Symptoms: discomfort after eating, heaviness in the abdomen, heaviness after eating, abdominal pain, abdominal pain, stomach pain, epigastric pain, burning in the abdomen, burning in the stomach, bloating, intestinal upset, bloating, intestinal discomfort, frequent stool, frequent urge to stool, indigestion, diarrhea (diarrhea), constipation, stool retention, abdominal distension, flatulence, gas in the intestines, heartburn, belching after eating, food intolerance, bitter taste in the mouth, dry mouth.
Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, or digestive problems, are manifested by various symptoms: constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, pain, stinging, a burning sensation or heaviness in the abdomen, discomfort in the intestines, as well as heartburn, belching and unpleasant sensations in the mouth (dryness, bitterness). Quite often, symptoms may worsen immediately after eating. Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract may be accompanied by deterioration of appetite, general weakness and irritability.
Defecation with such disorders always brings noticeable discomfort: starting with pain in the abdomen and sensations of bloating, it occurs either too slowly and difficultly (with constipation), or, conversely, too often, and the stool has a liquid consistency (with diarrhea). In both cases, increased gas formation (flatulence) is observed.
Gastrointestinal disorders can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the vegetative centers responsible for the functioning of the digestive organs. In such cases, diets and standard drug treatment for gastritis, dysbiosis and other diseases of the digestive system remain ineffective. Gastroenterological studies do not reveal serious problems, and the patient continues to suffer from the inability to eat and go to the toilet calmly. In this case, the patient is recommended to check the autonomic nervous system of the body. When the functioning of the affected vegetative centers is restored, the digestive process normalizes independently.
Diagnostic methods
Before treating stomach discomfort, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. For this purpose, they contact a gastroenterologist and undergo a comprehensive examination. It is important to find out whether the disorder is associated with pathological conditions - ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis. To do this, the following diagnostic procedures are carried out:
- ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- X-ray pictures;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine.
If there is discomfort in the stomach area, phagogastroduodenoscopy is performed using a probe. The technique evaluates the condition of the mucous membrane of the internal organ.
Discomfort after bowel movement
Many people are familiar with the phenomenon of pain during bowel movements. Regardless of whether it is permanent or occurs from time to time, it causes fear and misunderstanding. You may also feel discomfort after constipation or diarrhea.
Many people are familiar with the phenomenon of pain during bowel movements.
Pain and discomfort during constipation is explained by mechanical damage to the mucous membrane from dense and hard feces, as well as excessive straining during bowel movements.
A healthy person has a bowel movement every one to two days. If defecation does not occur during this period, the feces become denser, expand and begin to put pressure on the walls, which leads to irritation of the nerve endings. A person feels pain in the lower abdomen. However, in some cases, a person feels pain not only in the locations of the intestines.
Proctitis, or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum and sigmoid colon, is another possible cause of discomfort during bowel movements. In addition to anal pain symptoms during bowel movements, patients complain of constantly irritating itching in the anus, blood in the stool, the inability to sit in one place for a long time, as well as a feeling of incomplete bowel movement after defecation.
Pain after bowel movements is often a consequence of irritable bowel syndrome. In this case, a spasm appears in the lower abdomen and on the left, and cold sweat may appear on the skin. It is worth noting that with the syndrome the spasm is very strong, it begins to radiate to the lumbar region, and it all ends with severe diarrhea.
Often discomfort in the intestines is a consequence of worms. It is especially dangerous when they begin to actively reproduce. In this case, every six months you need to take the drug Dekaris, with its help you can quickly destroy the parasites. pain in the intestines after defecation appears for a reason. You should not drown it out with analgesics; it is better to be treated once and effectively than to constantly take many drugs.
What to do and how to treat?
Effective drugs
If your stomach hurts, discomfort and other unpleasant sensations appear, you should not delay treatment. In case of severe pain, you can take painkillers “No-shpa”. Discomfortable sensations must be relieved comprehensively, having previously established the source of their occurrence. It is possible to relieve unpleasant symptoms with the help of tablets, powders, and oral solutions. The table shows popular drugs used for discomfort in the stomach.
