How to examine the pancreas
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract usually cause people a lot of problems, but despite this, many delay treatment, trying to cope with the disease on their own. This approach is not only not beneficial, but can provoke dangerous complications and concomitant diseases. So how to check the pancreas? What tests should I take to avoid mistakes? In case of any disturbances in the body, the first thing a person should do is consult a doctor for qualified help. It is the doctor who will prescribe the necessary tests to determine the disease and plan treatment.
Self-check of the pancreas
If, due to various circumstances, it is impossible to visit the clinic, there are signs indicating the state of the pancreas that can be identified at home.
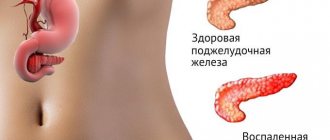
Acute inflammation of the organ is usually recorded after heavy feasts. Intense girdling pain occurs; the person feels as if the upper half of the abdomen is being squeezed by a hoop. Unpleasant sensations spread to the back, increasing in the position of lying with the stomach up. Conventional painkillers do not help.
Often the condition is aggravated by vomiting without a feeling of relief, flatulence, weakness, low blood pressure, rising temperature and a yellowish tint to the whites of the eyes. If you have the listed symptoms, self-medication is excluded; you need to go to the hospital and get tested. Only a specialized doctor will be able to correctly assess the functioning of the gland and prescribe appropriate medications.
We also recommend viewing: What is a pancreatic pseudocyst called?
Chronic pancreatitis progresses gradually. It is signaled by:
- weight loss,
- intermittent pain in the left hypochondrium area, radiating to the lower back,
- diarrhea with a strong odor and light-colored stools,
- nausea,
- bitter taste in mouth
- strong feeling of thirst and hunger.
However, even if a full set of symptoms is detected, a non-specialist may well make an incorrect diagnosis. Therefore, it is better to thoroughly examine the patient in a medical institution, where they know exactly how to check the pancreas and what tests are necessary.
General rules for preparing for analysis
Before you take pancreatic tests, you need to know how to do it correctly. Doctors usually instruct patients because errors in collecting biological material can lead to significant deviations in the results obtained.
General recommendations come down to several points:
- Studies are carried out on an empty stomach, in the first half of the day. A few days before the tests, you should avoid junk food (fried, spicy, fatty, salty, canned food, coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks). It is also not recommended to consume legumes that can cause increased gas formation;
- Before taking blood, you must refrain from smoking for at least two hours;
- For problems such as constipation, care should be taken to ensure that toxins retained in the intestines do not affect the test result;
- All containers must be sterile and hands must be thoroughly washed with soap;
- When collecting urine, women must perform genital hygiene, after which it is better to use a tampon to guarantee the purity of the collected material;
- To study a general urine test, you need to take an average portion.
These simple recommendations will help you get tested correctly and avoid possible false results. However, it is worth remembering that sometimes laboratories make mistakes, so if you have the slightest doubt, you should undergo the examination again.
Laboratory diagnostics
In diseases associated with inflammation of the pancreas, the main task is to determine its condition. Acute episodes are accompanied by increased release of enzymes, which, depending on the type, can be found in the blood, urine and feces. A study of the liver will also be informative, since its function is closely related to the pancreas. The main tests, on the basis of which the doctor can confidently talk about the disease, are usually the following:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test, including testing for the enzymes diastase and amylase;
- coprogram (very informative for pancreatitis);
- Ultrasound, which can be used to detect fluid in the abdominal cavity, determine the condition of tissues and see possible neoplasms, including cancer;
- MRI and endoscopy. These modern diagnostic methods can provide excellent information about inflammation in the organ being examined.
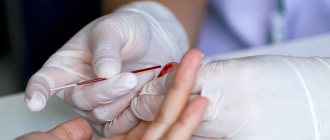
Blood tests
Every person suffering from pancreatitis wonders what tests need to be taken to diagnose this disease. Usually the doctor prescribes several at once.
- General blood analysis . The first thing that will indicate problems with the pancreas is a high number of leukocytes against the background of an increase in the number of segmented and band neutrophils, as well as an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). It must be remembered that an inflamed liver can also give similar results, so the examination must be approached comprehensively;
- Blood chemistry . The most obvious sign of major problems with the pancreas will be an increase in total and direct bilirubin, which will indicate the presence of an icteric form of pancreatitis. Alarming signals are the growth of sialic acids, seromucoid and gamma globulins;
- Alpha amylase blood test. If its indicator increases (the norm is 16–30 g/l per hour), the doctor has the right to suspect chronic or even acute pancreatitis, stones in the gland and blockage of its duct. If the data obtained is below normal, which indicates insufficient production of this enzyme, we can assume pancreatic necrosis, serious pathologies associated with organ destruction;
- Pancreatic enzyme tests: trypsin and lipase;
- Blood sugar test. In case of serious problems with the pancreas, the results will exceed 6 mmol/l, but this data alone will not indicate a developing disease.
Analysis of urine
When the pancreas is diseased, the level of amylase in the urine, as well as in the blood, increases. This type of diagnosis is not expensive at all, so doctors are happy to prescribe it. In addition to a general urine test, the following studies are used:
- Lasus's test. The results of this test show the amount of amylase and its activity in the urine. In this analysis it will be called “diastasis”;
- Proserine test. Its essence boils down to the fact that after a single administration of proserin, the patient’s urine amylase concentration is checked every half hour. If it doubles and does not return to normal within two hours, the doctor can diagnose pancreatitis. In the case when the body does not respond to the administration of proserin, doctors talk about sclerosis of pancreatic tissue and pancreatic necrosis.
Hormone analysis
The pancreas is an organ that produces hormones, so by their content in the body one can judge its health.
- Insulin is a hormone involved in the breakdown of glucose, the synthesis of protein and fatty acids. A decrease in its content in the blood indicates a disorder.
- C-peptide is a hormone produced together with insulin.
- Glucagon, which performs the opposite function of insulin.
- In various situations, blood is examined for the content of hormones such as gastrin and amylin.
Coprogram
Stool analysis is of great importance in the diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including pancreatitis. A clear sign of deviation from the norm will be the presence of undigested muscle fibers, fats and fiber.
