Features of the flow and classification
In 90% of cases, liver cancer occurs against the background of cirrhosis. Predisposing factors include alcoholism, prolonged inflammation (infectious, autoimmune, toxic hepatitis) and steatosis.
It is not always possible to overcome cancer, but it is quite possible to prolong a patient’s life and improve its quality. To do this, you need to accurately diagnose and begin treatment.
Treatment regimens correspond to the stage of the malignant process. The TNM classification is often used, which includes characteristics of the main tumor, involvement of regional lymph nodes, and the presence of distant metastases. Typically, clinical signs of the disease appear in the second stage, but the patient most often ignores them.
As the cancer progresses and the tumor grows, the patient’s general condition worsens, which prompts him to visit a doctor.
The liver metastasizes to the lymph nodes, diaphragm, bone structures, intestines, lungs and brain with the development of symptoms typical for damage to these organs.
Symptoms of advanced liver cancer
Due to the peculiarities of the blood supply, the liver is an organ that is often subject to metastatic damage. The transfer of malignant cells is carried out hematogenously, that is, through the blood, lymphogenously (with lymph), and also by implantation - during the growth of a nearby tumor.
When metastasis appears in the liver, the following symptoms occur:
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, heaviness in the stomach, intestinal dysfunction);
- weight loss;
- icteric syndrome;
- hyperthermia (usually no higher than 38 degrees);
- pallor;
- skin itching;
- liver pain.
Depending on the location of the primary lesion, the patient may be concerned about:
- with intestinal cancer - abdominal pain, constipation up to complete intestinal obstruction, admixture of pus, blood in the stool, fever and severe weakness;
- with gastric carcinoma - epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting with blood, exhaustion and lack of appetite;
- for lung cancer - chest pain, hyperthermia, coughing up blood, severe shortness of breath, cyanosis (blue discoloration) of the skin due to hypoxia, dizziness and weakness.
As the tumor grows and surrounding tissues become involved in the pathological process, the patient experiences:
- signs of increased bleeding. Their appearance is due to protein-synthetic dysfunction of the liver, resulting in a deficiency of coagulation factors. Clinically, this is manifested by nasal, pulmonary, uterine or gastric bleeding. In addition, telangiectasias and hematomas are recorded on the skin. Against the background of progressive portal hypertension, varicose changes in the esophageal veins occur. If they are damaged, massive bleeding develops;
- fluctuations in hormonal levels, which are accompanied by menstrual irregularities, exacerbation of chronic endocrine diseases and decreased libido;
- an increase in the severity of jaundice against the background of an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. As the tumor grows, compression of the biliary tract occurs, which is accompanied by cholestasis. The patient's skin acquires a greenish tint, stool becomes discolored, and urine darkens. Intense itching is also observed;
ascites, pleurisy are a consequence of portal hypertension and protein deficiency. Fluid accumulates in the abdominal and pleural cavities, causing the patient to experience pain in the chest, abdomen, shortness of breath and cough with sputum;- severe pain in the liver, which is associated with an increase in tumor formation, stretching of the organ capsule and irritation of nerve receptors;
- hepatosplenomegaly – increased volume of the liver and spleen;
- swelling of the limbs, which makes it difficult for the patient to move and self-care;
- rapid loss of body weight;
- pronounced weakness.
Vomiting in stage 4 cancer with bile
Vomiting in cancer patients can occur for the following reasons:
- brain damage by metastases, increased intracranial pressure;
- from anticancer drugs;
- from narcotic analgesics to reduce pain in the patient;
- poisoning of the body due to tumor enlargement and metastasis;
- renal and hepatic failure;
- after chemotherapy;
- gastrointestinal tract damage;
- the appearance of infections and bacterial therapy;
- hypercalcemia;
- nervous exhaustion, stress, depression.
Each case of vomiting in a person with cancer requires observation by a doctor, diagnosis of the cause, and collection of anamnesis. Particular attention should be paid to the medications the patient is taking, as they may cause side effects. Important data from laboratory tests are: urea, creatinine, electrolytes, calcium. When diagnosing, you need to check intestinal patency.
The degree of vomiting can be determined using the following table:
- degree - once a day;
- degree – 2-5 times per day;
- degree more than six times per day;
- degree very frequent vomiting – near-death state;
- degree - lethal outcome.
