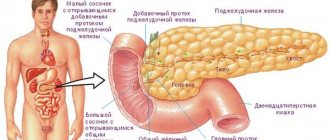
How long does an exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis last?
Pancreatitis is caused by self-destruction of pancreatic tissue by activated enzymes.
Activation of enzymes that break down proteins and fats occurs in response to inflammatory changes in tissues. Pancreatic changes in the activity of the pancreas occur as a response to the vigorous activity of enzymes. Excessive enzyme activity develops due to a number of factors:
- Mechanical destruction. It consists of blocking the duct and blocking the outflow of gland juice. Develops due to adjacent diseases of the bile ducts and edema. Injuries are distinguished separately.
- Neuroendocrine disorder. General disorders of the body's hormonal function - fat metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism. Reasons: abuse of fatty foods, alcohol.
- Toxic and allergic disorders. Allergic reactions to systemic drugs, droppers.
Regardless of the factor in the development of pain, a pancreatic attack is often caused by a combination of factors and a negligent attitude towards health.
Local changes leading to pain
The ducts of the gland close, but the release of enzymes into the food taken does not stop. The active substances are released into the tissue of the gland itself. Enzymes are highly active proteins. The fat-digesting enzyme molecule is capable of breaking down 154 fat molecules. If a small part of the enzymes gets on the gland tissue, it leads to the death of cells and tissues.
Necrosis occurs - acute pancreatitis. During necrosis, enzymes of the tissue itself are released, enhancing the effect of active substances, worsening the outflow from the affected area, increasing the vulnerability of blood vessels. The cycle of chronic pancreatitis closes.
Pain syndrome in chronic pancreatitis
The key process of chronic pancreatitis is the replacement of gland tissue with connective tissue. Sometimes salt compounds, often calcium, settle in the connective tissue, clogging the ducts of the gland (calculous pancreatitis). The closed ducts continue to function, accumulating fluid, forming cysts. When an exacerbation of pancreatitis occurs, dull pain appears in the area under the stomach, increasing after a diet violation. More often, the sensations occur after heavy feasts or an excessive amount of food eaten. This happens due to the expansion of the stomach, pressing on the head of the pancreas, causing spasm, leading to pain. It occurs under the stomach, it feels deep in the abdomen. Depending on the eating disorders, the pain is short-term or becomes permanent.
The pain spreads to the area of the left sternum, affecting the shoulder, spreading to the back. If the disease progresses in the head of the gland, it spreads to the liver area. If the pathology affects the entire organ, the pain encircles.
There is an increase in pain in certain positions of the patient - lying on his back. Becomes weaker when sitting. Instinctively, the patient presses his legs to his chest in a sitting position - with this position the pain weakens.
According to statistics, with chronic pancreatitis, pain is observed in 9 out of 10 patients, and only 1 in 10 pancreatitis is not accompanied by painful sensations.
The attacks may recur. Doctors have created a scale of attacks:
- Type A. Pain lasts up to 10 days, interspersed with long periods without it.
- Type B. Long periods of pain up to 30-60 days. This type is more common in alcoholic pancreatitis.
- Persistent, ongoing pain. It is an indication for surgical intervention and the use of narcotic painkillers.
Forms of the disease
Gastroenterologists distinguish several forms of pancreatitis. The classification is based on the clinical picture. The form of the pathological process and the presence of concomitant diseases determine how long pancreatitis is treated.
The acute phase is divided into several subtypes:
- edematous;
- fat;
- hemorrhagic;
- purulent.
When an inflammatory process begins in the body during an exacerbation, the chemical breakdown of enzymes responsible for the breakdown of proteins and peptides is activated. Provided that the nerve endings are not damaged, the pain syndrome is severe. Dangerous cases requiring immediate medical intervention are accompanied by intoxication and severe dehydration.
The period during which exacerbation of pancreatitis continues can range from 2-3 hours to one week. Most often, the acute form of the disease lasts 3-4 days. Medical practice and statistics say that it is at this stage that the most deaths occur - from 7 to 15% of all cases of inflammatory process in the pancreas.
The main signs of acute pancreatitis are:
- attacks of nausea, often accompanied by vomiting;
- increased gas formation;
- change in skin tone (it becomes white, gray);
- increased body temperature without other signs of colds;
- Halstead, Coolden and Gray-Turner symptoms.
The chronic form manifests itself differently. With the onset of this stage, an inflammatory-degenerative process begins to develop in the body of a sick person. Chronic pancreatitis can be divided into the following subtypes:
- recurrent;
- painful;
- latent.
Unpleasant sensations are most often observed with the onset of the second type of disease. Most often, the pancreas hurts with chronic pancreatitis for seven days. But if the disease reaches a recurrent stage, pain will be observed constantly.
An ambulance should be called even when the patient does not know that he has an exacerbation of pancreatitis. After all, such pathological processes are dangerous because they can subside for a certain period of time, and then suddenly relapse.
The chronic form of pancreatitis may be accompanied by other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract:
- gastritis;
- ulcerative process;
- cholecystitis;
- hepatitis.
Signs of exacerbation of pancreatitis include the following symptoms:
- Pronounced dull, sharp pain of a girdling nature. It covers the epigastric region, left or right hypochondrium.
- The patient has diarrhea, while the stool has an unpleasant odor, is gray in color and contains pieces of food. The coprogram shows a high content of fiber, muscle fibers, and fat.
