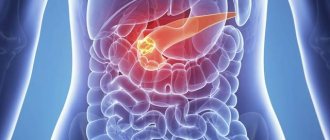
Under the influence of unfavorable factors, squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus is formed. The pathology varies histologically, has 4 degrees of severity and is accompanied by vomiting with blood, increased salivation, heartburn, and difficulty swallowing. At the first symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor who will diagnose, perform surgery, prescribe therapy, nutritional therapy, home treatment and give preventive recommendations.
Causes
The reasons that provoke the emergence of a dangerous disease have not yet been fully studied by medicine. However, experts identify risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing squamous cell non-keratinizing esophageal cancer and diseases that can lead to tissue degeneration into malignant neoplasms.
Risk factors include:
- Disruption of the human immune system;
- Presence of bad habits (smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol);
- Constant exposure to ultrasonic radiation;
- Consumption of foods high in nitrates and preservatives;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Eating errors associated with the consumption of excessively hot, spicy, smoked food, as well as insufficient amounts of fresh fruits and vegetables in the daily menu.
- Mechanical injury to the esophagus caused by a foreign object or hard food.
The risk group includes people who are overweight. This can be explained by the fact that the pressure in the abdominal cavity is increased, as a result of which there is an increased likelihood of food being thrown from the stomach into the esophagus and the appearance of a burn from the mucous membrane with hydrochloric acid.
Important! The risk of developing such a disease is much higher in patients suffering from esophageal achalasia (impaired swallowing and the throwing of food from the stomach back into the esophagus).
All of the above reasons cannot cause cancer by themselves, but they can lead to chronic ailments in the digestive system and create a favorable platform for pathological changes.
Therapeutic measures for inflammation of the esophagus
When inflammation of the stomach and esophagus is observed, the doctor gives recommendations that can eliminate the irritation.
Drug therapy
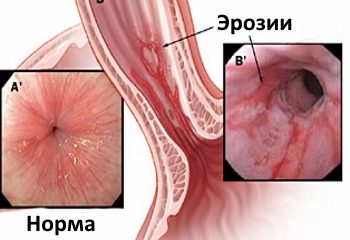
Treatment of inflammation of the esophagus is based on taking the following medications.
- Antacids. Their effect is aimed at neutralizing hydrochloric acid. The doctor prescribes Almagel, Rennie, Gastal, Phosphalugel.
- Prokinetics. This type of medication increases the tone of the lower part of the esophagus. This category of drugs includes Motillium, Motilak.
- Antisecretory agents. They suppress the formation of hydrochloric acid and normalize the composition of gastric juice. Frequently prescribed drugs include Omeprazole and Famotidine.
- Proton pump inhibitors. Allows you to restore the surface layer. They are prescribed not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of exacerbations. These include Rabeprazole, Ranitidine.
Physiotherapy is used as an additional method.
It implies:
- performing electrophoresis. The procedure involves the constant application of an electrical impulse to the affected area;
- amplipulse therapy. One of the treatment methods, which consists in the stimulating effect of electrical frequencies on diseased areas;
- mud therapy and water procedures;
- physical therapy.
During acute or severe forms of the disease, physiotherapeutic treatment is contraindicated. This can further irritate the mucous membrane.
Types of squamous cell non-keratinizing esophageal cancer
Having discovered a tumor, the oncologist must first determine what type it belongs to.
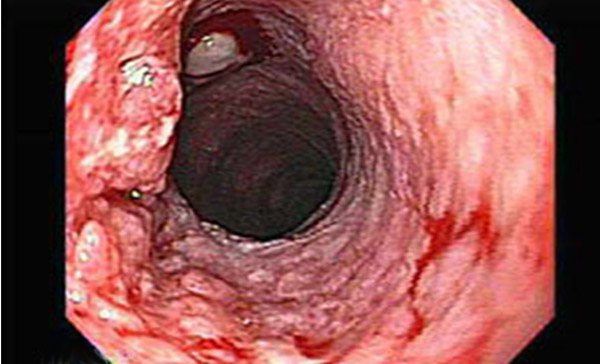
There are three types of pathology of this kind. Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus
- keratinizing;
- non-keratinizing;
- moderately differentiated.