Based on the appearance: color, composition of the vomit, you can determine the degree of the patient’s condition. Types of vomit:
- Vomiting without impurities. Appears when tissue is damaged. Such vomiting is a consequence of the onset of putrefaction processes. Discharge without impurities appears regularly, in small volumes, and has a sour odor.
- Vomiting with bloody discharge. This is a common occurrence in cancer, which indicates vascular damage. If the vomit is scarlet in color, this indicates internal bleeding.
- Black vomit. Such discharge indicates hidden bleeding - a very dangerous condition for a cancer patient. If there is mucus in the vomit, it means that there is a problem in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Light vomit with bile. Such discharge indicates blockage of the ducts and the formation of metastases in the liver.
Vomiting often occurs in the final stages of cancer, immediately after eating. Nausea may also appear as the tumor disintegrates.
If vomiting appears without impurities, then urgent hospitalization of the patient is not required. It is enough to take special antiemetic drugs and provide the cancer patient with rest. There are cases when vomiting can lead to death.
You should urgently call an ambulance if blood or black impurities appear in the masses. In this case, vomiting indicates internal bleeding. If you do not see a doctor in time, it can lead to death.
It is dangerous if vomiting occurs more than 5-6 times a day. Constant vomiting aggravates the situation and leads to dehydration, the development of heart disease, problems with the gastric mucosa, and the risk of thrombosis.
If vomiting repeats every hour and is mixed with blood and blackness, then it is important to immediately call an ambulance. The cancer patient must be placed on the bed and ensure maximum calm. Further instructions:
Important! It is forbidden to eat after vomiting has stopped.
To alleviate the patient’s general condition, it is necessary to take special medications that have an antiemetic effect. The tablets are prescribed by a doctor. List of drugs prescribed for patients at stage 4 of cancer:
- Atropin and Suprastin. Prescribed for intestinal obstruction, if surgery is impossible. These drugs are practically ineffective at the last stage, so they are prescribed in rare cases;
- Haloperidol and Torekan. These are drugs that are no longer as effective as more advanced modern drugs;
- Methylprednisolone. The drug is prescribed in most cases to patients at stage 4, and is effective for vomiting;
- Diazepam. The drug reduces the excitability of the cerebral cortex and helps calm the urge to vomit, reduces nausea;
- NTZ receptor blockers. The drugs have an effect on the central nervous system. effective against poisoning of the body, especially after radiation therapy;
- Scopolamine. Relaxes the muscles of the stomach and reduces gastrointestinal tract.
If vomiting occurs due to increased intracranial pressure, the doctor prescribes corticosteroids. While taking the drug, do not drink a lot of water or eat food.
To reduce the symptoms of vomiting in stage 4 cancer, you need to follow the following instructions:
- Drink more water, herbal teas and any other liquid to avoid dehydration. Do not drink a lot of water or eat food while taking corticosteroids. In other cases, warm drinks in small sips are recommended;
- You need to take food in small quantities up to 8 times a day;
- It is forbidden to eat spicy, fatty, fried and too salty foods.
Vomiting at the last stage of oncology is a common occurrence and you can only help the patient to reduce the symptoms, but you cannot stop the process. It is important to be able to determine the stage of vomiting in time and provide medical assistance in a timely manner.
You can apply for treatment in Israel. The administrator doctor will contact you within 24 hours
Vomiting in cancer is a fairly common symptom; there are enough reasons for its development in a cancer patient. Most often, the pathological condition accompanies chemotherapy and is potentially preventable in three quarters of courses; 25% is due to a psychogenic vomiting reaction from the anticipation of vomiting itself. A vomiting reaction is often initiated by taking medications.
Types of vomiting as the disease progresses
In the medical literature, there is no classification of emetic reactions by type, since the clinical manifestation is always the same: a sharp contraction of the diaphragm and stomach with the release of gastric contents.
The appearance of the vomit itself can suggest the root cause of the pathological symptom, but not in all situations, including because as cancer progresses, the appetite suffers, the patient does not experience hunger, on the contrary, an aversion to food is characteristic, therefore the scarcity of vomit makes it difficult to analyze.
Depending on the time of occurrence of vomiting after eating, the following types are possible:
- When the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract is blocked, vomiting mainly occurs some time after eating, when the food masses have already undergone partial digestion; brown inclusions can be detected in them - altered blood.