Antacids
| "Almagel" | |
| "Phosphalugel" | |
| "Maalox" | |
| Enzyme preparations | "Panzinorm" |
| "Festal" | |
| "Mezim Forte" | |
| Medicines that improve fiber absorption | "Fibogel" |
| "Tselevak" | |
| Prokinetics that normalize gastric motility | "Cerucal" |
| "Sturgeon" | |
| "Motilium" |
Return to contents
What folk remedies can you take?
If you are worried about stomach discomfort after eating, you can take medications that include natural ingredients. It is recommended to use alternative therapy with caution, after consulting with a doctor. For uncomfortable sensations, the following recipes are useful:
- Tea with honey and a slice of lemon. The drug is aimed at normalizing gastric function when it stops.
- Fig juice. Necessary for irritable reactions in the intestines.
- A healing infusion including peppermint, lemon, ginger root and baking soda. Effective for flatulence and discomfort.
- Warm slightly salted water with the addition of cumin and lemon. The medicine helps relieve symptoms during exacerbation of the condition.
- A solution with potassium permanganate and activated carbon. Cleanses the stomach and intestines of accumulated toxins and waste.
- Carrot and potato juice. Natural substances cope with unpleasant sensations, in particular heartburn.
It is possible to improve peristalsis and get rid of discomfort with the help of self-massage and therapeutic exercises.
Prevention measures
It is possible to avoid discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract and prevent serious illnesses by following a proper diet and consuming more foods with fiber. You should not overeat, especially before going to bed, so that food can be digested normally. It is recommended to avoid conflicts, stress, and overwork, which negatively affect the functioning of the digestive system. During long-term drug therapy, probiotics are used to protect the mucous membrane from aggressive substances.
DO YOU STILL THINK THAT IT IS HARD TO CURE YOUR STOMACH?
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not yet on your side.
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the stomach is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Frequent abdominal pain, heartburn, bloating, belching, nausea, bowel dysfunction. All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? We recommend reading the story of Galina Savina, how she cured her stomach. Read the article >>

Before we talk about the reasons, let's define what we mean by discomfort in the stomach or intestines. Discomfort is, by and large, any feeling that cannot be called comfortable. That is, these are simply unpleasant sensations and various kinds of pain. on exactly what sensations a person experiences when complaining of discomfort in the stomach or intestines . But still, there are diagnoses that doctors almost associate with the terms “discomfort in the stomach” and “discomfort in the intestines.” These are dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome.
What to do if your stomach hurts
If the pain is on the left side, under the ribs, the stomach is most likely to blame. It can make itself felt for a number of reasons - both safe and not so safe.
But there are often cases when pain signals problems with completely different organs.
When to see a doctor immediately
Call an ambulance if the pain in the stomach area is severe and accompanied by the following symptoms:
- you experience discomfort and tightness in your chest;
- you suspect that the pain may be related to a recent blow to the stomach;
- your temperature is above 38 °C;
- there is constant vomiting or vomiting of blood;
- the skin on the body has turned yellow;
- you are experiencing breathing problems;
- You are pregnant.
An ambulance is not needed, but try to get an appointment with a therapist as soon as possible if:
- the pain is not severe, but lasts 2–3 hours or longer;
- the stomach is sensitive to touch;
- in addition to the pain, you notice that you need to go to the toilet more often than usual, or the pain intensifies when you urinate.
If there are no alarming symptoms, relax.
Most pain in the stomach area is not dangerous and, most likely, this is your case.
Nevertheless, it is worth understanding what exactly causes discomfort in the upper left part of the abdomen, so as not to miss dangerous “bells”.
Why does my stomach hurt?
Here are some of the most common reasons.
You swallowed air
This often happens, for example, with those who like to chew gum. Excess air in the stomach can cause muscle spasms and pain.