The last type is intermediate, affecting half of all patients.
The size of the malignant formation can vary from 1 cm to 15 cm.
Survival prognosis
The survival prognosis for esophageal cancer depends on the stage of the oncological process, since severe disease almost always has a fatal outcome:
- The first stage guarantees patient survival up to 90%;
- Second stage about 50%;
- The third stage is no more than 10%;
- At the fourth stage of cancer, the prognosis is unfavorable, since the sick patient dies. There is a good chance of cure if squamous cell carcinoma is detected, and if the lesion is diagnosed in the middle section of the esophagus, the tumor will spread to the trachea and lungs, which can be fatal.
At the initial stage of tumor development, diagnosis is possible only by ultrasound, CT or endoscopy. Stage 4 cancer is currently incurable. Determining the type of tumor is possible only after taking a biopsy and performing histology. In some cases, the neoplasm may turn out to be benign, so you should not panic ahead of time.
Symptoms
In the first stages, the disease may not manifest itself at all. The person does not feel any discomfort. The first signs appear later. One of the main manifestations is a feeling of discomfort or difficulty swallowing food.

This symptom will progress as the disease develops. At first, when swallowing, there is a feeling that food is stuck in the esophagus and needs to be washed down with liquid. Over time, swallowing begins to be accompanied by pain.
Important! This symptom does not cause concern in many patients. It is classified as a temporary difficulty, delaying a visit to the doctor, while timely treatment significantly increases the chances of a favorable treatment outcome.
Other signs to look out for include:
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- Pain behind the sternum or burning sensation in the chest area;
- Feeling weak;
- Performance decreases;
- Belching;
- Weight loss;
- The appearance of shortness of breath and cough;
- At later stages, the timbre of the voice may change.
As the disease progresses, patients may have to give up solid foods. They are advised to eat only cereals and dishes with a puree consistency.
Esophageal tumors
Symptoms of benign esophageal tumors
Benign tumors of the esophagus are quite rare and account for no more than 1% of all neoplasms of this digestive organ.
The lion's share of benign neoplasms are non-epithelial tumors, 70% of which are esophageal leiomyoma. Intraluminal tumors are usually represented by polyps of epithelial (glandular polyps, papillomas, adenomas) or mesenchymal (fibromas, lipomas, mixed polyps) origin. A separate group includes rare tumors such as myxoma, chondroma, hamartoma, and hemangioma. Benign neoplasms are found in all parts of the esophagus. Usually these are single tumors on a wide stalk, having a smooth or tuberous structure. Considering the rather slow growth of such neoplasms, the clinical course is often asymptomatic, and when the tumor reaches a large size, signs of esophageal obstruction and compression of the mediastinal organs appear. However, most often benign tumors of the esophagus are an incidental finding during a plain radiography of the abdominal organs.
Different types of benign tumors have certain clinical and radiological features. Thus, a polyp of the esophagus can be single or multiple, located in any part of the organ. It clearly protrudes into the lumen of the esophagus and has pronounced mobility due to its wide base and pedicle. It manifests itself as dysphagia, which occurs periodically over many years. A characteristic sign during X-ray examination is a displaced barium filling defect with clear and even contours, preserved relief and peristalsis at the level of the defect.
Papilloma is usually larger than the polyp, with a lobulated or warty surface. Prone to malignancy. Leiomyomas are the most common tumors of the esophagus. They are located in the lower and middle sections, intramurally on a broad base. The course is usually asymptomatic; the first signs are ulceration of the tumor and bleeding. Lipomas are very rare and have no clear clinical differences from other tumors.
Diagnosis and treatment of benign tumors of the esophagus
When performing radiography of the esophagus with contrast, filling defects, deformation of the lumen of the esophageal tube, and changes in the relief of the mucous membrane are revealed. Based on the X-ray picture, tumors that are completely located in the lumen of the organ can be identified; growing both into the lumen and intramurally; spreading from the inner layers of the esophagus outward and compressing it from the outside. The difference between benign nonepithelial tumors and cancer is the preserved relief of the mucosa and the elasticity of the walls of the esophagus at the level of the location of the tumor. The diagnosis is confirmed histologically.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with diseases such as foreign body, varicose veins, malignant neoplasms of the esophagus. To establish the correct diagnosis in a hospital setting, esophagoscopy and chromoscopy of the esophagus, endoscopic biopsy of tumor tissue followed by histological examination, plain radiography of the chest cavity and radiography of the esophagus with contrast are performed. If there are diagnostic difficulties, magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the chest organs is indicated.