- Bitterness in the mouth, white coating on the tongue.
- Nausea, often accompanied by vomiting of bile.
- Increase in general body temperature.
- Violation or even complete lack of appetite, which is why the patient begins to rapidly lose weight.
- General weakness, decreased blood pressure.
The symptoms of pancreatitis are complicated by the fact that they are difficult to eliminate with medications. At the same time, the risk of another type of manifestation of pathology, reactive, remains.
The main sign of the reactive form is the immediate appearance of the clinical picture. It occurs due to food that has an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the pancreas. When it is consumed, the ducts of the organ are clogged, all the produced enzymes remain inside. This damages the walls, causing an aggravation. The acute nature of the pain requires prompt medical attention. The attack is short-lived. Provided that the treatment is correctly prescribed, it stops after 4 days.
How long does an attack of pancreatitis last?
The answer to the question of how long an attack of pancreatitis lasts lies in the stage of pancreatitis and aspects of development. Violation of the outflow of pancreatic juice and an increase in pressure in the lumen of the duodenum lead to the reflux of contents into the gland duct. The duct is not designed for this; small breaks occur, into which active bile enzymes from the intestines enter. They activate their own pancreatic enzymes. The process of inflammation and destruction of pancreatic tissue begins.
Pain in chronic pancreatitis varies. Dull infrequent accompanies patients who violate their diet due to illness.
A different type of pain is acute, with intensification, without spasm. Women are more often haunted by pressing pain after eating. According to statistics, in women, pancreatitis is often combined with biliary tract disease. Pain after eating the wrong food goes away after 2-3 hours and occurs in periods with a chronic course.
Key nursing tasks
The nursing process is a list of specific rules and instructions that a nurse must follow when a person with a pancreatic diagnosis comes into their professional care. The totality of their direct responsibilities in the workplace is defined as a nursing process, which involves the implementation of the necessary steps that are focused on creating the necessary conditions for successful therapy and effective healing of the patient.
Although medical prescriptions are made exclusively by the doctor, not only the patient’s health, but also his life depends on the correct actions of the nurse and the implementation of medical instructions. For this purpose, there is a special nursing care card for the patient, which clearly indicates all the actions of the nursing staff, and also contains recommendations on nutrition and hospital regime for the patient.
During treatment, the patient is given attention and care, and the nurse supervises whether hospital routines, prescribed medications, diet, and necessary procedures and special events are being followed correctly. Nurses also work closely with the relatives of their patients.
Nursing process for chronic pancreatitis involves:
- Examination of the patient.
- Diagnostics.
- Drawing up patient care plans.
- Analysis of therapeutic effectiveness and effectiveness of care.
Based on the fact that damage to the pancreas is manifested by extremely severe symptoms, and primarily by excruciating painful discomfort and other unpleasant clinical pictures, a person usually arrives in a difficult situation. It should also be emphasized that the inflammatory process is usually aggravated by alcohol intake, so the nursing process for pancreatitis has some peculiarities.
Treatment of pain due to pancreatitis
The issue of treating pain syndrome in chronic inflammation of the gland is complex; pain and gland disorder have to be treated simultaneously.
The golden mean is observed when the functions of the gland are restored. Favorable conditions are created for the organ through a strict diet and pain relief. After the pain disappears, the inflammatory process in the gland is relieved and treatment is carried out to restore function.
It is necessary to occupy the gland by restoring the outflow of pancreatic juice, then the pain will subside. For these purposes, non-narcotic analgesics and antispasmodics are used in a hospital setting. Good results are observed when using drugs that block choline receptors, using ganglion blockers.
For persistent pain of an increasing nature, analgesics are administered intravenously - novocaine, diphenhydramine, papaverine, combined with saline, magnesium sulfate and ascorbic acid.
What is the nurse's help with inflammation of the gland of both forms?
Nursing care for pancreatitis in the first days after the patient’s admission to the hospital is focused on eliminating his serious condition, as well as providing maximum rest to the inflamed gland, and eliminating painful signs.
Let us consider in more detail what the nurse’s help is in the acute and chronic phases.
Acute presentation of illness and nursing responsibilities
Treatment of acute pancreatitis first of all begins with primary actions aimed at saving human life. In the event of a severe attack of the disease, the patient is taken by ambulance to the hospital, where he is prescribed bed rest and given rest.
The nurse's treatment plan for acute pancreatitis includes:
- Applying ice to the area where the pancreas is located.
- When chills occur, and if necessary, wrap the person up.
- Give painkiller injections.
- Monitor fluid intake and how fast you observe for the first 3 days after a relapse.
- A conversation with the patient’s family about the need for a strict diet, as well as about giving up bad habits.
Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis and nurse assistance
The nursing process when chronic pancreatitis worsens consists of similar stages that are performed during acute manifestations of the pathology. The chronic course of the disease is characterized by frequent relapses and the likelihood of developing complications, therefore the scheme of nursing care for a patient with this form of the disease has some differences from the actions taken for acute pancreatitis.
The fact is that with chronic inflammation of the pancreas, the pancreas is gradually destroyed, and this anomaly does not have the best effect on neighboring organs, so the necessary therapy and nursing care are much longer than in the acute form of the disease, since it implies the implementation of an extensive list of necessary therapeutic measures.
The main actions for this clinical picture are:
- Maximum restoration of the working functions of the gland.