What to do about it
Wait it out. Pain due to stomach spasms is usually not severe and quickly goes away on its own. If they recur regularly, be sure to consult a physician or gastroenterologist. He will find out why air gets into the stomach and tell you what to do about it. For example, he will suggest giving up chewing gum, changing your diet, or taking medicine that reduces the amount of gas.
You have stomach (intestinal) flu
This is the colloquial name for gastroenteritis - an inflammatory process in the stomach. As a rule, its causative agents are viral infections. Stomach flu, in addition to abdominal discomfort, is accompanied by diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and fever - sometimes slight.
What to do about it
If the stomach flu is caused by a virus, it is treated only symptomatically: do not allow dehydration, and prescribe antiemetic drugs. However, only a doctor can diagnose viral gastroenteritis and prescribe treatment. Don’t try to do anything on your own - you could make a mistake and worsen your condition.
You ate something wrong
In addition to viral gastroenteritis, bacterial gastroenteritis is also common. In this case, the inflammatory process in the stomach is caused by bacteria that enter it with food - the same salmonella.
There are other ways to get gastroenteritis:
- take a sip of water from a dirty pond full of parasitic microorganisms;
- drink or eat something that contains heavy metals - arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury;
- get too carried away with sour foods - citrus fruits or tomatoes;
- take certain medications - certain antibiotics, antacids (stomach acid reducers), laxatives, chemotherapy drugs.
What to do about it
Let us repeat: if you have symptoms of gastroenteritis, be sure to consult a physician. The bacterial form of the disease is treated only with antibiotics. Other types require their own treatment strategies. Only a qualified physician can accurately establish a diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy.
You have indigestion (dyspepsia)
This is the name for the feeling of fullness and discomfort that occurs in the stomach after eating. This is a common problem, and it is often impossible to immediately determine its causes. And they can be different:
- binge eating;
- poorly chewed food;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- chronic constipation;
- smoking;
- stress, fatigue;
- taking medications - the popular aspirin and some other painkillers, birth control pills, some types of antibiotics, steroids, thyroid medications;
- a condition known as irritable bowel syndrome;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- diabetes;
- stomach cancer.
What to do about it
As you can see, indigestion can have dangerous causes, so it should not be ignored. If dyspepsia recurs regularly, be sure to consult a gastroenterologist.
You have heartburn
It is also known as gastroesophageal reflux. This is the name for a condition in which the contents of the stomach, along with acidic gastric juice, enter the esophagus. In addition to discomfort in the stomach area, a person feels a burning sensation in the middle of the chest.
Most often, heartburn depends on the diet: for example, it appears after drinking coffee, carbonated drinks, fatty and spicy foods. But sometimes it is the first symptom of serious diseases - stomach or esophageal ulcers, cancer and even heart attack.
What to do about it
If heartburn is a one-time occurrence, there is no need to worry. But if it recurs, and is also accompanied by other symptoms - nausea, loss of appetite, difficulty swallowing, consultation with a gastroenterologist is required.
You have gastritis or a stomach ulcer
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining. In the initial stages, it is accompanied by the same symptoms as indigestion, heartburn or stomach flu, so only a physician can diagnose gastritis itself. Noticeable pain appears only if the mucous membrane is already severely damaged or gastritis has developed into a stomach ulcer.
What to do about it
Go to a gastroenterologist with complaints. The doctor will send you for tests that will help establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. You should not delay this in case of gastritis, as it increases the risk of developing stomach cancer.
You have stomach cancer
It is difficult to diagnose this most dangerous disease in the early stages. Like gastritis, cancer hides behind innocent symptoms, including:
- frequent and prolonged heartburn;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating, as with dyspepsia;
- nausea, slight drooling;
- loss of appetite.
What to do about it
Understand that any regular symptoms cannot be ignored. If you have discomfort and pain in the stomach area (even if they do not seem serious to you), be sure to consult a doctor.