- During a meal or immediately after eating, the release of stomach contents is caused by an increase in pressure in the brain, psychomotor agitation, and tumor damage to the esophagus.
- In case of intoxication, metastases in the liver, complications of drug and radiation therapy, the release of vomit is possible at any time.
With some degree of probability, the appearance of the vomit can suggest the leading cause of the complication:
Vomiting after radiation and chemotherapy
Severe nausea and frequent vomiting discredit an effective method of treating malignant neoplasms, so prevention and prevention of extremely unpleasant complications are no less important than selecting the optimal combination of anticancer drugs.
During chemotherapy, an acute vomiting reaction occurs during the first 24 hours, and a delayed vomiting reaction occurs in the following days after the administration of the cytostatic. There are indomitable or breakthrough vomiting and refractory vomiting, that is, not preventable by special antiemetics - antiemetics.
For all chemotherapy drugs, the emetic - emetogenic potential and methods for its prevention and treatment have been determined, and prevention must begin from the first day and be completed 2-3 days after the end of the course.
Every fourth woman after the first course may develop a reflex - psychogenic vomiting reaction; this type of vomiting is not typical for men. To stop a possible reflex reaction on the eve of the course, tranquilizers are used, acupuncture and psychotherapeutic techniques help.
During irradiation, an emetogenic - vomiting reaction does not have typical symptoms; it often depends on the irradiation zone and the patient’s internal mood. The frequency of complications is influenced by being female, youth, nervousness and life experience in the occurrence of vomiting and nausea from other causes.
Treatment methods for different types of vomiting in cancer, first aid
Oncology has achieved considerable success in the treatment of chemotherapy vomiting, despite an incomplete understanding of the mechanism of action of antiemetics. Not only standard prevention and treatment regimens have been developed, but also basic principles for taking antiemetic drugs:
- early prediction of the intensity of complications and individual selection of a combination of antiemetics;
- start taking it not when a complication develops, but ahead of time and strictly on an hourly basis;
- the advantage of intravenous and rectal forms over those taken orally - orally;
- adding tranquilizers for nervousness;
- introduction of PPI drugs into the regimen that protect the mucous membrane;
- adequate levels of microelements in the blood and a sufficient volume of circulating plasma are maintained by intravenous drips.
When vomiting, the likelihood of gastric contents refluxing into the respiratory tract in a conscious patient is minimal. If the patient is unconscious, which is possible in the terminal stage of cancer, especially with metastases to the brain or liver, the head is turned to the side, trying to tilt it lower.
It is impossible to interrupt the urge to vomit; interference with the process will worsen its course and irritate the patient. After vomiting, it is advisable to rinse your mouth and replenish lost fluid throughout the day by drinking cool water with electrolytes - rehydron - and only in small sips.
In all cases of the development of an emetic reaction, it is necessary to prescribe antiemetic drugs; an initially effective combination does not guarantee a constant result; constant monitoring of the condition and regular adjustment of the regimen are important.
What type of cancer can cause bleeding?
The most common type of gastric carcinoma is infiltration with ulceration or ulcerative-infiltrative type; the size of the lesion and ulcerative defect can be any size, up to total damage to the organ.
A cancer ulcer has rough, protruding and uneven boundaries; its walls and bottom form a kind of folded funnel.
Saucer-shaped carcinoma is distinguished when the ulcer has very clear and uniform boundaries.
In addition, cancerous infiltration can pass through the gastric wall and penetrate into the pancreas and pull the abdominal omental bursa into the conglomerate. Even with tiny early cancer with a minimal ulcerative defect, organ-preserving surgery - mucosal resection - is excluded, because the true boundaries of the tumor are in the deep layers of the gastric wall.
The ulcerative form of cancer in appearance is almost no different from a banal chronic gastric ulcer, and that is why during each gastroscopy, a biopsy is taken from the edges of the mucosal defect from all absolutely ulcer patients.
It is almost impossible for carcinoma growing outside the stomach to bypass the vessel, because in the thickness of the wall the arterial vessels form four interconnected vascular networks: inside and under the mucous layer, between the muscular and under the serous layers. That is why bleeding is the most common complication of the disease.