- Elimination of the factor that provoked the exacerbation.
As you can see, drug therapy and diet are the main components of comprehensive medical care.
The following are planned nursing care actions for chronic pancreatitis:
- Administration of painkillers (injections).
- Monitoring the implementation of the recommended dietary intake and the extent to which drinking norms are observed.
- Control over the regularity of physiological needs, that is, timely bowel movements.
- Organizing an optimal environment for normal sleep (no less than 8-9 hours) and healthy rest.
- Daily dispensing of medications and enzymatic agents prescribed by a doctor.
- If necessary, assistance in moving to medical procedures and so on.
- Providing the patient with stable communication with hospital staff in case of a sharp deterioration in his health.
- Systematic monitoring of the patient’s body temperature, as well as the rhythmic level of pulse and blood pressure.
- Periodic check of the patient's body weight.
- Providing water, tissues and utensils in case of vomiting, and providing anti-emetic medications.
When the patient's condition is stable, the nurse should:
- Provide the patient and his relatives with complete information about the disease and its treatment.
- Inform the patient about the dangers of alcohol and tobacco products.
By following the instructions of the nursing process, the nurse helps the patient get rid of relapse of pancreatitis and, with his competent actions, brings the patient closer to the day of recovery.
How long does chronic pancreatitis last and its exacerbation: the exact timing of the development of the disease
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, accompanied by disruption of carbohydrate metabolism and the digestive process. The outflow of enzymes is disrupted, as a result of which the organ tissues are broken down by their own product. It occurs against the background of alcohol abuse, pathology of the biliary system, insufficient intake of proteins and fats from food, disorders of amino acid metabolism, exposure to toxic factors, infections and injuries. It can occur in chronic or acute form.
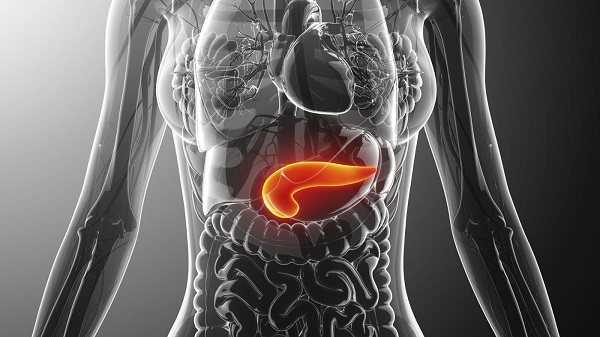
Pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas
How long does pancreatitis last in remission?

The main reason for the termination of remission is an error in diet
Tissues that have undergone fibrosis do not restore their original structure. Therefore, functional impairments persist for life. The disease may not manifest itself for a long time, for many years, if the patient follows the recommended diet and takes medications prescribed by the doctor. Inpatient therapy is not required.
Maintenance treatment - non-absorbable antacids, replacement therapy drugs, drugs that eliminate gastroduodenal motility disorders. Taking these medications allows you to slow down the progression of the disease, delay the onset of diabetes mellitus, and significant digestive disorders.
Duration of treatment
Substitution treatment continues throughout the patient's life. When the tail of the pancreas is affected with destruction of the bulk of the islets of Langerhans, daily administration of insulin is required in a volume corresponding to the level of glycemia and bread units of food consumed. If exocrine insufficiency prevails, pancreatic enzymes after meals (Pancreatin, Creon) are indicated.
Patients who have developed an exacerbation of the disease are admitted to the hospital. As a rule, this occurs when the recommended diet is violated by consuming:
- acute;
- salty;
- overly sour;
- pickled products;
- fried.
Most often, remission is interrupted after taking even small doses of alcohol or non-alcoholic energy drinks (Red Bull, Adrenaline Rush).
Information! It takes from one week to a month or more to restore the condition of the pancreas. The duration depends on the severity of the lesion and the patient’s response to the drugs used.
Correction of the condition is carried out using a large number of saline and colloidal solutions (Trisol, Reopoliglucin), agents that inactivate the patient’s own enzymes (Gordox), histamine H2 receptor blockers (Famotidine), antispasmodics (Drotaverine). With the development of hemorrhagic syndrome, transfusion of coagulation factors and fresh frozen plasma is performed.
Pain syndrome requires the administration of analgesics. For moderate pain, NSAIDs (paracetamol, analgin) can be prescribed. In some cases, there is a need to use drugs.
In the first 2-3 days from the onset of an exacerbation, the patient needs to be hungry. Then they begin to feed him liquid food, gradually expanding the diet.
The list of permitted products includes:
- cottage cheese;
- steam omelette;
- lean fish;
- boiled vegetables;
- steam puddings;
- enveloping mucous porridges;
- baked apples.
You should avoid canned food, whole milk, fatty or smoked fish, difficult-to-digest meat, meat and mushroom broths, and fresh rye bread. In addition, you should avoid other foods that are irritating to the stomach and intestines.
How is pancreatitis treated in a hospital?
The main dangers of pancreatitis are the development of sepsis (blood infection) and peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneal tissue).
They develop in the absence of timely treatment of the disease , and their correction is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting.
The article will discuss the main principles of providing first aid to patients diagnosed with pancreatitis, medications and other forms of medical intervention to eliminate the severe consequences of the disease.
How and with what is pancreatitis treated in the hospital?