You have problems with other organs
The left hypochondrium contains not only the stomach. The pancreas, bile ducts, spleen, left lobe of the liver can hurt...
In addition, the organs in the abdominal cavity are closely connected: pain in one radiates to the other. Therefore, if there are strong cutting, stabbing sensations in the left side, it could be:
- appendicitis;
- pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder);
- cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts of the liver);
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder);
- duodenal ulcer;
- kidney stone disease;
- colitis and other pathologies of the large intestine...
What to do about it
Don't tolerate it. Any acute pain in the stomach area, especially if it recurs or lasts longer than a couple of hours, fading and reappearing, is a reason to visit a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. Your life may depend on this visit. Don't take risks.
Source: https://Lifehacker.ru/bolit-zheludok/
Stomach discomfort: dyspepsia
In general, dyspepsia is not one diagnosis, but a number of different digestive disorders. At the same time, symptoms of dyspepsia, including discomfort in the stomach , can occur both against the background of organic (associated with problems in the functioning of organs) and against the background of functional disorders.
Among the organic disorders that lead to the development of dyspepsia, chronic pancreatitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastric ulcer, and cholelithiasis are often noted.
As for functional disorders that can cause dyspepsia and, accordingly, discomfort in the stomach, these include nutritional disorders (or nutritional disorders), stress, taking medications, increased secretion of hydrochloric acid, and others.
Functional (nutritional) dyspepsia, depending on the nature of nutritional disorders, can be fatty, putrefactive or fermentative. All three types cause stomach discomfort , but fatty dyspepsia is associated with excessive consumption of fats, putrefactive dyspepsia is associated with protein abuse, and fermentative dyspepsia is associated with too frequent and prolonged consumption of carbohydrates.
How does dyspepsia manifest? Discomfort in the stomach, or more precisely, in the epigastric region, is only one of the symptoms. In addition, patients with dyspepsia often complain of a feeling of satiety almost immediately after starting a meal and note that food seems to stop in the stomach. Nausea and bloating in the epigastric region are also possible, which doctors need to differentiate from visible bloating.
During differential diagnosis, doctors determine whether the patient has diseases that could contribute to the development of organic dyspepsia, and also exclude all other possible diseases that are characterized by stomach discomfort and other symptoms of dyspepsia. If no organic diseases are detected during diagnosis, doctors come to the conclusion that the patient has organic dyspepsia.
Depending on what causes dyspepsia, treatment is prescribed. But in any case, regardless of other doctor’s recommendations, to cure dyspepsia it is imperative to improve your diet.
Pain in the epigastric region, its causes | Heartburn.net - information portal
Constant discomfort in the stomach is often a consequence of the development of dangerous diseases in the digestive system.
If a person occasionally feels nauseous, experiences discomfort and mild malaise, then the likely cause lies in an unbalanced diet or nervous tension.
In case of pathological manifestations, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor and conduct a comprehensive examination, finding out the source of discomfort in the stomach area.
Why worries: main reasons
Unpleasant sensations in the stomach area can be associated with physiological and pathological sources. Constantly disturbing discomfort may be the first sign of the development of a serious illness. The following pathologies are common causes of discomfort:
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- peptic ulcer;
- gastritis;
- formation of stones in the gallbladder;
- gastroesophagitis.
A person may notice discomfort and bloating in the stomach, but it is impossible to independently determine their causes. Therefore, before self-medicating, it is recommended to consult a doctor and get a diagnosis.
There are also non-pathological factors that influence the occurrence of discomfort. These include:
Unpleasant sensations from the digestive system can occur due to stress.
- Disturbed nutrition. The most common cause of stomach pain. Discomfort may occur after eating or when you want to eat. Often unpleasant symptoms are observed in the morning.
- Abuse of tobacco and alcohol products. Negative substances affect digestive function, resulting in discomfort, heartburn, nausea and belching.
- Stressful situations and lack of sleep. Disorders of the nervous system lead to dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Long-term drug therapy. The use of certain medications disrupts the functioning of the stomach and intestines. Constant discomfort in the abdomen can lead to serious illnesses, including the development of ulcers.