You should pay attention to such unfavorable prognostic signs as rapid tumor growth, ulceration, atypical shape of the tumor node, changes in the relief of the mucosa and the elasticity of the walls of the esophagus at the location of the tumor. These symptoms may indicate malignancy of a benign tumor and require a gastroenterologist to prescribe an esophagoscopy with a biopsy.
Treatment is only surgical; removal of benign tumors of the esophagus can be carried out endoscopically or abdominally. In the postoperative period, a special diet and long-term course of proton pump inhibitors are prescribed (if the tumor was accompanied by symptoms of esophagitis or cardial insufficiency).
Diagnostics
As part of the diagnosis, a comprehensive examination of applied patients is carried out. To make an accurate diagnosis it is necessary:
- Take a blood test for tumor markers, also general and biochemical;
- To identify the degree of narrowing of the lumen and detect the presence of metastases, an x-ray examination is performed;
- Esophageal cancer is usually classified as a visual form, so one of the diagnostic methods is endoscopy. During such an examination, a puncture is taken from the affected area, and the material is sent for histological analysis.
- The patient should undergo a CT scan;
- Bronchoscopy is indicated;
- Ultrasound.
Based on the results of the examination, the type of malignant formation is finally established, and further actions are determined.
Treatment methods and cost of recovery
The treatment method for esophageal cancer is prescribed by a council of specialist doctors after all the studies have been carried out and the diagnosis has been accurately established. The main methods of therapy are discussed in more detail in the list below.
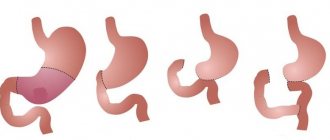
- Surgery is performed only if the tumor is located in the lower or middle part of the esophagus. The affected part of the organ is removed, and its remains are sewn to the stomach. With complete removal, recovery lasts a year, and then an artificial esophagus is created from the small intestine.
- Operations using an endoscope are performed at the initial stages of the development of the oncological process. The device is inserted into the esophagus, bougienage is performed and the formation is removed. About 70% of patients receive the opportunity to have adequate nutrition after such an intervention.
- Radiation therapy is carried out using special radiation that destroys cancer cells and significantly increases the chances of obtaining a positive prognosis. The rays break DNA bonds in the cellular structure and eliminate division processes. As a result, the tumor decreases in size, and the aggressive form of the disease subsides.
- Chemotherapy is based on the use of potent drugs (toxins and poisons) that destroy cancer cells. Moreover, such treatment has many side effects for the body. But it is most effective in combination with radiation therapy according to a combined treatment regimen.
If we talk about the cost of treatment, then diagnostic and recovery procedures in medical centers of foreign countries will cost on average 30,000–60,000 thousand dollars. The amount is quite high, but the prognosis for survival is high even with the third stage of the disease.

Treatment of cancer in clinics or hospitals in the country is much less (about 10,000 thousand dollars). However, patients with stage three or four have a low survival prognosis. Only 5–10% live an average of 3–4 years.
Treatment
A distinctive feature of squamous cell carcinoma is that its cells react very little to chemicals, but they are sensitive to radiotherapy. However, radiological radiation alone will not be able to get rid of the disease. You can only count on a good result if you take an integrated approach to treatment.
Among the main methods of treatment for squamous cell non-keratinizing cancer of the esophagus are surgical and endoscopic operations. Radiation therapy is often used in combination with radical methods.