Upon admission to the hospital, a sick person begins to be treated according to the following principles of pancreatitis therapy (arranged in sequential order):
- relief of pain (with exacerbation of the disease, patients suffer intolerable pain that requires immediate relief);
- neutralization and prevention of complications (at the stage of organ suppuration, antibiotics are used in loading doses or surgical intervention (if drug correction of the condition is impossible));
- detoxification of the body (during the inflammatory process and purulent formations, a large number of toxins are released into the blood, which must be expedited and neutralized) - forced diuresis tactics are used (administration of large doses of diuretics) and abundant infusion of salt solutions (sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride). They restore the water-salt balance, eliminating the development of dehydration, which is especially dangerous for a sick person in a similar condition;
- decreased production of enzymes inside the gland (the main reason for the development of pancreatitis is the stagnation of enzymes produced by the gland within itself; reducing their further production will help to quickly stop the inflammatory process). Drugs from the group of proton pump inhibitors (reduce the production of digestive juices at the cellular level) and H1-histamine blockers (reflexively reduce the production of enzymes) are used;
- symptomatic therapy - elimination of dyspeptic disorders (vomiting, stomach pain, intestinal colic and flatulence). Antacids (Almagel, Phosphalugel), antiemetics (Metoclopramide, Cerucal) and fixatives (Loperamide) are used;
- prescription of a diet (complete fasting during the first days of treatment eliminates the inflammatory process and swelling of the pancreas).
Attention! Exacerbation of pancreatitis is a life-threatening condition for the patient. Do not try to treat it yourself at home.
In the first month after an exacerbation of the disease, the patient is prescribed a strict diet. During the first week of hospital stay, complete abstinence from food is indicated. It is allowed to use only :
- heated mineral water;
- sweet tea;
- decoction of dried fruits.
Excellent options for giving to the patient these days would be: “Borjomi”, ready-made compotes from dried apricots and dried apples, tea, sugar.
From the second week you are allowed to consume:
- vegetable broths;
- boiled meat ( low-fat varieties );
- boiled fish;
- porridge with water from ground or grated cereal;
- dried bread.
You can bring sweet crackers, ready-made broths (potato, carrot), ground cereals, which just need to be poured with boiling water for cooking, boiled protein products.
From the third week the menu expands significantly. It becomes the usual diet for patients with pancreatitis , which will need to be followed for several more months after recovery.
It excludes the consumption of the following dishes and food ingredients:
- fat;
- roast;
- salty;
- smoked;
- spicy;
- fresh vegetables and fruits ( except sweet apples, strawberries, pears, apricots );
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
- meat broths (fat);
- salo;
- fatty meat and fish;
- alcohol.
Important! It is advisable to discuss the patient’s upcoming diet with the doctor, and only then plan the composition of the meals.
, the following types of assistance can be provided in a hospital :
- resuscitation measures (for complications that threaten the patient’s life);
- surgical intervention (in case of extensive necrosis (death of cells) of the organ or blockage of the pancreatic ducts);
- intensive drug therapy;
- physiotherapy (during the recovery period);
- constant monitoring by specialists of the patient’s condition.
How long does it take?
The operation is performed only if there is a threat to human life and if it is impossible to correct the situation using traditional means of treatment . There are several areas of surgical intervention for pancreatitis:
- organ resection (removal of the dead part in order to stop further necrotic process);
- eliminating blockage of the pancreatic ducts, which prevents the excretion of enzymes into the small intestine;
- removal of abscesses and pseudocysts filled with pus and remnants of dead tissue.
The operation takes about an hour. Further treatment can last from 3 days to 2 weeks, depending on the severity of the patient’s condition upon admission to the hospital.
Intensive conservative methods
Intensive conservative treatment usually includes antibiotics in large doses, which instantly destroy infection in the peritoneum and inflammation in the organ .
Applicable:
- "Tetracycline";
- "Bactrim";
- "Biseptol" ("Co-trimoxazole");
- "Sigmamycin."
If these medications are intolerant, other broad-spectrum antibiotics may be prescribed. It is extremely important to have information about your own drug allergies and provide this information to your doctor in a timely manner.
How is the acute form treated?
The main tasks in the treatment of the acute form will be:
- elimination of swelling and inflammation of the organ;
- prevention of complications;
- detoxification.
The swelling goes away due to a decrease in enzyme production with the help of centrally acting antienzyme agents - Sandostatin, Octreotide (they affect the brain centers responsible for activating the process of production of digestive juices in the gastrointestinal tract).
Attention!
These medications cannot be taken on your own. There is a high risk of developing complications associated with the central nervous system.
Antispasmodics are actively used. They neutralize blockage and spasm of the pancreatic ducts and additionally promote the outflow of enzymes from the organ. In the absence of spasms, the pain syndrome also goes away.
Used: “Duspatalin”, “Sparex”, “No-shpa”, “Trimedat”.
Complications go away thanks to the introduction of large doses of antimicrobial drugs. Detoxification is carried out by “diluting” the blood with salt preparations (saline, etc.) and diuretics.
Important! It is in the acute form that conditions that threaten human life develop.
In the acute form of the disease, the patient remains in the hospital for about a month (perhaps he will be discharged earlier, but subject to strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions and bed rest). After the main treatment, there follows a long period of recovery of the body and a rehabilitation period (if surgery was performed).
Correction of conditions during exacerbation of the chronic form occurs faster - about two weeks. Afterwards, the patient returns home with an extract and a prescribed diet.