Pathogenesis
The most common symptom of such ailment is constant nausea, indicating a pathology of the digestive system. In this case, it is possible to diagnose diseases of the digestive system, poisoning, and infectious diseases.
Discomfort in the abdomen may be accompanied by the following symptoms: flatulence, pain, heaviness in the epigastric region. Classification of dyspepsia: functional and organic.
Provocateurs of this syndrome are stressful situations, the presence of increased acidity of gastric juice, Helicobacter pylori, unhealthy diet, impaired motility of some parts of the gastrointestinal tract, and the use of medications.
We should not forget about irritable bowel syndrome, which is a chronic pathology caused by improper functioning of the intestines. Causes of IBS: stress, lack of fiber in the diet, abuse of carbonated foods, caffeine and junk food.
Additional symptoms
Discomfort in the stomach area may be accompanied by other symptoms that can help determine a specific disorder. Discomfort often manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- dizziness and headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- feeling of heaviness in the intestines and stomach;
- quick satiety after eating;
- reluctance to eat;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- bloating, enlarged abdomen;
- weakness and malaise;
- increased accumulation of gases;
- burning sensation in the upper abdomen;
- nagging pain.
Attacks of nausea
Nausea can complement the unpleasant symptomatic picture.
Discomfort and bloating of the stomach are often accompanied by a similar symptom. Often the disorder provokes vomiting with undigested pieces of food. To cope with nausea, it is recommended to drink plenty of still water.
Unpleasant sensations can be associated with severe food or alcohol poisoning, intestinal or stomach dysfunction, or infectious infection. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor to avoid complications.
Dyspeptic disorders
Mild stomach discomfort may be associated with problems with the breakdown of foods. Dyspepsia is often the first symptom signaling problems with the gastrointestinal tract. A violation can manifest itself in 2 forms, presented in the table:
| View | Peculiarities |
| Organic | Associated with chronic gastrointestinal diseases |
| May occur with gallstones | |
| Functional | Not associated with digestive system dysfunction |
| More often appears in the evening | |
| Pathological signs arise and change throughout the year |
Irritable stomach syndrome
By putting the nervous system in order, you can get rid of such a disorder of the digestive system.
Discomfort in the abdominal cavity can be caused by a similar chronic condition characterized by dysfunction of the intestines and stomach.
The disorder is not a disease, but is accompanied by flatulence, heartburn, and bloating. The source of irritable stomach syndrome is a disrupted diet and constant stress and nervous strain.
Remove the discomfort caused by SRS, possibly by normalizing the state of the nervous system.
Treatment of discomfort
The genitourinary system can be treated in several available ways and according to the individual characteristics of the patient. So, the treatment methods include the following:
Medication
Most often, doctors prescribe various medications based on test results. This method is more optimal. If the disease is mild, then discomfort, burning and other symptoms disappear after a couple of days.
List of drugs:
Source: https://gb4miass74.ru/simptomy/diskomfort-v-kishechnike-posle-edy.html
Bowel discomfort: IBS
This is how irritable bowel syndrome is commonly referred to using the abbreviation IBS. Along with dyspepsia, this syndrome is a disease that very often does not depend on any organic disorders. What then becomes the reason for its development? There are several reasons, and each of them can cause IBS, and, accordingly, discomfort in the intestines :
- psychosomatic disorders, neuroses;
- stress, chronic traumatic situations;
Much less often, intestinal discomfort caused by IBS occurs due to poisoning or intestinal infection. But even these phenomena, in order to provoke the occurrence of IBS, must be accompanied by psychological problems.
Diagnosing the presence of irritable bowel syndrome is not easy because doctors have to rule out a significant number of other diseases that also cause IBS symptoms. But in general, a number of symptoms have been identified, in the presence of which (especially when accompanied by psychosomatic disorders) one can suspect the presence of irritable bowel syndrome.
