual intolerance to gluten, which is part of most bread and other baked goods, and cereal products.
In people suffering from lymphofollicular gastritis, the body's defenses attack this protein (gluten), considering it a health threat. Having dealt with gluten, immune cells are mistaken for the tissues of the digestive tract.
Doctors are convinced that Helicobacter pylori, which causes various pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, also makes its destructive contribution.
Her favorite organs are the stomach and duodenum.
With lymphocytic gastritis, lesions characteristic of this pathogenic bacterium are found in the tissues of these organs, and its presence is confirmed by the results of laboratory tests.
Doctors believe that people who abuse sweet soda, alcoholic beverages, and “junk” foods (chips, crackers, sandwiches) are at risk and can develop this type of gastritis. The list of potential victims also includes fans of fatty, spicy, fried and smoked foods.
In addition to lymphocytic, there is also plasmacytic gastritis, and also of unclear etiology. This form is characterized by the accumulation of a large number of leukocytes in the organs of the digestive tract.
The symptoms of the disease are similar to typical manifestations of chronic inflammation of the inner lining of the stomach.
Without a thorough medical examination and laboratory test results, pathology cannot be diagnosed.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out as follows:
- general and detailed blood test;
- stool test (to determine the presence of blood);
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- histological analysis (determines the degree of damage to injured tissues).
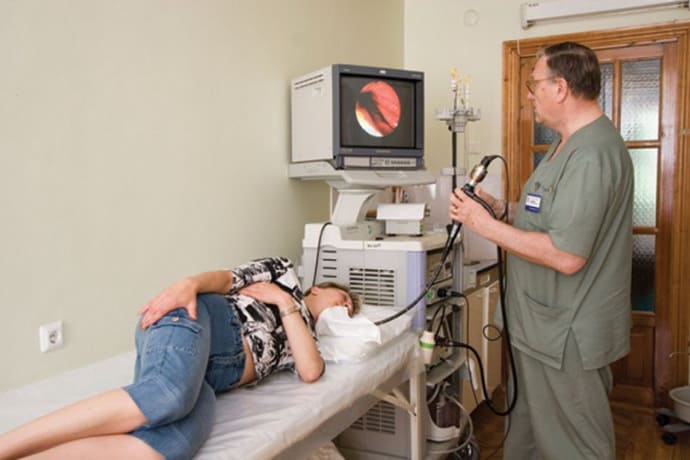
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed with a special flexible tube device with a microscopic video camera installed at its end. The probe helps to examine the condition of organ tissue and allows you to take samples for further microbiological research.
This procedure provides an accurate diagnosis of the type of pathological process and allows one to identify characteristic lesions: an increase in the amount of mucus in the folds, multiple small erosions, the presence of granular, papillary-like accumulations.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this form are very similar to Helicobacter gastritis. Characteristic features include:
- Pain in the upper abdomen. This is the main manifestation. Acute pain appears during prolonged hunger, on an empty stomach, 1-2 hours after eating. Also, pain can intensify when eating food that irritates the mucous membrane.
- If the secretory function is reduced, then heartburn, belching with a sour taste, nausea, and vomiting will occur. A coated tongue is also observed. Accompanied by dry mouth, burning sensation when eating sour foods.
- Stool disorder. Diarrhea often alternates with constipation.
- The condition worsens if vomiting occurs and then relief is observed.
- If the disease becomes chronic, the patient rapidly loses weight and suffers from aversion to food.
Lymphocytic gastritis is a very rare form of the disease. Very little is known about its manifestations and causes. In the initial stage, the disease may appear without pronounced symptoms. As gastritis develops, digestive disorders occur. Diseases such as pancreatitis, peptic ulcer, and colitis occur. Increased susceptibility to infections.
Lymphoid gastritis of the stomach description of the disease
The exact cause of the development of this particular pathology is unknown. One thing is clear - lymphoid gastritis occurs against a background of chronic gastritis. Also, when examining patients, it turns out that each patient has an active growth of Helicobacter, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane. After entering the stomach, the pathogenic microorganism begins to secrete a special substance - urease, which strongly irritates the mucous membrane.
The exact reason for the development of this particular pathology is unknown; it is clear that lymphoid gastritis occurs against the background of chronic
The body responds with a protective reaction - it enhances the synthesis of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. A rare form of gastritis has distinctive features in the form of accumulations of lymphocytes that unite into follicles in the area of irritation and degeneration of the epithelium.