Source: https://mmc-optima.ru/simptomatika/korichnevaya-rvota-pri-onkologii.html
Liver cancer symptoms before death
At the fourth stage of the disease, when many internal organs are damaged and multiple organ failure develops, the patient experiences:
- severe drowsiness. It is caused by both severe weakness due to exhaustion and dehydration, and brain hypoxia;
- lack of appetite. A cancer patient gradually begins to eat poorly, as it is difficult for the body to digest food. He quickly develops a feeling of fullness in his stomach. He eats in small portions and very rarely. In addition, the patient may even refuse water, which is associated with increasing pain;
- lack of physical activity. The daily increase in weakness leads to the fact that a person cannot get out of bed on his own or even turn on his side. This often causes bedsores;
- change in psycho-emotional state. The cancer patient becomes lethargic, apathetic, and even lethargic at times. His speech is slow, quiet and slurred. Dysfunction of certain brain structures is accompanied by the appearance of hallucinations. A person is not oriented in space, place and his own personality. He does not recognize close people, often forgets information and may be delusional;
- rare breathing, shortness of breath. With the development of pulmonary edema, moist rales can be heard in the distance. The patient cannot cough;
- severe swelling. It is important to remember that fluid accumulates not only in free cavities (abdominal), but also in the tissues of internal organs;
- urination disorder. Renal failure is manifested by a decrease in the rate of diuresis, which causes a decrease in the daily volume of urine. Organ dysfunction is caused by impaired blood supply to the kidneys and severe intoxication;
- decreased blood pressure;
- temperature fluctuations. The patient may have both fever and hypothermia, which is associated with a disorder of thermoregulation, blood circulation and brain function.
Antiemetic drugs
What to prefer - tablets or injections?
Cerucal tablets and injections are used to achieve the same therapeutic effects associated with the need to stop vomiting and speed up the movement of food through the stomach and
Non-drug methods of influencing the urge to vomit in stomach cancer include:
- complete rest and tranquility;
- frequent meals in small portions containing easily digestible food;
- using rehydration drinks to restore lost fluids and nutrients;
- after vomiting, drink 30 ml of liquid every 20 minutes for an hour. Gradually increase the dose. This can be water, non-acidic juices, jelly, broth. Carbonated and “spicy” drinks should be avoided;
- if it is impossible to drink liquid, it is advisable to use ice shavings in the form of frozen juices, broths, water, etc.;
- in case of intestinal obstruction, the doctor may insert a probe to facilitate the passage of vomit;
- acupuncture and acupressure;
- relaxation techniques;
- resort to homeopathic remedies.
Important to know: Stomach cancer stage 4: symptoms, how long do they live?
The action of all of the above drugs is based on blocking the so-called trigger zone of the vomiting center.
Deadly complications of cancer
Death from liver cancer can be caused by both the growth of the tumor itself and complications associated with metastasis, portal hypertension and cerebral edema.
The life-threatening consequences of the progression of the malignant process include:
suppuration, decay of tumor formation, which increases the risk of massive bleeding, severe intoxication and sepsis. Given the exhaustion of the patient, the immune defense in the body is practically absent, which is why it cannot fight the infection;- encephalopathy, depression of consciousness due to hyperbilirubinemia. The toxic effect of the pigment on the central nervous system leads to changes in the psycho-emotional state, lethargy and coma;
- intestinal obstruction. If the intestine is involved in the pathological process, the tumor may partially or completely block its lumen. Thus, the stool does not move forward. Clinically, the complication is manifested by bloating, abdominal pain, constipation and delayed passage of gases;
- bleeding from the esophageal veins. Note that 40% of patients die during the first episode of bleeding;
- pronounced swelling. The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity is accompanied by pain and difficulty breathing. The volume of ascites can exceed 10 liters;
- addition of infection. Against the background of a weakened immune system, the patient may experience an exacerbation of chronic bacterial diseases (pyelonephritis, pneumonia), or a new infection may occur;
- peritonitis – develops when the integrity of the bile ducts or intestines is disrupted due to the germination and disintegration of the tumor. The entry of feces or bile into the abdominal cavity is accompanied by pain, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, fever and weakness;
- pneumonia is a consequence of adynamia. When a patient lies for a long time, he develops stagnant processes in the respiratory system. This leads to inflammation of the lungs, which is clinically manifested by hyperthermia, shortness of breath, cough and chest pain;
- DIC syndrome. Disruption of the coagulation system is accompanied by vascular thrombosis. Particularly dangerous is a cerebral stroke, the location of which determines the clinical symptoms. These may be movement disorders, deterioration in speech, vision, hearing, as well as breathing and heart problems;
- vascular damage and circulatory disorders lead to changes in sensitivity and organ dysfunction. In areas that are in close contact with the bed (coccyx, shoulder blades), zones of hyperemia appear, which over time are replaced by erosions and ulcerative skin defects.