— discomfort in the intestines , which can be expressed both in mild discomfort and in significant pain;
- stool disorder. Both diarrhea and constipation are possible;
Causes of intestinal discomfort
Intestinal discomfort can occur with chronic abdominal pain, stress can also cause intestinal discomfort, and problems with intestinal discomfort can also occur with intestinal spasms. Intestinal cramps occur with irritable bowel syndrome with bloating, constipation or diarrhea, or due to poor diet: eating fatty, fried or large amounts of sweet foods, alcohol, as well as fasting or overeating.
The most characteristic symptoms of intestinal discomfort are:
- abdominal pain: observed in 50-96% of patients, they are localized around the navel or in the lower abdomen, and have varying intensity (from slight aching to very severe intestinal colic). As a rule, pain decreases or disappears after bowel movements or passing gas. An important distinguishing feature of IBS is the absence of pain and other symptoms at night;
- bowel dysfunction: observed in 55% of patients and expressed in the appearance of diarrhea or constipation. Diarrhea often occurs suddenly after eating, sometimes in the first half of the day. The stool contains mucus. Many patients experience a feeling of incomplete bowel movement after bowel movements. Often the urge to defecate occurs immediately after eating. Possible alternation of diarrhea and constipation;
- flatulence: one of the characteristic signs of discomfort in the intestines, usually worsens in the evening. As a rule, bloating increases before bowel movements and decreases after it. Quite often, flatulence is local in nature.

The main cause of intestinal discomfort is non-compliance with the principles of a balanced diet, consumption of foods rich in indigestible carbohydrates, which are fermented by bacteria in the intestines. Discomfort in the intestines also occurs when a person eats quickly, swallows food in large pieces or drinks in large sips, talks while eating and ends up swallowing a large amount of air, which accumulates excessively in the intestines.
Intestinal discomfort is provoked by stressful situations, in which spasm of intestinal smooth muscles occurs and slowing of peristalsis, which can be caused by problems of the oral cavity (for example, the absence of some teeth, deformation of the palate).
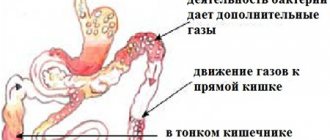
Intestinal discomfort can occur with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Bacterial overgrowth syndrome, in which some bacteria from the colon are thrown into a thin, sterile environment, which causes fermentation and putrefaction processes in the small intestine, which always release a lot of gases.
Functional dyspepsia, or “offended stomach”
I receive a lot of letters with the following content: “I am 40 years old, for 20 of them I have been suffering from constant belching, bitterness in the mouth, heartburn, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, and pain. They find gastritis, chronic pancreatitis, chronic cholecystitis and bile duct dyskinesia, but no one can help me! Help!".
When you start to analyze medical documents, in 99% of cases it turns out that there is no significant pathology there! But our doctors don’t like or don’t know how to say “no”. There will always be “possible inflammatory changes”, “superficial gastritis”, “indirect signs of chronic pancreatitis”, “suspension and flakes in the gallbladder”.
Or they are afraid of responsibility: “The patient has so many complaints, but I will say that there is nothing, what if I miss something?!” Or are they themselves induced by patients and themselves believe: “Well, there must be something, some kind of explanation?!” Probably this shadow on the pancreas during ultrasound is the inflammation that has been suffered!”
So: 75% of people who complained of a full stomach, bitterness in the mouth, heartburn, stomach pain and discomfort, upon objective examination, do not have any real pathology!
In medicine, this is called “functional dyspepsia.” Another option: “upset stomach”, which literally translates as “offended stomach”!
So, think about it - 75%! This is despite the fact that such complaints in clinics are registered in 25% of all calls! As a result, millions of people are involved in a cascade of unnecessary studies, receive treatment that does not help anyone, and often end up on the operating table!