Surgery
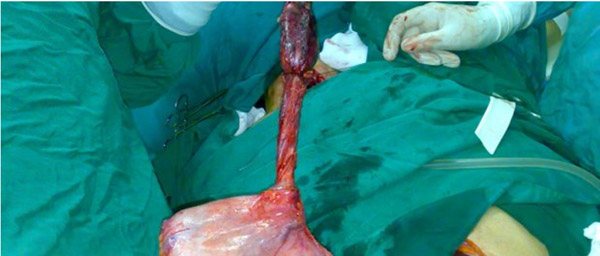
The preparatory, preoperative method is chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The main goal is the destruction of a malignant tumor and sites of metastasis.
Surgery is a radical method, as a result of which not only the tumor is removed, but also all tissues and lymph nodes located nearby. The affected area of the esophagus is removed. To provide parenteral nutrition, a special tube is temporarily installed.
After surgery, a second course of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is carried out. As soon as the metastatic cells are completely removed, the next stage of the operation can be scheduled, during which the esophagus, in particular its integrity, is restored.
The required fragment is usually a section of the large intestine, which is taken from the patient during the operation. The transplanted tissue should not be exposed to radio rays; its cells will die from this.
After surgery, no one is immune from the development of complications. In such a situation you may encounter:
- with tissue divergence;
- rejection of the anastomosis;
- inflammation of the mediastinal tissue;
- cicatricial narrowing of the lumen.
The appearance of scars is not as scary as, for example, an inflammatory reaction of the mediastinum or the death of the area that was transplanted.
However, operations of this kind are not suitable for everyone. For patients with severe concomitant diseases, surgical intervention is not recommended due to the increased risk of death during the procedure. These categories of citizens include:
- patients with severe heart failure;
- suffering from alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver;
- with cancer of other organs.
The operation cannot be performed if the tumor has already grown into vital organs, the removal of which is incompatible with life. In such situations, a palliative is prescribed.
Palliative treatment methods
If the cancer was detected at the last stage, when surgery cannot be performed, the patient is prescribed palliative treatment, the essence of which boils down to the process of destroying the tumor formation with a laser and stenting the affected area.
You should definitely adjust your diet. Palliative treatment gives patients hope for prolonging life and improving its quality. The last stage of cancer is characterized by intense, excruciating pain. They can be controlled with narcotic analgesics prescribed by the doctor.
Palliative care
In the later stages of the disease, surgical treatment is usually not carried out.
If carcinoma is diagnosed at a late stage, then surgical intervention will not bring the desired results. To help the patient in this case, laser treatment is carried out, with the help of which it is possible to stop the growth of the cancerous tumor. With this type of treatment, it is possible to improve the patient’s condition and prolong his life, however, during this period it is necessary to strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations and follow all his instructions. In order for the patient to be able to eat properly, a special tube is inserted into the affected esophagus, which will help expand the walls of the esophagus so that food can pass normally. In case of cancer, the patient will require drug therapy, in which it is necessary to relieve the pain symptom. Often, cancer patients require psychological help, which is aimed at eliminating fear of the disease and depression.
Treatment prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma
The survival prognosis is directly dependent on when the tumor was discovered, the extent of the lesion and how timely treatment was started.
Important! Squamous cell non-keratinizing cancer of the esophagus is characterized by a slow progression and an average degree of malignancy.
- In cases of tumor detection at the very first stage, survival rate is 90%.
- If active therapy was started at stage 2, then 50% of patients can count on overcoming the five-year mark.
- Stage 3 is characterized by the penetration of metastases into the lymph nodes. Survival rate is about 25%.
- Thanks to modern treatment methods, even patients with stage 4 cancer can prolong life and improve its quality.
Prevention
If you are at risk for esophageal cancer, then to prevent the development of a malignant tumor, be sure to follow a number of simple rules:
- Give up bad habits.
- Eat right.
- Treat other diseases and injuries of the esophagus promptly.
- Get an ultrasound of the esophagus, especially if you have a family history.
- Prevent the development of obesity.
- Do not overuse too cold or hot food, as well as hot and spicy dishes.
How they die from cancer: everything about cancer patients before death
Cancer is a very serious disease, which is characterized by the appearance in the human body of a tumor that grows rapidly and damages nearby human tissues. Later, the malignant tumor affects the nearest lymph nodes, and at the last stage metastases occur, when cancer cells spread to all organs of the body.