Primary diagnosis
Checking the health of the pancreas is necessary at the first sign of a malfunction in its functioning. The main symptoms are:
- 1. Fatty, copious liquid, foul-smelling stools.
- 2. Bloating.
- 3. Nausea.
- 4. Pain in the upper abdomen after eating.
- 5. The appearance of petechiae on the skin - small hemorrhages in the form of red rashes.
- 6. Weakness, anxiety or sudden flushing of the face, changes in blood sugar levels.
- 7. The smell of acetone or rotten fruit from urine and sweat.
The pancreas is an organ of mixed secretion, so it is necessary to check both its enzymatic and hormonal activity.
Diagnosis of this organ includes the following methods:
- 1. Instrumental examination (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, CT).
- 2. Laboratory blood diagnostics - analysis for insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, sugar levels, fermentemia, determination of diastase in urine, fecal elastase, undigested food components (coprogram).
- 3. Diagnostic tests – proserine, iodolipol, for insulin resistance.
- 4. Endoscopy with sampling of the contents of the duodenum.
These research methods help identify exocrine insufficiency, type 1 diabetes, pancreatitis (inflammation of the organ).
Tests for pancreatic disease are usually prescribed by a gastroenterologist, internist or family doctor. First of all, you need to pass standard tests: a clinical blood test, a general urine test, a biochemical blood test. Biochemical analysis will show changes in the level of glucose and amylase in the blood, which has diagnostic value (glucose norm - 3.3-5.5 mmol/l, amylase -28 -100 U/l)
One of the first laboratory tests for diagnosing chronic diseases of the pancreas is a coprogram, which helps to study the content of hydrolysis products and pancreatic enzymes in stool (the norm of elastase in stool is 200 - 500 mcg/g). The advantage of this method is that it is non-invasive, but it is not enough to make a diagnosis.
To determine the functioning of the glandular apparatus, the secretin-pancreozymine test is most effective. To carry out the test, it is necessary to use a probe with alternate injection of secretin intravenously, and then cholecysto-pancreozymin. After this, the aspirated intestinal contents are examined in the laboratory. The following indicators are the norm: secretion volume - 180±19.2 ml/h, amount of bicarbonates - 85.4±16.3 mmol/l, amylase - 111.1±13.6 nkat, lipase - 61.2±9.73 nkat /kg, trypsin - 4.86 nkat/kg.
Laboratory diagnostics make it possible to quantitatively determine the functional state of the pancreas, and for its qualitative assessment, a variety of instrumental studies are indispensable.
Studies allow you to assess the condition and functions of the organ. Acute lesions are accompanied by increased enzyme activity.
Some of them are most conveniently identified by blood, while stool or urine tests are best suited to identify others. The severity of gland damage is assessed based on an analysis of liver and kidney function indicators.
For laboratory diagnostics, patients are required to undergo certain tests. The list of recommended examinations should only be prescribed by a doctor. Most often, to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the organ, parameters of blood, urine, and feces are checked. Based on the results obtained, problems with the functioning of the pancreas can be confirmed or refuted.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Ultrasound of the pancreas - indications and contraindications, preparation and conduct of the study. Decoding the results. The size of the pancreas according to ultrasound is normal in children and adults.
List of studies:
- General blood analysis. It reflects the presence of an acute or chronic pathological process. Changes in the organ are indicated by a significant number of leukocytes, an increased level of ESR, neutrophils (band and segmented), and blood clotting indicators.
- Biochemistry. In such a study, laboratory staff identify the level of bilirubin, both total and direct, and evaluate the parameters of seromucoid and sialic acids.
- Blood for sugar. The norm for this indicator is 3.3-5.5 mmol/l. Deviation from these values indicates obvious disturbances in the performance of the organ.
- Analysis of urine. This study reflects the levels of amylase, protein and amino acids. Organ damage can be judged when these indicators increase.
- Coprogram. The analysis allows you to determine enzyme deficiency by studying data on the content of fat, fiber (not completely digested), starch, elastase and muscle fibers.
Additional blood tests that are prescribed specifically to evaluate the functioning of the gland:
- Alpha amylase - normal values range from 16 to 30 g/l per hour (an increase indicates inflammation, and a decrease indicates necrosis of organ tissue);
- Trypsin – a sign of deviation is considered to be an excess of 60 µg/l;
- Lipase – its value should not exceed 190 units/l.
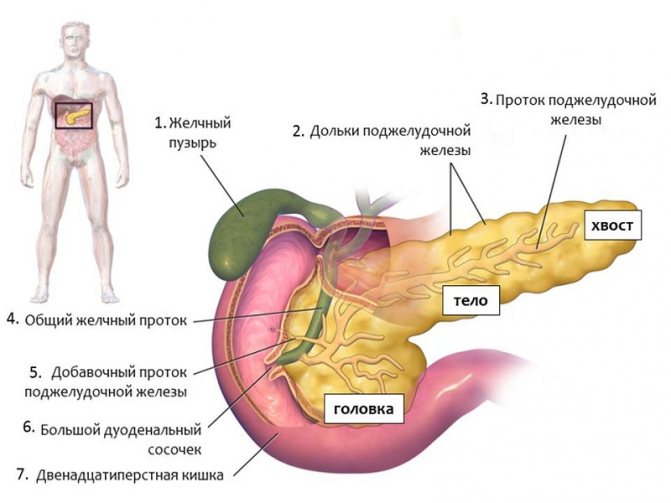
Each laboratory selects acceptable values of enzymatic activity independently, depending on what analysis methods are used. Most tests can be done on an empty stomach, but some may need to be prepared in advance.
It is important to understand that the results of the examinations must be shown to the doctor, since laboratory diagnostics are only a tool for making a diagnosis, but cannot confirm or refute it.
Diagnosis of the pancreas in case of suspected general diseases includes a whole range of studies that can reveal not only pancreatitis, but also other pathologies, including those of an oncological nature.
To accurately make a diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are needed:
- coprogram, during which the condition of feces, intestinal microflora and the entire gastrointestinal tract is assessed;
- determination of the concentration of diastase and amylase in the blood;
- ultrasound and computed tomography to determine the amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity, tissue growth, the presence of cysts and other neoplasms;
- Endoscopy and magnetic resonance imaging, which can be used to detect the presence of inflammatory processes in the pancreas and the patency of its ducts.