Full recovery after an attack occurs in 3-4 months.
Further adherence to the diet and medication will record a positive result and promote recovery.
Next steps after discharge
Main rules after leaving the hospital :
- compliance with the diet (basic rule);
- moderate physical activity ( physical therapy classes );
- adequate sleep and rest regime;
- taking all medications prescribed by the doctor as scheduled.
Attention! Bad habits must be completely abandoned. They can greatly influence the success of treatment.
Explore the video below:
Conclusion
To successfully get rid of pathological symptoms, you must follow your doctor’s recommendations. Inflammation of the pancreas in most cases occurs due to errors in nutrition, lack of a meal plan and consumption of low-quality, harmful foods.
Menu correction is the main condition for recovery for people with the described diagnosis. Restrictions will be imposed for a period of no more than 1-2 years, but the result will be worth it - restoration of the function of the digestive organs will make it possible to return to the original lifestyle and soften the diet.
Source: https://prozhivot.com/pankreatit/lechenie-v-stacionare.html
Signs of exacerbation
Exacerbation is accompanied by pain
The main symptom of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is pain. It can be localized in the left hypochondrium, epigastric zone, or have a encircling nature. As a rule, it occurs 40-60 minutes after breaking the diet. Lying on your back - it intensifies, sitting with a bend forward - it weakens. The sensation is sharp or dull, pressing.
Patient complaints during exacerbation:
- Belching, heartburn, nausea.
- Steatorrhea, diarrhea.
- Stools up to 6 times/day, mushy, with an unpleasant odor.
- Bright red round spots on the skin may appear (Tuzhilin's symptom).
Information! Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis lasts from 1 to 4 weeks, but acute manifestations persist for 2-7 days. Further, during therapy, the clinical picture becomes less pronounced.
Acute pancreatitis
Initially, aseptic inflammation of the pancreas tissue, in which an acute disruption of its function occurs. May occur in mild, moderate or severe degrees.
A mild course is characterized by swelling of the organ and does not lead to the formation of necrosis. The duration of the attack under the condition of volumetric infusion therapy is about 3-7 days.
Lack of treatment leads to the development of necrosis, which requires surgical intervention. Without surgery, death usually occurs. Cardiac arrest occurs due to intoxication and damage to nearby organs by digestive enzymes. This usually occurs on the 7-10th day of illness.
How long do they stay in the hospital with pancreatitis: treatment of pancreatitis in adults in the hospital
Often, at the first attacks of pancreatitis, a person requires immediate hospitalization, especially if the abdominal pain becomes unbearable.
Due to this, planned activities have to be postponed, so many patients are interested in how long they stay in the hospital with pancreatitis. The answer to this question may depend on the type of inflammation of the pancreas, the speed of diagnosis and many other factors.
What to do in case of an acute attack of pancreatitis?
If a person exhibits symptoms of an attack of pancreatitis, the first step is to call an ambulance. While doctors are getting to the patient, it is important to quickly provide first aid. To do this, follow these steps:
- Place the patient on a sofa or bed.
- Apply a heating pad filled with cold water or a wet cloth to the painful area. It is strictly forbidden to heat the abdominal area.
- Open a window indoors. Ventilate it.
When the doctor arrives at the site, he will carry out the necessary procedures based on the presented clinical picture. Most often, Papaverine is administered during attacks of pain. Next, the patient is admitted to the hospital, but hospitalization cannot be refused.
At the first attacks of pain in the abdominal area, you must call a doctor or go to the hospital. A delay of even a few hours can seriously affect the patient’s condition and cause complications. In addition, acute pancreatitis without proper treatment can quickly develop into chronic pancreatitis.
Hospitalization
How long does it take to treat pancreatitis after hospitalization? In case of exacerbation, infusion treatment is usually required, after which the patient is discharged to continue therapy at home. As soon as the patient is admitted to the hospital, his blood pressure is measured and he is sent for an initial examination to the doctor. Next, it is necessary to carry out the following diagnostic measures:
- blood test to determine leukocytes and enzymes;
- laparoscopy;
- ultrasound examination.
After carrying out all the necessary procedures, the doctor evaluates the pancreas and the patient’s condition and identifies the form of pancreatitis. Based on the data obtained, a method and treatment plan are selected and medications are selected. Treatment for moderate severity is carried out in the intensive care unit; for severe pain and intoxication, resuscitation may be required.
Treatment in hospital
Acute pancreatitis in adults is treated in a hospital using the following measures:
- First of all, it is necessary to relieve pain. For this purpose, medications such as Baralgin, Novocain, Analgin, Promedol in the form of tablets and injections are used.
- The second step is to carry out hypertension of the bile outlet channels. A drug such as No-Shpa is suitable for this.
- It is imperative to remove the load from the pancreas and ensure rest. Water fasting will help with this. In the first few days after starting treatment, you can drink regular drinking and mineral water.
- Prevention of thrombosis is often important.
How long do emergency measures last? This usually takes a few minutes, but sometimes it takes the whole day. After they are completed, a period of intensive therapy begins.
It includes taking sorbents (Smecta, Almagel) and anti-inflammatory medications (Gordox and Mannitol by drip, Contrikal). To reduce hydrolysis, diuretics (Furosemide) are prescribed.
To prevent the patient's condition from worsening, the stomach must be cleaned and drained, as well as the condition of other internal organs checked, but a full medical examination is not carried out due to its dangerous condition. To facilitate the work of the pancreas, insulin injections are given.