Lymphatic vesicles formed in large quantities, necessary for the restoration of areas affected by Helicobacter, are often confused with hypertrophied gastritis or tissue atrophy - this is the difficulty of diagnosis. The uneven distribution of formations and thickening of the folds of the mucosa impede the normal functioning of healthy cells and the production of enzymes.
Another name for the disease - follicular gastritis - was given to it due to the appearance of formations - follicles, which can grow to significant sizes and form a dense layer, thereby complicating not only the digestion process, but also the diagnosis of the pathology itself. The development of a rare form of the disease is facilitated by inflammation of the mucous membrane, which was ignored for a long period of time, and there was no necessary treatment and prevention.
A rare form of the disease usually does not cause much suffering to the patient. The initial stage of the disease is often confused with superficial gastritis, which develops with increased acidity and an increase in the number of Helicobacter. Diagnosis of gastritis is often difficult due to the lack of specific manifestations of lymphoid pathology, and at the initial stage – very disturbing symptoms. Follicular gastritis is easily confused with the hypertrophic or atrophic form.
Diagnostics
Taking into account the diagnostic results, the doctor can prescribe treatment. Initially conducts a visual examination of the patient. Takes into account his complaints, studies the anamnesis. To confirm the diagnosis, the following examination methods are prescribed:
- Blood analysis. At the initial stage, indicators in the general blood test cannot be changed. Over the long course of the disease, the level of red blood cells decreases. The hemoglobin level decreases significantly and anemia develops. An increase in ESR indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Blood test for biochemistry. The results show metabolic disturbances.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. During the study, the mucous membrane is collected for detailed study.
It is worth considering that this form can develop against the background of other types of gastritis. Most often this is Helicobacter pylori.
What symptoms indicate pathology?
A nonspecific form of dangerous pathology may not manifest itself in any way, and the sick person will not even know about the stomach problem.
Symptoms of the initial stage of lymphocytic gastritis can be manifested by the following sensations:
- Pain in the stomach area;
- The appearance of belching or heartburn;
- Nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- Bloating, flatulence;
- Constipation or diarrhea.
With a prolonged course of the disease, the pain syndrome manifests itself as cutting or cramping pain. A person loses appetite and weight, signs of iron deficiency anemia develop, and there is a risk of gastric bleeding.
In the case of gastritis that develops with low acidity, the tongue remains dry, but the patient complains of rumbling in the stomach with its distension. A likely sign is severe vomiting with blood fragments and a sour smell. With a reduced level of acid secretion, no weight loss or appetite occurs.
Treatment
Drug therapy can be medicinal or non-medicinal. Non-drug treatment:
- Dieting. It is important to adhere to a diet; it must be balanced, healthy, and comprehensive. It is recommended to include a large amount of protein foods in your diet. Healthy eating should be combined with a healthy lifestyle.
- For chronic gastritis, you should not eat foods that irritate the mucous membranes. It is strictly forbidden to eat food containing coarse plant fiber. Dishes must be warm. Cold and hot foods can cause stomach cramps.
Chronic lymphocytic gastritis during remission requires a special diet. A diet has been developed for people who suffer from diseases of the digestive system.

Diet
Peculiarities:
- boiled dishes;
- lean meats;
- porridge;
- vegetable broth soups;
- non-fatty fish;
- stewed or baked vegetables.
The main rule is to divide meals into 6 times. The following should be excluded from the diet: sour fruits and vegetables, coffee, tea, preservatives, fatty foods, fried foods, processed foods, processed foods, nutritional yeast, alcohol, carbonated drinks. All products must be soft, pureed, and have a puree consistency.
Dietary nutrition is observed for at least 5 months. The diet is expanded gradually. It is worth noting that diet is the key to successful treatment.

Drug therapy
Drug therapy consists of taking the following drugs:
- histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine);
- proton pump inhibitors;
- antacids (Almagel, Maalox);
- medications to protect the gastric mucosa (De-nol);
- motor enhancers (mezim);
- enzymes.

Traditional methods of treatment
In very severe cases, surgical treatment is used. Folk remedies are also used as adjuvant therapy:
- Chamomile. Tea and decoction from this plant will be useful. Chamomile has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. It is recommended to take half an hour before meals, or 1 hour after meals.