There is another diagnostic method that is often used when examining the pancreas. This is palpation. It is carried out primarily during examination of the patient and allows not only to accurately determine the location of pain, but also the presence of cystic formations in the organ.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D1SrX4QxYlw
Since disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas can provoke various diseases, diagnostic measures often include a probe check for the amount of enzymes. If their level is reduced, then this may indicate the presence of some mechanical obstacle to their release into the duodenum. In this case, it may be a stone in the excretory duct or a benign or malignant tumor.
The most common method for diagnosing pancreatic diseases is magnetic resonance imaging. It is this that allows one to obtain information about the condition of the walls or parenchyma of the organ, as well as the presence of cancer cells in it, which, if identified, will require urgent radiation therapy.
However, computed tomography is still considered the most informative diagnostic method. Using it, you can identify all the changes occurring in the pancreas and other organs of the digestive tract. A special feature of CT is that it allows you to obtain a 3D image of all internal organs, making it possible to examine them from all sides.
As for x-ray examination, it is carried out extremely rarely. All that can be found out when carrying out this diagnostic method is the state of the excretory ducts of the pancreas - whether they are narrowed or dilated. More X-ray examination does not provide any information.
If, during questioning and examination, signs suspicious for pancreatic diseases are identified, the doctor prescribes a full examination of the pancreas. For this we use:
- blood test for biochemical tests;
- biochemical examination of urine, revealing the level of diastase;
- stool analysis for scatology to identify undigested food residues, fats (steatorrhea);
- Ultrasound helps in detecting the size, shape, tumors and cysts;
- diagnostic tests provide information about the impaired functional abilities of the organ;
- X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography of the pancreas and neighboring organs are used as additional sources in the search for indirect signs;
- tissue biopsy.
We suggest you read: Shilajit for pancreatitis, treatment of the pancreas
How do doctors check the pancreas? The specialist initially interviews the patient about complaints. First of all, I will dwell on the diet in detail. The doctor will ask if you had any illnesses before seeking advice and for how long.
Read more about how the pancreas hurts and what happens during an attack of pain here.
Patient examination:
- The skin is dry, elastic and has decreased turgor, which indicates the progression of the disease (weight loss and muscular dystrophy).
- The tongue is dry, white with a coating, the papillae on it are atrophied - a sign of the presence of a chronic gastrointestinal disease.
- The abdomen is distended due to the presence of a large number of gases in the gastrointestinal tract.
Feeling the abdomen:
- Upon superficial palpation near the epigastrium and left hypochondrium of the abdomen, pain is observed.
- During deep palpation, the gland can be palpated (with normal readings, the pancreas cannot be palpated). The organ is increased in size and has solid content.
- After the interview, the doctor will tell you what tests are needed to check the pancreas.
MRI of the pancreas
The pancreas often exhibits symptoms of the disease only when serious disorders have already occurred. If the patient managed to detect changes in his condition in time, then this is already half the success. Modern medicine allows us to examine the affected organ quite well. To check the pancreas using magnetic resonance imaging, the following organ parameters are important:
- size;
- form;
- tissue density;
- the presence of formations of any nature;
- features of intrapancreatic ducts. The spleen-pancreas canal is examined separately, since the health of the body directly depends on its patency;
- vascularization.
An examination of the pancreas involves using a contrast agent to check every area and see even the smallest changes in the image.
In what cases is it necessary to resort to MRI:
- detection of any changes in the epigastric region during ultrasound diagnostics;
- tumor;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- intraductal hypertension;
- cysts;
- incessant pain in the abdominal area.
So, if you have complaints about the pancreas, you should not delay your visit to the doctor. Timely tests and research will help you maintain your health.
source
X-ray signs
An x-ray of the abdominal organs may reveal indirect signs or consequences of damage to the pancreas. These include:
- rare detection of stones or lime salts in the pancreatic ducts at the level of the upper lumbar vertebrae (a sign of chronic pancreatitis);
- a large cyst in the form of a homogeneous formation with clear boundaries;
- deformation and displacement of the bend of the duodenum with an enlarged head of the pancreas;
- filling defects along the posterior wall or greater curvature of the stomach with a tumor (cyst) in the body or tail area.
In order to improve visibility, before the examination, the patient is injected with an atropine solution, which reduces the tone of the duodenum, then a barium suspension is administered through a probe.
A more targeted study is retrograde pancreatography, Wirsungography. The contrast must be injected directly into the pancreatic duct. Then photographs are taken that reveal its expansion or sharp narrowing to a complete break (stone). Angiographic examination is highly complex. In this case, a contrast agent is injected through a catheter into the aorta and celiac artery through the femoral approach.
General signs of pathology
Deterioration of the pancreas does not always appear suddenly. Many people simply do not attach importance to the noticeable discomfort in the upper abdomen, which intensifies after a feast. The following signs may indicate the development of the disease:
- Nausea. Intensifies after drinking alcohol, fatty and fried foods. In severe cases, it is accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring relief.
- Pain. Aching or sharp pains are concentrated in the epigastric area, but can radiate under the scapula, behind the sternum or under the ribs.
- Problems with stool. This is either constipation or diarrhea, depending on the type of pathology and the prerequisites for its development. If there are visible food particles in the stool, this is not entirely normal.
- Belching and flatulence. Disruption of the digestive process leads to fermentation of food residues and accumulation of gases. Belching is accompanied by a feeling of unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Temperature. An increase in temperature is an obvious sign of an inflammatory process. In this case, you need to act immediately - call an ambulance.
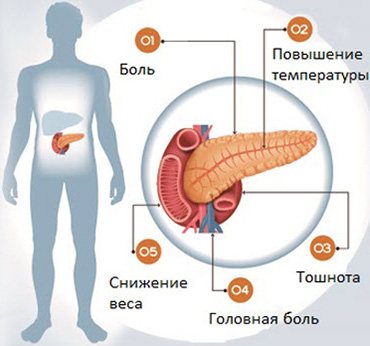
Such symptoms are a reason to immediately go to the hospital
With the development of complications, symptoms such as jaundice, blurred vision, and coordination disorders may occur. Weight also decreases noticeably and appetite disappears.