What does black vomit mean?
The eruption of brown vomit with foamy impurities may indicate pulmonary hemorrhage, characteristic of oncological diseases of the respiratory system. The appearance of profuse, continuous black vomiting is a serious phenomenon that poses a potential threat to the life and health of the patient. Black vomiting is especially dangerous, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- signs of intoxication of the body;
- sharp pain in the abdominal area, with a tendency to increase;
- vomiting in masses that have been in the gastric cavity for several days.
If at least several of the above alarming signs are present, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, and before the doctors arrive, provide the patient with all possible first aid. In addition, black vomit may be a sign of intestinal obstruction or acute internal bleeding, which, if not promptly taken, can cause death.
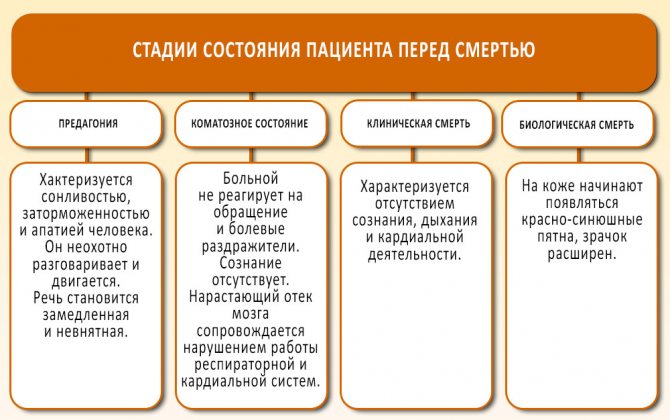
How do people die from liver cancer?
Before death, the patient's condition changes according to the following stages:
- predagonia. It is characterized by drowsiness, lethargy and apathy of a person. He is reluctant to talk or move. Speech becomes slow and slurred. The skin is pale with a bluish tint, blood pressure gradually decreases, there is no appetite, and the heart rate increases. The daily volume of urine decreases, and the patient experiences constipation. Sometimes he becomes aggressive and may moan loudly;
- signs of death in liver cancer at the agonal stage are represented by a coma. The patient does not respond to treatment or painful stimuli. There is no consciousness. Increasing cerebral edema is accompanied by disruption of the respiratory and cardiac systems. Clinically, this is manifested by rare deep breathing, which gradually becomes shallow. Blood pressure drops to 50 mmHg, the skin becomes bluish, involuntary urination and bowel movements are noted. Death occurs from cardiac and respiratory arrest;
- clinical death is characterized by the absence of consciousness, breathing and cardiac activity;
- biological. Red-bluish spots begin to appear on the skin, the pupil is dilated.
How to alleviate the condition of a cancer patient?
The pre-death period for a cancer patient is the most difficult, so it is so important to make every effort to alleviate his condition. For this purpose it is necessary:
- provide food. First, you need to give liquid or porridge food from a spoon, then tube feeding is carried out;
- regularly water and moisten your lips, which will make breathing easier and reduce dehydration;
- monitor the hygiene of the cancer patient;
- turn in bed, massage the back and buttocks, which is required to prevent bedsores. It is also recommended to use camphor alcohol for reddened areas and Desitin for skin ulcers;
- raise the head end of the bed, which will make it easier for a person to breathe;
- talk to the patient, do not argue with him when delusions and hallucinations appear;
- reduce the severity of pain using narcotic medications or alternative methods of analgesia (epidural pain relief);
- administration of sedatives – for convulsions, aggression and psychomotor agitation;
- do breathing exercises, which will prevent the development of congestive pneumonia.
Without treatment, the life expectancy of a patient with liver carcinoma does not exceed one and a half years.
Depending on the cellular composition of the tumor, the extent and stage of the oncological process at which therapy was started, the patient can live 2 or more years. The main thing is to seek help in time and fight the disease without giving up.