Why then does all this happen?! After all, the symptoms are completely real: it really makes you feel sick, and it really hurts! The most common theory is that such people have increased sensitivity of the digestive organs both to the slightest distension of the stomach and to fluctuations in the chemical composition of bile and gastric juice that are normal for others.
Irritable bowel syndrome
It is characterized by the presence of symptoms and the complete absence of any pathological changes in the intestine. It is clear from this that “irritable bowel syndrome” is a kind of diagnosis of exclusion. First, you need to check everything carefully so as not to miss a serious pathology, be sure to perform a colonoscopy, and only after that can the presence of this syndrome be considered.
What exactly is this disease? You need to have an idea about it, if only because 30–50% of all visits to a gastroenterologist are patients with this particular syndrome! Reason number 2 (after a cold) for issuing sick leave!
Let's look at the symptoms in a little more detail.
- Cramping pain in the abdomen. But not those that lead to weight loss or wake a person up at night! Here you immediately need to tune in to another diagnosis.
- Loose stools. In small portions, usually during the day. Almost never with mucus or blood, again not at night.
- Diarrhea often gives way to constipation. Not constant: against their background there are periods of normal stool, and even diarrhea. A feeling of incomplete emptying even with an empty bowel is characteristic.
- Belching, gas, heartburn are frequent companions.
- Close relationship with depression, sexual dysfunction, pelvic pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis.
This is the picture, plus a normal colonoscopy result, the absence of anemia and other abnormalities in blood tests.
Where does this attack on our heads come from? Oddly enough, we still don’t know the exact reason! The hypotheses are as follows.
- Spasm. After all, this disease used to be called “spastic colitis.” Without going into details, I will say that not everything is so simple. Although antispasmodics often help. Often develops after gastrointestinal infections. However, not all!
- Depression and stress. The most statistically supported theory.
- Intolerance to certain foods, such as lactulose, or food allergies. Again: not everyone.
- Intestinal hypersensitivity. The nerve endings in some patients react to ordinary irritants - gases, peristalsis - inappropriately, excessively, hence all the troubles. This does not answer the question of what the root cause is, but it does explain well why antidepressants are effective here.
Intestinal discomfort, bloating
Bloating is the process of increasing the volume of gases in the intestines from the usual 700-1500 ml to 3000 or more. An increase in the amount of gas is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, often quite painful, which cause discomfort in the intestines. Intestinal discomfort during bloating is explained by two factors - actually strong distension of the intestinal walls and high visceral sensitivity.
If the symptoms of intestinal discomfort during bloating are caused by diseases, correcting the diet will not produce significant results. Without proper treatment, the condition will worsen and be complemented by other symptoms - loss of appetite, chronic constipation, diarrhea, heartburn, belching, severe pain.
Intestinal discomfort with bloating, which is indicated by:
- Intestinal discomfort due to bloating appears on a regular basis in conjunction with diarrhea: dysbacteriosis, worms, enterocolitis caused by allergies, and infections can be suspected. The same symptoms occur with cirrhosis;
- with intestinal discomfort, severe pain is observed along with bloating: indicates chronic enterocolitis, biliary dyskinesia, peritonitis, Crohn's disease, intestinal obstruction. Some diseases of the female reproductive system also provoke these symptoms;
- in case of intestinal discomfort, bloating and vomiting, difficulty with bowel movements, belching: in addition to the listed problems, gastritis, liver and pancreas diseases are sometimes diagnosed;
- with intestinal discomfort, pain in the middle part of the abdomen (at the navel) is added to the symptoms of bloating: after eating, rumbling and flatulence are observed - problems of the small intestine;
- with intestinal discomfort , loose stools appear, weight loss, deterioration of the epithelium, weight loss, irritability, belching with a taste: exacerbation of enteritis.
- yellowness of the skin, bubbling sounds, a feeling after defecation as if the process is not yet completed, and this is with bloating: biliary dyskinesia.
Diagnosis of bloating is carried out by a therapist or gastroenterologist. In some cases, infectious disease specialists, neurologists, oncologists, and gynecologists are additionally involved.