Important! Patient complaints and a superficial examination alone are not enough. Only after a comprehensive diagnosis of the pancreas has been made, treatment can be prescribed by your attending physician.
Laboratory research
After an examination by a doctor and a medical history, laboratory tests are prescribed. What tests need to be taken to examine the pancreas will be determined by the doctor, since their list depends on specific circumstances.
The following categories of such studies can be distinguished:
- Standard. Taking samples of blood, urine or stool for testing using standard routine parameters.
- With load. Consist of several stages. The baseline indicators are compared with the test results after the use of special substances.
- Special. Designed for the diagnosis of specific pathologies, they imply a special procedure for collecting and examining material.

Basic methods of laboratory diagnosis of the pancreas
Blood tests
The first thing prescribed for diseases of the pancreas is blood tests. Blood is taken from a finger and a vein for a complete examination. Of the general indicators, the number of leukocytes and neutrophils, as well as ESR, are of particular importance.
What tests are done for the pancreas? A biochemical blood test determines the following indicators:
- total and direct bilirubin;
- glucose;
- alpha amylase;
- lipase;
- trypsin.
The pancreas produces the most important substances: digestive enzymes and insulin for the breakdown of glucose. A decrease in enzyme synthesis leads to an inability to fully process and absorb nutrients, and an increase causes self-damage to the organ. Insulin is necessary for processing glucose, otherwise a person will face a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.

A blood test is a basic procedure in diagnosing any disease.
Important! It is necessary to donate blood on an empty stomach. The day before, it is not recommended to consume alcohol, sweet carbonated drinks, desserts and other foods that can distort the results.
Urine and stool examination
No less important are tests for the functioning of the pancreas, based on the study of urine and feces samples. They reflect the process of processing substances entering the body. It is best to submit material in the morning, especially for urine.
In the laboratory, urine samples are examined for biochemical indicators such as glucose, amylase and amino acids. In diseases of the pancreas, they are the ones that undergo the greatest changes.
Feces are examined to conduct a coprogram. External indicators are analyzed (consistency, color, presence of undigested food particles, etc.), as well as biochemical ones. The most important evaluation criteria are:
- the presence of dietary fiber and fiber;
- identification of digestive enzymes;
- amount of elastase;
- analysis of the hydrolysis process.
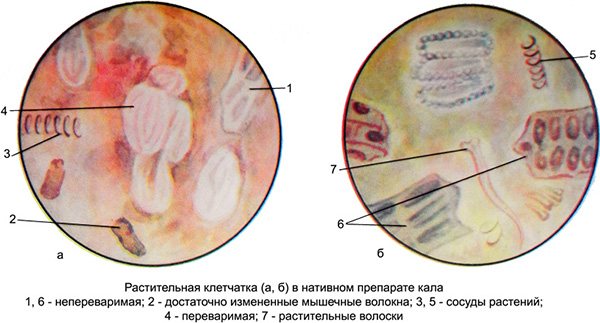
Laboratory tests can reveal the amount and type of fiber in stool
Other indicators
This is where the laboratory diagnosis of pancreatic diseases ends only if no significant deviations have been identified. If there are questionable results, additional tests are required to check the pancreas using stress tests.
The following research options are used:
- Glucose tolerance - blood is drawn at the beginning of the test, then the patient drinks a glucose concentrate, and the blood draw is repeated an hour later.
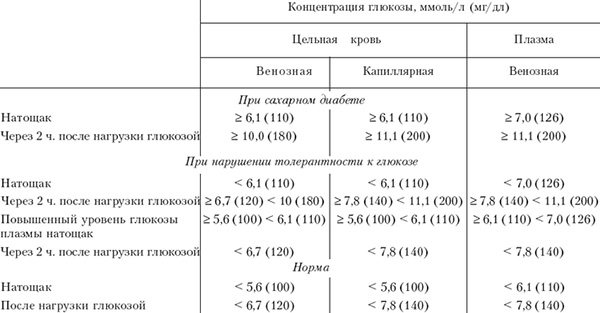
Glucose tolerance test results
- Diastase in urine - the initial level is measured, after the administration of proserin, samples are taken every half hour for 2 hours.
- Iodolipol test. The morning urine sample serves as a control. After taking iodolipol, regular measurements are taken within 2.5 hours to establish the iodide concentration.
- Antibodies to beta cells - detect autoimmune pathologies of insulin production.
- Enzymes in the duodenum. Base samples are also taken after the introduction of hydrochloric acid.
- Secretin-pancreasimin test. The production of amylase, trypsin and lipase is stimulated by the administration of secretin and cholecysto-pancreozymin; after this, the level of enzymes in the duodenum is compared with the initial level.
List of analyzes
A laboratory test to check the pancreas can be prescribed by a physician or gastroenterologist. During acute inflammation, pancreatic enzymes are activated. Some of them are clearly detected in urine, others in blood, and others in feces.
A comprehensive study of the patient's condition is as follows.
- First of all, you will have to take a classic set of samples: a general blood test, urine test, and the biochemical composition of the blood.
- To identify chronic problems, scatological tests are widely used for various diseases of the pancreas. The coprogram determines the concentration of hydrolysis products and corresponding enzymes in the feces.
- In order to scan the functioning of the glandular apparatus, a secretin-pancreozymin test is performed. It is carried out using a probe with sequential administration of secretin and cholecysto-pancreozymin.
- An iodolipol test is often performed. The patient drinks the drug, and after 2.5 hours the level of iodide in the urine is measured. This diagnosis of pancreatic diseases records the activity of the lipase enzyme synthesized by this organ.
- Glycoamylasemic test - the initial level of amylase in the blood is determined after taking 50 g of glucose. This enzyme test should record an increase in concentration from the original value by about a quarter.
- If it is necessary to determine the extent of pancreatic deformations, doctors will additionally examine the patient’s liver, since the functionality of these organs is largely intertwined.
How else is the pancreas checked? The interpretation of the obtained data is usually supplemented by methods of examining the pancreas using various instruments.
We also recommend viewing: Functions of pancreatic hormones
Hardware diagnostics
More information about the size and structural changes of internal organs can be obtained through hardware diagnostics. When examining the pancreas, the following methods are used:
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound waves are reflected from the gland tissue and converted into an image on the monitor. Changes in the level of echogenicity, the size of the organ and its contours, as well as the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity indicate the presence of pathology.