Thus, it usually takes about 7–10 days to eliminate an attack of acute pancreatitis or an exacerbation of its chronic form, with the first 2–3 days being the period of the most intensive therapy. After discharge from the hospital, the patient must be under the supervision of doctors for one and a half to six months.
Chronic pancreatitis should be treated with periodic examinations, adherence to the regimen and self-administration of recommended medications.
Surgical intervention
How many people stay in hospitals with pancreatitis if surgery is necessary? This form of treatment can take varying amounts of time, depending on the scale of the problem.
Treatment of pancreatitis with surgery may be prescribed when complications are diagnosed. It is indicated for jaundice, lack of benefit from medications, and detection of formations in the pancreas on ultrasound.
In this case, time will be needed not only for preparation and actual surgical intervention, but also for the rehabilitation period. Thus, the patient spends about a week in the hospital after it and spends another 1.5-2 months in home treatment.
He is prescribed a special diet, drug therapy, physical exercise, and a daily routine plan is drawn up. It is necessary to be admitted to the hospital again at the first signs of complications.
Conclusion
When a person experiences severe pain and signs of acute pancreatitis, there is a high likelihood that they will be admitted to hospital. In such cases, you cannot hesitate and it is important to immediately seek qualified help.
In the most successful cases, it is thus possible to get rid of the disease within a week, however, with delay and violation of the regime, therapy can drag on for up to several months.
Source: https://pankreatsindrom.ru/pankreatit/skolko-lezhat-v-bolnice-s-pankreatitom.html
Reactive pancreatitis

Reactive pancreatitis may result from drug toxicity
It occurs with pronounced clinical manifestations, but responds well to treatment. Usually does not lead to the formation of pancreatic necrosis. It occurs as a reaction to the influence of a provoking factor: shock, intoxication, exacerbation of a peptic ulcer, poisoning, taking certain medications. Treatment is no different from mild acute pancreatitis. Recovery time is 3-5 days if therapy is started early.
How long pancreatitis lasts depends on:
- forms of pathology;
- doctor's qualification level;
- the initial state of the pancreas in particular and the patient’s entire body as a whole.
The above are average terms, which may differ significantly both up and down. The speed of initiation of treatment measures is of great importance. Therefore, at the first signs of pathology, you should immediately contact the clinic for examination and prescribing the necessary therapy.
How long can an exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis last in adults?
Pancreatitis is one of the most common diseases of the pancreas. Treatment of this disease in the acute stage should be carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. This is due to the fact that the disease can lead to disability or even death.
If the first suspicion of the presence of this pathology arises, the patient should be immediately taken to the surgery or intensive care department.
Treatment of the disease is carried out using medicinal methods, and in severe cases they resort to the use of surgical methods of treatment.
Stages of monitoring a patient with pathology
The nursing process for an acute illness reveals characteristic signs due to the development of urgent anomalies in the patient, for example, loss of consciousness, collapse, and so on. It is often necessary to turn to the patient’s relatives for help.
The nursing process is divided into three stages.
What is done in the first stage
So, the first stage of the nursing process is to conduct an examination, and is carried out according to the mandatory scheme:
- Examination of the patient and interview with him, as well as his relatives, to obtain the necessary information.
- Measuring blood pressure, establishing a pulse rate and measuring temperature.
- Taking a blood and urine sample for analysis.
- Recording the necessary data in the nursing history of the disease.
In more detail, the nurse collects information about the characteristics of the disease:
- Presence of risk factors.
- What exactly could lead to the development of the disease.
- Features of the course of pathology.
- What illnesses did the patient suffer?
- Examines the obtained test results.
- Reveals what treatments have been performed in the past.
- What complications are present?
The nurse also draws up an anamnesis about the patient’s life:
- Hereditary factor.
- Patient's profession.
- What diseases did the patient suffer from?
- Possible risk factors.
- Living conditions of the patient.
Features of the second stage
The second stage involves identifying the following symptoms (diagnosis):
- Having severe pain.
- The presence of nausea and the urge to feel it.
- How stable and healthy is the patient’s sleep?
- Clarifies the presence or absence of body temperature.
- Is there fever and chills?
- The presence of symptoms of intoxication of the body.
- The degree of weakness, as well as how confused and depressed the patient is.
- Present or absent: diarrhea, bloating and belching.
In addition, when diagnosing, the nurse performs:
- Ultrasound.
- Computed tomography.
- Endoscopic examination (ERCP) and other hardware examination.
Laboratory diagnostics means:
- Biochemical blood sampling.
- Taking blood for sugar.
- OAMU.
- UAC.
Main tasks of the third stage
With regard to the next stage of the nursing process - the third, it consists in developing a plan of care for the patient based on the available information obtained in the first stages. When drawing up this plan, the nurse uses special literature and medical guidelines, which define:
- Step-by-step therapy for acute pancreatitis.
- Treatment prescriptions for chronic gland pathology.
- Necessary therapeutic measures and recommended manipulations, as well as their standards.
- Instructions for patient care are indicated.
- Therapeutic protocol for chronic pancreatitis.
- Protocol for the treatment of patients with acute inflammation of the pancreas.
- Practical medical advice (recommendations).
The list of all these standards is based on many years of research and experience gained in treating this serious illness, and the presented schemes have been tested and are quite effective in their application.