- Olive oil. Take 1 tablespoon of oil on an empty stomach, 40 minutes before breakfast. Olive oil produces a protective effect on the surface of the stomach, therefore reducing inflammation and irritation from eating.
- Honey. This is a unique remedy that is popularly used for many diseases. It has an antiseptic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effect. More effective for bacterial gastritis. Take in pure form, dilute with water, add to tea.
- Flax seeds. A decoction is prepared from the seeds. It has a viscous consistency and coats the walls of the stomach well. An effective remedy in the treatment of lymphocytic gastritis. I take the prepared decoction before each meal.

Folk remedies are useful in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Despite this, you should consult your doctor before using them.
Treatment and prevention of lymphoid gastritis
The duration and effectiveness of treatment for gastritis depends on how long the sick person decided to seek help from a doctor, on a full examination, and on following all prescribed therapeutic recommendations.
Follicular gastritis, which appears against a background of chronic gastritis, requires the use of various medications that relieve inflammation of the gastric mucosa, eliminate pain, have an enveloping effect, the ability to reduce and regulate the production of hydrochloric acid, and help break down food with the help of enzymes. If Helicobacter is detected in the gastric environment, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to suppress pathogenic microorganisms.
A course of treatment for follicular gastritis should be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
A course of treatment for follicular gastritis should be prescribed by a qualified specialist. Ignoring the symptoms of a developing dangerous disease, waiting for everything to “resolve” on its own, and self-medicating is unacceptable.
Taking the recommended medications strictly according to the prescribed regimen allows you to effectively fight gastritis and quickly improve your well-being.
In addition to the use of medications, it is important to exclude all factors that provoked the development of gastritis:
- establish a meal schedule, optimize the composition of food products, eliminate heavy meals, stick to a diet;
- not just minimize bad habits, but get rid of them, no matter how difficult it may be;
- maintain a sleep and rest schedule;
- try to provide a comfortable emotional environment at home and at work that is favorable for healing;
- spend more time outdoors.
Among the most popular tips for eliminating the symptoms of lymphoid gastritis are recommendations for drinking plantain juice
Traditional medicine in the treatment of lymphoid gastritis
Among the most popular tips for eliminating the symptoms of lymphoid gastritis are recommendations for drinking plantain juice, which you should drink ¼ glass for two weeks. Using the same scheme, you can take freshly squeezed juice from recently harvested white cabbage or potatoes. It is believed that such drugs can have an effect on Helicobacter, which is often the cause of gastritis.
A good effect in treating and relieving the symptoms of lymphoid gastritis is provided by preparations based on mint, licorice rhizomes, butterfly root, linden blossom, and flax seeds. The same amount of each component is mixed, the mixture at the rate of a tablespoon per glass of water is placed in a thermos, poured with boiling water, and left to infuse for an hour. Then filter, drink warm 250 ml twice a day 30 minutes before meals.
Chronic follicular gastritis can be treated with a tincture of chamomile, yarrow and crushed flax seeds, taken 10 g each, poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water, and wrapped. After half an hour, the collection is filtered through a fine strainer or gauze, and drunk half a glass three times a day before meals for a month.
Sources:
- https://ozdravin.ru/gastrit/limfoidnyy-gastrit-redkoe-no-izlechimoe-zabolevanie-zheludka.html
- https://tvoyzheludok.ru/bolezni/giperplaziya-zheludka.html
- https://zhkt.guru/gastrit/vidy/limfoidnyy
- https://zhkt.ru/zheludok/gastrit/follikulyarnyj.html
- https://bul.ehealthtreats.com/limfoidnye-follikuly-v-zheludke
- https://gem-prokto.ru/news/limfoidnyj_gastrit_lechenie/2016-02-16-49
Prevention
Prevention of lymphocytic gastritis is the key to successful treatment. It is easier to prevent the development of a disease than to treat it. Especially the chronic form. Preventive measures:
- proper, healthy nutrition;
- high-quality, fresh products;
- meat, fish, milk must undergo heat treatment;
- diet regimen - meals should be taken at the same time;
- It is forbidden to overeat and abuse alcohol.
If you have symptoms of lymphocytic gastritis, a person should contact a gastroenterologist or therapist. If you start treatment on time, you can avoid serious complications.