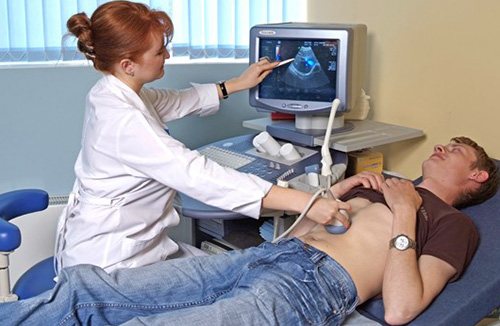
Ultrasound is a standard procedure for problems with the pancreas
- Endoscopic examination. Using an endoscopic probe, the condition of the tissues at the junction of the pancreatic and duodenal ducts is examined.
- ERCP. The method of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography allows us to examine the condition of the pancreatic ducts themselves.
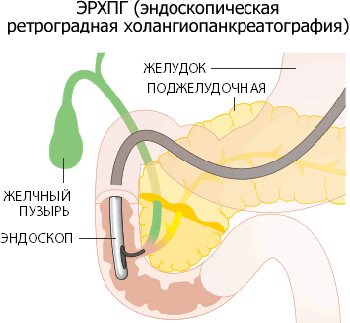
During ERCP there is a risk of organ damage due to insufficient qualifications of the diagnostician
- CT. Thanks to a CT scan of the pancreas, the structure of the organ is examined in detail, neoplasms and places of transformation of healthy tissue are identified.
- Endoultrasonography. It is used for a detailed study of the condition of the gland and its ducts, as well as the lymph nodes associated with it.
- Biopsy. If suspicious neoplasms are detected, tissue is collected using a fine-needle puncture for further histological examination. This allows you to detect oncology or ensure that the tumor is benign.
Important! Thanks to comprehensive diagnostics, it is possible to most accurately determine the type of pancreatic disease, as well as the possible causes of its development.
Based on the research results, a treatment program is drawn up, which may include diet and drug therapy using enzymes. In more severe cases, surgery is required to preserve less damaged areas of the gland.
source
Blood tests for the pancreas: which ones to take, CT diagnostics, urine test
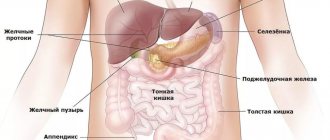
The functioning of the entire organism depends on the condition of this organ.
Deterioration of the pancreas does not always appear suddenly. Many people simply do not attach importance to the noticeable discomfort in the upper abdomen, which intensifies after a feast. The following signs may indicate the development of the disease:
- Nausea. Intensifies after drinking alcohol, fatty and fried foods. In severe cases, it is accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring relief.
- Pain. Aching or sharp pains are concentrated in the epigastric area, but can radiate under the scapula, behind the sternum or under the ribs.
- Problems with stool. This is either constipation or diarrhea, depending on the type of pathology and the prerequisites for its development. If there are visible food particles in the stool, this is not entirely normal.
- Belching and flatulence. Disruption of the digestive process leads to fermentation of food residues and accumulation of gases. Belching is accompanied by a feeling of unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Temperature. An increase in temperature is an obvious sign of an inflammatory process. In this case, you need to act immediately - call an ambulance.
Such symptoms are a reason to immediately go to the hospital
With the development of complications, symptoms such as jaundice, blurred vision, and coordination disorders may occur. Weight also decreases noticeably and appetite disappears.
Important! Patient complaints and a superficial examination alone are not enough. Only after a comprehensive diagnosis of the pancreas has been made, treatment can be prescribed by your attending physician.
Laboratory research
After an examination by a doctor and a medical history, laboratory tests are prescribed. What tests need to be taken to examine the pancreas will be determined by the doctor, since their list depends on specific circumstances.
The following categories of such studies can be distinguished:
- Standard. Taking samples of blood, urine or stool for testing using standard routine parameters.
- With load. Consist of several stages. The baseline indicators are compared with the test results after the use of special substances.
- Special. Designed for the diagnosis of specific pathologies, they imply a special procedure for collecting and examining material.
Basic methods of laboratory diagnosis of the pancreas
Urine and stool examination
No less important are tests for the functioning of the pancreas, based on the study of urine and feces samples. They reflect the process of processing substances entering the body. It is best to submit material in the morning, especially for urine.
In the laboratory, urine samples are examined for biochemical indicators such as glucose, amylase and amino acids. In diseases of the pancreas, they are the ones that undergo the greatest changes.
Feces are examined to conduct a coprogram. External indicators are analyzed (consistency, color, presence of undigested food particles, etc.), as well as biochemical ones. The most important evaluation criteria are:
- the presence of dietary fiber and fiber;
- identification of digestive enzymes;
- amount of elastase;
- analysis of the hydrolysis process.
Laboratory tests can reveal the amount and type of fiber in stool
Other indicators
This is where the laboratory diagnosis of pancreatic diseases ends only if no significant deviations have been identified. If there are questionable results, additional tests are required to check the pancreas using stress tests.
The following research options are used:
- Glucose tolerance - blood is drawn at the beginning of the test, then the patient drinks a glucose concentrate, and the blood draw is repeated an hour later.
Glucose tolerance test results
- Diastase in urine - the initial level is measured, after the administration of proserin, samples are taken every half hour for 2 hours.
- Iodolipol test. The morning urine sample serves as a control. After taking iodolipol, regular measurements are taken within 2.5 hours to establish the iodide concentration.
- Antibodies to beta cells - detect autoimmune pathologies of insulin production.
- Enzymes in the duodenum. Base samples are also taken after the introduction of hydrochloric acid.
- Secretin-pancreasimin test. The production of amylase, trypsin and lipase is stimulated by the administration of secretin and cholecysto-pancreozymin; after this, the level of enzymes in the duodenum is compared with the initial level.
Hardware diagnostics
More information about the size and structural changes of internal organs can be obtained through hardware diagnostics. When examining the pancreas, the following methods are used:
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound waves are reflected from the gland tissue and converted into an image on the monitor. Changes in the level of echogenicity, the size of the organ and its contours, as well as the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity indicate the presence of pathology.