Hospitalization and treatment of acute pancreatitis in the hospital
Patients admitted to the hospital are primarily interested in questions about how long pancreatic inflammation lasts, as well as how long pancreatitis is treated.
Treatment of the disease in a hospital setting does not last long. If the form of the disease is mild, then the use of infusion therapy is prescribed. After the course of therapy, the patient is sent home.
The time spent in a hospital depends on the timeliness of seeking medical help and the correctness of the diagnosis. In addition, the length of stay in the hospital depends on the correctness of the chosen method of therapy.
If acute pancreatitis is suspected, the patient's condition is assessed after hospitalization. For this purpose, appropriate examinations of the body are carried out using special equipment.
During the diagnostic process, the presence and location of the source of inflammation is revealed. Not only the method of treatment, but also the tactics of therapeutic measures depends on the correctness of the diagnosis.
A patient with an acute form of pancreatic damage is prescribed the following types of examination:
- hemogram – helps to assess the presence of leukocytes;
- biochemical blood test - allows you to detect the presence of pancreatic enzymes;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs - makes it possible to determine the localization of the inflammatory focus;
- laparoscopy.
After conducting initial examinations and identifying the form of the disease, the volume of the inflammatory focus is determined. In addition, the likelihood of complications occurring is assessed. Only after all assessment and diagnostic procedures have been completed, a decision is made on the methods and tactics of treatment used.
Treatment of the inflammatory process can be medicinal or surgical; surgical treatment does not replace the use of specialized medications.
Methods of medical care in a hospital setting
The standard of treatment for pancreatitis in a hospital involves the following actions:
- Relieving pain syndrome.
- Relieving spasms of the smooth muscles of the pancreas.
- Elimination of puffiness.
- Stopping the activity of digestive enzymes of the gland.
- Therapy of the disease.
- Normalization of digestion.
- Elimination of side effects of drugs.
How is pancreatitis treated in the hospital? This question interests many patients with long-standing inflammation of the pancreas. Doctors prescribe medication therapy (including IVs, injections), diet and surgery. The use of traditional methods in hospitals is not practiced.
Conservative therapy
In most cases, pancreatitis is treated with medications. However, the first step in treating the disease will be to ensure pancreatic rest. For this, the patient is prescribed water fasting. For 3-4 days he is prohibited from eating anything except mineral still water (it is advisable to drink it slightly chilled).
In addition, a catheter can be installed in the patient’s stomach for several days, through which its contents will be released.
Treatment of the disease involves the use of the following drugs:
- Diuretics, to remove fluid and eliminate swelling.
- Painkillers (Novocaine, Promedol, Lexir, etc.).
- Antispasmodics to relieve spasms of the smooth muscles of the gland (No-shpa).
- Antienzymes that suppress the production of gland secretions to renew its tissues
- Drugs may be prescribed to prevent thrombosis in blood vessels.
- For purulent processes, antibiotics are prescribed.
- Drugs aimed at restoring normal gastrointestinal acidity.
- Vitamin therapy for general strengthening of the body, raising tone and immunity.
Medicines must be taken strictly according to the dosage prescribed by the doctor so as not to harm the body. At the same time, it is necessary to take medications that will support the functioning of the liver and kidneys, since during the treatment period they are subject to enormous stress.
To detoxify the body from medications, gastric lavage is performed with a soda solution.
Throughout the entire period of treatment, protein, electrolyte, and carbohydrate metabolism are monitored.
Surgical intervention
If necrotic processes have already begun in the gland, surgical intervention is performed. There are three ways to operate the pancreas:
- Removal of the tail and body of the gland.
- Removal of the tail, body and part of the head of the gland.
- Removing fluid formations from the pancreas and washing it.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia in the surgery department. Subject to stable health, after 1-2 weeks the patient is transferred to home treatment, lasting on average 1.5-2 months.
Emergency
If a person is admitted to the hospital with acute necrotizing pancreatitis, and his condition is very serious, action must be taken immediately. Therefore, in such cases, emergency laparoscopy is used.
Before it is carried out, the patient is given a general blood and urine test, blood biochemistry, a urine test for toxicology and a blood test for tumor markers. In addition, the patient is given an enema and anesthesia is administered.
During the operation, dead organ tissue is removed; in some cases, removal of the gland into the abdominal cavity is required. In order to prevent infection, the patient is given strong antibiotics after the procedure.
With this type of treatment, the patient’s stay in the clinic can vary from 5 to 7 days, provided there are no complications.
The main signs of exacerbation of pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is not a disease that occurs suddenly. Most often, the development of the disease is a consequence of the influence of one or more unfavorable factors on a person.
Very often, exposure to unfavorable factors leads to the emergence of a chronic form of the disease, characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbation.
Often the chronic form of pancreatitis develops against the background of other diseases of the digestive system, in particular cholecystitis and gastritis.
The main signs of the development of acute pancreatitis are:
- the appearance of severe pain in the hypochondrium or in the area just above the navel;
- the appearance of vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- increased body temperature;
- the occurrence of tachycardia.
The appearance of these symptoms is a reason for urgent hospitalization.
The signs of the development of the chronic form of the disease are in many ways similar to the symptoms characteristic of the acute form, the main difference being their less intense manifestation.
The main manifestations of the chronic variety are:
- The occurrence of pain in the hypochondrium when exerting physical stress on the body.
- The occurrence of a sharp decrease in body weight.