The terrible thing is that at stages 3 and 4, cancer treatment for some types of oncology is impossible. Because of this, the doctor can reduce the patient’s suffering and slightly prolong his life. At the same time, he is getting worse every day due to the rapid spread of metastases.
At this time, the patient's relatives and friends should roughly understand exactly what symptoms the patient is experiencing in order to help survive the last stage of life and reduce his suffering. In general, those dying from cancer due to complete damage by metastases experience the same pain and ailments. How do people die from cancer?
Why do people die from cancer?
Cancer occurs in several stages, and each stage is characterized by more severe symptoms and damage to the body by the tumor. In fact, not everyone dies from cancer, and it all depends on at what stage the tumor was discovered. And here everything is clear - the earlier it was found and diagnosed, the greater the chances of recovery.
But there are still many factors, and even stage 1 or even stage 2 cancer does not always provide a 100% chance of recovery. Since cancer has many properties. For example, there is such a thing as the aggressiveness of malignant tissues - the higher this indicator, the faster the tumor itself grows, and the faster the stages of cancer occur.
The mortality rate increases with each stage of cancer development. The largest percentage is at stage 4 - but why? At this stage, the cancerous tumor is already enormous in size and affects nearby tissues, lymph nodes and organs, and metastases spread to distant parts of the body: as a result, almost all tissues of the body are affected.
At the same time, the tumor grows faster and becomes more aggressive. The only thing doctors can do is reduce the growth rate and reduce the suffering of the patient himself. Usually chemotherapy and radiation are used, then the cancer cells become less aggressive.
Death with any type of cancer does not always occur quickly, and it happens that the patient suffers for a long time, which is why it is necessary to reduce the patient’s suffering as much as possible. Medicine cannot yet fight advanced stage cancer, so the earlier the diagnosis is made, the better.
Causes of the disease
Unfortunately, scientists are still struggling with this question and cannot find an exact answer to it. The only thing that can be said is that there are a combination of factors that increase the chance of getting cancer:
- Alcohol and smoking.
- Junk food.
- Obesity.
- Bad ecology.
- Working with chemicals.
- Incorrect drug treatment.
In order to somehow try to avoid cancer, you must first monitor your health and regularly undergo examination by a doctor and take a general and biochemical blood test.
Symptoms before death
That is why the correct treatment tactics, chosen at the last stage of the disease, will help reduce pain and illness for the patient, as well as significantly prolong life.
Of course, each oncology has its own signs and symptoms, but there are also common ones, which begin immediately at the fourth stage, when almost the entire body is affected by malignant formations.
How do cancer patients feel before death?
- Constant fatigue. This happens because the tumor itself takes a huge amount of energy and nutrients for growth, and the larger it is, the worse it is. Let's add metastases to other organs here, and you will understand how difficult it is for patients in the last stage. The condition usually worsens after surgery, chemotherapy and radiation. At the very end, cancer patients will sleep a lot. The most important thing is not to disturb them and let them rest. Subsequently, deep sleep can develop into a coma.
- Appetite decreases. The patient does not eat because general intoxication occurs when the tumor produces a large amount of waste products into the blood.
- Cough and difficulty breathing. Often, metastases from any organ cancer damage the lungs, causing swelling of the upper body and coughing. After some time, it becomes difficult for the patient to breathe - this means that the cancer has firmly settled in the lung.
- Disorientation. At this moment, there may be memory loss, the person ceases to recognize friends and relatives. This happens due to metabolic disorders with brain tissue. Plus, there is severe intoxication. Hallucinations may occur.
- Blueness of limbs. When the patient’s strength becomes low and the body tries with all its might to stay afloat, the blood mainly begins to flow to the vital organs: heart, kidneys, liver, brain, etc. At this moment, the limbs become cold and acquire a bluish, pale tint. This is one of the most important harbingers of death.
- Spots on the body. Before death, spots appear on the legs and arms due to poor circulation. This moment accompanies the approach of death. After death, the spots become bluish.
- Muscle weakness. Then the patient cannot move and walk normally, some can still move slightly but slowly to the toilet. But the majority of them lie down and move around.
- Coma state. It may come suddenly, then the patient will need a nurse who will help, wash and do everything that the patient cannot do in such a condition.