Ultrasound is a standard procedure for problems with the pancreas
- Endoscopic examination. Using an endoscopic probe, the condition of the tissues at the junction of the pancreatic and duodenal ducts is examined.
- ERCP. The method of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography allows us to examine the condition of the pancreatic ducts themselves.
During ERCP there is a risk of organ damage due to insufficient qualifications of the diagnostician
- CT. Thanks to a CT scan of the pancreas, the structure of the organ is examined in detail, neoplasms and places of transformation of healthy tissue are identified.
- Endoultrasonography. It is used for a detailed study of the condition of the gland and its ducts, as well as the lymph nodes associated with it.
- Biopsy. If suspicious neoplasms are detected, tissue is collected using a fine-needle puncture for further histological examination. This allows you to detect oncology or ensure that the tumor is benign.
Important! Thanks to comprehensive diagnostics, it is possible to most accurately determine the type of pancreatic disease, as well as the possible causes of its development.
Based on the research results, a treatment program is drawn up, which may include diet and drug therapy using enzymes. In more severe cases, surgery is required to preserve less damaged areas of the gland.
Source: https://pozhelezam.ru/podzheludochnaya/analizy-krovi-na-podzheludochnuyu-zhelezu
How to properly examine the pancreas
Good day, dear friends.
The pancreas is an organ that regulates the entire digestive tract and controls blood sugar levels. A person cannot live without the pancreas! In this article I will tell you how to properly check the health of the pancreas, what tests you need to take and what examinations you need to undergo.
General blood analysis
Without this analysis, there is no point in coming to see a doctor of any specialty. A general blood test allows you to determine the presence of inflammation in the body.
Blood chemistry
Alpha amylase
- relevant for 2-3 days after suffering inflammation of the gland. The maximum level in the blood is in the first 24 hours.
Lipase
- maximum level - in the first 24 hours. Tracked in the blood for 8-10 days. An increase of 10 times is life-threatening.
Pancreatic elastase 1
- increases, but is studied much less frequently, since this analysis is more expensive. Shows previous inflammation of the pancreas. Relevant for 10 days after inflammation. The maximum level in the blood is on the second day.
C-reactive
protein
is important to check for any inflammatory diseases in the body. With pancreatitis, it can increase several times.
Total
protein
decreases in diseases of the pancreas.
Blood glucose
is a very important parameter that needs to be monitored in diseases of the pancreas . If the tail of the pancreas is inflamed or destroyed, blood sugar levels may increase. This indicates a serious lesion and the consequences of severe pancreatitis.
Tumor markers
Tumor markers are biomarkers (special substances) produced by tumor cells. There are more than a hundred of them, but only four are used to diagnose pancreatic cancer: CA-19-9 (the most specific), CA-125, CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen), CA-15-3. It is worth noting that an increase in tumor markers in the blood does not indicate the 100% presence of cancer in a specific location.
The above biomarkers are also increased in cancer of the liver, stomach, breast, colon and small intestine.
Coprogram and urine analysis
To check the condition of the pancreas, you should definitely take
urine and stool tests .
Digestive enzymes pass through the intestines, are absorbed into the blood and enter the kidneys, where urine is formed. in
urine
is determined. During serious inflammatory processes, alpha-amylase is detected not only in the blood, but also in the urine.
Coprogram.
This study should be carried out in chronic diseases with decreased production of digestive enzymes. Hyposecretion can be caused by blockage of the gland canal with a tumor or stone. If the secretion becomes insufficient, then food is poorly digested, the amount of feces increases, they become semi-liquid, with a greasy sheen and a rotten smell.
Instrumental diagnostic methods for studying the pancreas
Ultrasound diagnostics
– assessment of the structure of the gland, changes in size, assessment of the presence of neoplasms.
The channel has a detailed analysis of ultrasound diagnostics of pancreatic diseases. You can read it HERE
.
CT/MRI
– can be used with or without contrast. It is used only in difficult situations when it is necessary to evaluate the presence of effusion or when diagnosis cannot be made using ultrasound. These methods are not used in routine screening.
conclusions
If you want to check how your pancreas works, you need to take:
- General blood analysis
- Biochemical blood test: lipase, amylase, pancreatic elastase -1, glucose, C-reactive protein.
- To assess the structure and visualization - ultrasound examination.
I hope this article was useful to you. Good health to you. Did you like the article? Subscribe to the DOCTOR'S CONSPECT channel!
source
Types of pancreas tests
Now medicine offers more than 5 different methods for diagnosing pancreatic diseases. Studies of blood materials, tissues (tumor or suspected tumor), urine, etc. are used.
The doctor will tell you what tests you need to take. Usually, on the recommendation of a doctor, they do:
- biopsy studies, that is, taking tissue material;
- general or biochemical blood tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- coprogram.
Each method helps to identify certain diseases. Using these techniques, simple edema is separated from tumors, and pancreatitis is separated from cancer.
How is the pancreas checked?
Pancreatic disease is of serious importance to a person. Acute or chronic form of pancreatitis is currently not uncommon and the reason for this is:
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- improper and not entirely healthy consumption of food;
- incorrect dietary patterns for losing excess weight.
Diabetes mellitus and cancer also contribute to the occurrence of pathology. What is dangerous with pancreatitis is the occurrence of side problems during the acute phase of development, which lead to necrosis and death. Therefore, every person must know how to check the pancreas and prevent the development of the disease. After all, preventing the development of organ pathology is much easier than trying to cure it later.
General rules for preparing for analysis
To determine the disease, tests are taken, especially if pancreatitis is suspected. How to examine the pancreas and get the correct tests after diagnosing the body? This is a sensitive issue, since errors in collecting the required biomaterial will lead to some deviations and the prescription of incorrect treatment.
For the diagnostic procedure itself, general requirements have been developed, which include:
- Pancreatic tests are taken on an empty stomach, in the morning. In 1-2 days, stop eating salty, spicy, fatty foods, try to give up bad habits and alcohol, stop drinking carbonated water and legumes.
- To draw blood, stop smoking at least two hours in advance.
- If the patient has constipation, then it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with an enema and take enterosorbents (activated carbon and many others). After all, the accumulation of digested food has a toxic environment and will spoil the complete picture of the diagnosis of the body.