- The appearance of oily diarrhea.
- Development of aversion to fatty foods.
- Loss of appetite.
In addition, if the patient has CP, additional signs are revealed, such as:
- pain in the heart area;
- pain in the back;
- change in skin color, yellowing;
- development of diabetes mellitus in the event of an advanced form of the disease.
To alleviate the patient’s condition when acute pancreatitis occurs, before the ambulance arrives, he is recommended to take a certain position that helps reduce pain.
A person at risk should regularly examine the body and remember that there are very few visual manifestations.
Particular attention should be paid to such a type of pathology as reactive pancreatitis. Such a pathological disorder occurs suddenly even against the background of completely normal health. Most often, this pathology appears after a heavy intake of fatty and spicy foods. An attack of a reactive form of the disease is characterized by the presence of signs similar to those of an acute type of pathology.
Nursing process for pancreatitis
Patients presenting to the clinic with symptoms of pancreatitis are often in serious condition. Disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas are accompanied by excruciating pain and other unpleasant symptoms. Pancreatitis sometimes develops as a consequence of addiction to alcohol; the nursing process for pancreatitis differs in its features.
The main stages and features of caring for patients with pancreatitis
The nursing process in acute pancreatitis reveals peculiarities due to the occurrence of emergency conditions of the patient (fainting, collapse), and in some cases it is necessary to resort to the help of the victim’s relatives.
The first stage - nursing examination for pancreatitis is carried out in accordance with the methodology and includes:
- Examination of the patient and conversation with him and relatives.
- Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse rate.
- Blood sampling and urine collection for further laboratory testing.
- Entering the necessary data into the nursing medical history.

The second stage of the nursing process - nursing diagnosis identifies the patient's symptoms:
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Fever, chills.
- Nausea and bouts of vomiting.
- Intoxication of the body and dyspeptic syndrome.
- Bloating, belching, diarrhea.
- Sleep disturbance, excitability.
- Weakness.
- Confusion and fear.
Third stage. Based on the diagnostics performed and the obtained indicators, a nursing care plan for the patient is drawn up. When developing and implementing a plan, the nurse uses special medical literature and manuals in the form of a diagram:
- Standards for the treatment of acute pancreatitis.
- Standards for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
- Standards of manipulations and procedures.
- Patient care standards.
- Protocol for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis.
- Protocol for the management of patients with acute pancreatitis. Practical recommendations.
The list of documents is based on many years of research and experience in treating the disease; the described schemes have been tested and are effective in use. This literature contains detailed instructions, descriptions and recommendations, which is convenient for doctors and clinic staff.
Nutrition and use during treatment with medications
After the acute attack of the disease is over, the patient faces a long period of adaptation to a new life, which will begin after discharge from the hospital.
The patient will need to radically change their lifestyle and introduce restrictions on the list of products used in nutritional principles. When pancreatitis is detected in a child, parents should pay special attention to his diet.
Compliance with the recommended diet and nutritional schedule is the basis for therapeutic measures aimed at curing the consequences of pancreatitis.
The patient is advised to avoid eating fried foods, fatty foods and several types of meat.
Food recommended for consumption should be cooked either by steaming or by baking in the oven.
It is recommended to use rosehip decoctions and dried fruit compotes as a drink. You should avoid eating cakes and various pastries. This part of the diet can be replaced with dry cookies.
To follow a healthy diet, an adult must completely stop drinking alcohol and lead a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits such as smoking tobacco.
The patient must remember that failure to follow the diet and doctor’s recommendations leads to an exacerbation of the disease and its return in a more severe form.
When an illness occurs, the patient has a question about how long pancreatitis lasts, and with an exacerbation of the chronic form, the question arises about how long the exacerbation of pancreatitis lasts.
Most often, the duration of the acute period is one month, and the recovery period takes about a year. Inflammation in the pancreas can be cured only by strictly following all instructions and recommendations received from the doctor.
During the recovery period, it is necessary to take special medications for a long time. Taking such medications is part of the classical system of treating the disease.
The following medications are used in the treatment process:
- drugs that relieve spasms, such drugs include No-shpa, Platyfillin;
- medications that help improve the functioning of the digestive system - Mezim, Pancreatin 8000, Festal;
- agents that neutralize the increased acidity of the environment in the gastrointestinal tract - Almagel;
- vitamin complex, including vitamins A, B, C, D.
If the patient begins to recover, he is recommended to take decoctions prepared from plant materials. Herbal decoctions have a mild anti-inflammatory effect and normalize metabolic processes.
Particular care should be taken when choosing medications, methods and treatment tactics if pancreatitis develops in a pregnant woman.
How to speed up treatment and restore the gland
If an adult is diagnosed with chronic pancreatitis, complex treatment is required.
Only in this case will it be possible to restore pancreatic function. Be sure to follow these recommendations in the event of the onset of the acute phase of the disease:
- If acute pain occurs, it is recommended to refrain from eating any food for three days. To maintain the salt and mineral composition, use mineral water (still), rosehip decoction without sweeteners.
- By the third day, slimy porridges, soups, and jelly are introduced into the diet.
- You should not eat solid food for two weeks.
- In case of severe manifestations of pain, it is recommended to remain in bed and apply cold to the epigastric area (ice bag, no more than 15 minutes at a time).
You should definitely call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, you can take an anesthetic antispasmodic drug (only No-shpa or Drotaverine will do).