The dying process and main stages
- Predagonia. Central nervous system disorder. The patient himself does not feel any emotions. The skin on the legs and arms turns blue, and the face becomes earth-colored. The pressure drops sharply.
- Agony . Due to the fact that the tumor has already spread everywhere, oxygen starvation occurs and the heartbeat slows down. After some time, breathing stops, and the blood circulation process slows down greatly.
- Clinical death . All functions are suspended, both the heart and breathing.
- Biological death. The main sign of biological death is brain death.
Of course, some cancer diseases may have characteristic signs, but we told you about the general picture of death from cancer.
Symptoms of brain cancer before death
Brain tissue cancer is difficult to diagnose in the early stages. It doesn’t even have its own tumor markers, which can be used to determine the disease itself. Before death, the patient feels severe pain in a certain place of the head, he may see hallucinations, memory loss occurs, he may not recognize his family and friends.
Constant change of mood from calm to irritated. Speech is impaired and the patient may utter all sorts of nonsense. The patient may lose vision or hearing. In the end, motor function is impaired.
Last stage of lung cancer
Lung carcinoma develops initially without any symptoms. Recently, oncology has become the most common among all. The problem is precisely the late detection and diagnosis of cancer, which is why the tumor is discovered at stage 3 or even stage 4, when it is no longer possible to cure the disease.
All symptoms before death of stage 4 lung cancer relate directly to breathing and bronchi. Usually the patient has difficulty breathing, he constantly gasps for air, he coughs heavily with copious discharge. At the very end, an epileptic seizure may begin, which will lead to death. Terminal stage lung cancer is very nasty and painful for the patient.
Liver cancer
When a liver tumor is affected, it grows very quickly and damages the internal tissues of the organ. The result is jaundice. The patient feels severe pain, the temperature rises, the patient feels sick and vomits, and there is difficulty urinating (the urine may contain blood).
Before death, doctors try to reduce the suffering of the patient himself with medications. Death from liver cancer is very difficult and painful with a lot of internal bleeding.
Bowel cancer
One of the most unpleasant and most severe oncological diseases, which is very difficult at stage 4, especially if a little earlier an operation was performed to remove part of the intestine. The patient feels severe pain in the abdomen, headache, nausea and vomiting. This is due to severe intoxication from the tumor and retained feces.
The patient cannot go to the toilet normally. Since at the last stage there is also damage to the bladder and liver, as well as the kidneys. The patient dies very quickly from poisoning with internal toxins.
Esophageal carcinoma
The cancer itself affects the esophagus, and in the final stages the patient can no longer eat normally and eats only through a tube. The tumor affects not only the organ itself, but also nearby tissues.
Metastasis spreads to the intestines and lungs, so pain will appear throughout the chest and abdomen.
Before death, the tumor may cause bleeding, causing the patient to vomit blood.
Laryngeal cancer before death
A very painful disease when the tumor affects all nearby organs. He feels severe pain and cannot breathe normally. Usually, if the tumor itself completely blocks the passage, the patient breathes through a special tube. Metastases spread to the lungs and nearby organs. Doctors prescribe large amounts of painkillers at the end.
Last days
Usually, if the patient wishes, the patient’s relatives can take him home, and he is prescribed and given strong drugs and painkillers that help reduce pain.
At this moment, you need to understand that the patient has very little time left and you need to try to reduce his suffering. At the very end, additional symptoms may appear: vomiting blood, intestinal obstruction, severe pain in the abdomen and chest, coughing up blood and shortness of breath.
At the very end, when almost every organ is affected by cancer metastases, it is better to leave the patient alone and let him sleep. The most important thing is that at this moment there are relatives, loved ones, close people next to the patients, who will reduce pain and suffering by their presence.
How to alleviate the suffering of a dying person?
Often the patient's pain can be so severe that conventional medications do not help. Improvement can only be brought by narcotic substances that doctors give for cancer. True, this leads to even greater intoxication and quick death for the patient.
How many years can you live with stage 4 cancer? Unfortunately, in the best case, you will be able to live for several months with the right therapy.
(20 4,60 of 5) Loading...
Source: //OncoVed.ru/common/kak-umirayut-ot-raka