- All containers for test material are sterile, hands are washed with soap.
- For females, before donating urine, perform hygiene procedures with the genitals.
- When taking a general urine test, the middle part of the portion is taken.
The pancreas and its diagnosis require compliance with the general rules for collecting material for diagnosis. The correctness of the results obtained determines the clinical picture of treatment for pancreatitis or other complications of this disease.
In addition to diagnosing your health condition, there are symptoms that, together with the test data obtained, will confirm the disease pancreatitis:
- diarrhea;
- girdle pain;
- gagging;
- severe weakness in the body;
- sudden appearance of pain in the solar plexus and side of the stomach.
If such symptoms appear, urgently visit a medical facility and get tested for the pancreas and side diseases of pancreatitis. And also try to determine the disease yourself. It happens that it is not possible to visit a medical facility, therefore, based on the existing signs, you can understand at home that the pancreas hurts.
The acute phase of the disease mainly manifests itself after heavy consumption of alcohol or fatty foods, which gives impetus to the inflammatory process. In this case, a sharp girdling pain occurs, which extends to the back and intensifies when lying down. The pain will be dulled by lying on your side and tucking your knees under your stomach. In the acute phase of exacerbation, analgesics may not bring positive results.
Also, the condition of the affected person is aggravated by vomiting, bloating, and yellowed sclera of the eyes. In such a situation, self-medication is dangerous to health and requires urgent diagnosis. When you visit a doctor, he prescribes tests to get a complete picture of pancreatic disease, which will make it possible to correctly prescribe treatment.
In the chronic form of the disease, the symptoms differ slightly from the acute form of pancreatitis:
- gradual weight loss;
- periodic pain in the right and left hypochondrium;
- diarrhea with a strong odor and light-colored stool;
- vomiting with constant nausea;
- dry mouth;
- thirst;
- feeling of uncontrollable and constant hunger.
Without a medical education, a person can make an inaccurate diagnosis for himself. This will do you no good, so first of all, find a way to undergo diagnostic tests to identify damage to the pancreas.
What tests are there for pancreatitis and inflammation of the pancreas:
- General blood analysis.
- Biochemical blood test.
- Stool analysis.
Laboratory tests will help establish a diagnosis and determine the inflammatory process in the pancreas. The most important thing about them is the detection of the amount of enzymes in the blood. On the first day of exacerbation, they look at pancreatic amylase, on the second - the volumetric content of lipase and elastase.
What test should I take to check my pancreas?
Pancreatic disease is of serious importance to a person. Acute or chronic form of pancreatitis is currently not uncommon and the reason for this is:
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- improper and not entirely healthy consumption of food;
- incorrect dietary patterns for losing excess weight.
appointment with a gastroenterologist
Diabetes mellitus and cancer also contribute to the occurrence of pathology.
What is dangerous with pancreatitis is the occurrence of side problems during the acute phase of development, which lead to necrosis and death.
Therefore, every person must know how to check the pancreas and prevent the development of the disease. After all, preventing the development of organ pathology is much easier than trying to cure it later.
General rules for preparing for analysis
To determine the disease, tests are taken, especially if pancreatitis is suspected. How to examine the pancreas and get the correct tests after diagnosing the body? This is a sensitive issue, since errors in collecting the required biomaterial will lead to some deviations and the prescription of incorrect treatment.
For the diagnostic procedure itself, general requirements have been developed, which include:
- Pancreatic tests are taken on an empty stomach, in the morning. In 1-2 days, stop eating salty, spicy, fatty foods, try to give up bad habits and alcohol, stop drinking carbonated water and legumes.
- To draw blood, stop smoking at least two hours in advance.
- If the patient has constipation, then it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with an enema and take enterosorbents (activated carbon and many others). After all, the accumulation of digested food has a toxic environment and will spoil the complete picture of the diagnosis of the body.
- All containers for test material are sterile, hands are washed with soap.
- For females, before donating urine, perform hygiene procedures with the genitals.
- When taking a general urine test, the middle part of the portion is taken.
The pancreas and its diagnosis require compliance with the general rules for collecting material for diagnosis. The correctness of the results obtained determines the clinical picture of treatment for pancreatitis or other complications of this disease.
location of the pancreas
In addition to diagnosing your health condition, there are symptoms that, together with the test data obtained, will confirm the disease pancreatitis:
- diarrhea;
- girdle pain;
- gagging;
- severe weakness in the body;
- sudden appearance of pain in the solar plexus and side of the stomach.
If such symptoms appear, urgently visit a medical facility and get tested for the pancreas and side diseases of pancreatitis. And also try to determine the disease yourself. It happens that it is not possible to visit a medical facility, therefore, based on the existing signs, you can understand at home that the pancreas hurts.
manifestation of the acute phase after alcohol and fatty foods
The acute phase of the disease mainly manifests itself after heavy consumption of alcohol or fatty foods, which gives impetus to the inflammatory process. In this case, a sharp girdling pain occurs, which extends to the back and intensifies when lying down. The pain will be dulled by lying on your side and tucking your knees under your stomach. In the acute phase of exacerbation, analgesics may not bring positive results.
Also, the condition of the affected person is aggravated by vomiting, bloating, and yellowed sclera of the eyes. In such a situation, self-medication is dangerous to health and requires urgent diagnosis. When you visit a doctor, he prescribes tests to get a complete picture of pancreatic disease, which will make it possible to correctly prescribe treatment.
In the chronic form of the disease, the symptoms differ slightly from the acute form of pancreatitis:
- gradual weight loss;
- periodic pain in the right and left hypochondrium;
- diarrhea with a strong odor and light-colored stool;
- vomiting with constant nausea;
- dry mouth;
- thirst;
- feeling of uncontrollable and constant hunger.
Without a medical education, a person can make an inaccurate diagnosis for himself. This will do you no good, so first of all, find a way to undergo diagnostic tests to identify damage to the pancreas.
tests for pancreatitis and inflammation of the pancreas
What tests are there for pancreatitis and inflammation of the pancreas:
- General blood analysis.
- Biochemical blood test.
- Stool analysis.
Laboratory tests will help establish a diagnosis and determine the inflammatory process in the pancreas. The most important thing about them is the detection of the amount of enzymes in the blood. On the first day of exacerbation, they look at pancreatic amylase, on the second - the volumetric content of lipase and elastase.
Laboratory diagnostics
How to check the pancreas, what tests need to be done for this? Diagnosis of the pancreas is carried out by many methods and techniques. Among them there are diagnostic methods, these are laboratory tests and instrumental methods for diagnosing the pancreas.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D1SrX4QxYlw
Laboratory diagnosis of the pancreas is the control of enzymes and hormonal activity of the organ.
When suffering from pancreatitis, the outflow of digestive (pancreatic) juice from the organ into the duodenum is disrupted, which disrupts the activity of the gland.
Therefore, during inflammation, the accumulating juice reacts and enters the blood and lymphatic system of the body, which makes it possible to determine by analysis the full picture of damage to the organ and the body as a whole.
At the time of inflammation, the gland becomes damaged and disrupts the production of hormones and enzymes. A disruption in the production of enzymes and hormones provokes the occurrence of such pathologies that accompany this type of disease:
- diabetes;
- renal and liver failure;
- damage to the human lymphatic defense system;
- necrosis of tissues and organs;
- spleen damage.
If you define a disease by its symptoms, then an accurate diagnosis based on these symptoms is not possible and is subject to errors.
This is due to the fact that pancreatitis can be a secondary disease of other complex and no less serious diseases.
Therefore, diagnosing the disease with inflammation of the pancreas requires complete tests of blood, feces, and urine using instrumental methods.
The gland is an organ that produces enzymes and hormones that participate in the body's metabolism. Therefore, inflammatory processes in the pancreas lead to a malfunction of the digestive system and changes in the composition of blood, urine, and feces.
Blood tests
For pancreatitis, two types of blood tests are performed:
- clinical general;
- biochemical.
Clinical general, serves as an auxiliary to confirm other types of tests and is important in determining the disease.
What he will show the doctor:
- Firstly, the level and quantity of hemoglobin and red blood cells. If red blood cells are present in smaller quantities, this indicates blood loss, which confirms the progression of complications that caused inflammation of the organ.
- And also, if the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased, this is a sure sign of an inflammatory state in the body.
- Increase in leukocytes in the blood. This also serves as confirmation of the inflammatory process and possibly necrosis of the tissue of the gland organ.
- Increased hematocrit. This is an imbalance of blood and fluid (electrolytes).
A general blood test helps determine and confirm the presence of inflammatory processes in the pancreas.
A biochemical blood test shows a complete picture of the course of the disease and damage to the gland.
This analysis itself for pancreatic enzymes and hormones will show the following data:
- The amount of amylase is an enzyme for dissolving starch. It is the main pancreatic enzyme in the pancreas.
- The amount of glucose - in this case, the analysis shows that the production of insulin in the pancreas is insufficient.
- Elastase, lipase, phospholipase - the amount of these substances indicates a dysfunction of the pancreas.
- Transaminases - if an increased amount is detected, it indicates a change in the gland itself.
- Bilirubin is increased, indicating inflammation of the gland itself and blockage of the bile ducts.
- A reduced protein content will tell about the body’s starvation not only for protein foods, but also for energy shortage.
A biochemical blood test is detailed and according to it, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment and diagnosis of the disease and what type of developing pancreatitis is, chronic or acute.
blood chemistry
An inflamed pancreas requires two types of blood tests to determine the form of the disease - this gives a complete picture of the disease and an understanding of the progression of pancreatitis.
Analysis of urine
If inflammation of the pancreas is suspected, a urine test is prescribed. With pancreatitis, the patient's urine has an increased level of amylase. Diagnosis is carried out according to a general criterion:
- detection of leukocyte levels;
- squirrel;
- bilirubin;
- glucose;
- ESR.
They also look at the color and smell, the acidity of urea, which also serves as confirmation of the inflammatory process. Morning urine on an empty stomach is taken for analysis. Urine is placed in a special container. The procedure is carried out in compliance with hygienic rules, which will eliminate the risk of contamination of this diagnostic sample.
If necessary, monitoring of the amount of diastase is prescribed, so the analysis is carried out throughout the day with an interval of up to 2 hours.
Accordingly, urine analysis is also done biochemically. This will give a complete study of urine, determination of diastase in the urine, which indicates an inflammatory process.
urine collection using the Nechiparenko method
The Nechiporenko method is often used. Urine is passed through a special centrifuge, and the resulting sediment is carefully studied and a conclusion is made about the pathology of the kidneys, liver, and ureters, which are concomitant diseases of pancreatitis. A urine test for pancreatic enzymes is important and provides additional insight into the problem of the pancreas and associated diseases.
Hormone analysis
The production of hormones in the pancreas occurs in the pancreatic islets. These are cells that have capillary networks. The hormones produced by these islets improve the functioning of the digestive system. Hormones include:
The presence of hormones in the urine or blood indicates a strong inflammatory process in the body and pancreas. Therefore, an analysis of hormones for pancreatitis of the pancreas is important and shows the presence of concomitant diseases:
- diabetes;
- liver failure.
All these diseases, without their treatment, will not provide a successful fight against inflammation of the pancreas.
Coprogram
The appearance of pancreatic enzymes in the coprogram analysis indicates a severe malfunction of the pancreas. The pancreas and how to check its function? To do this, the doctor prescribes a coprogram diagnosis.
When diagnosing stool using this method, pay attention to the appearance and microscopic characteristic components. And also special attention is paid to color, shape, smell, possible blood discharge or undigested food.
general stool analysis (coprogram)
What a coprogram helps to identify:
- Disruption of the enzymatic functions of the pancreas.
- Malfunction of the intestines.
- Insufficient production of acid-forming substances in the stomach.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Malabsorption in the duodenum.
- Detects rapid evacuation of food from the stomach and intestines.
- Chronic diseases of all gastrointestinal organs.
MRI pancreas
Magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic method for visually identifying the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, liver, and spleen. With pancreatitis, the disease is difficult to detect, so this diagnostic method is of the highest quality, where the doctor can see with his own eyes the inflammation or enlargement of organs. MRI will allow you to quickly identify problems in the gastrointestinal tract and begin urgent treatment of the disease.
To begin the procedure, the victim removes metal objects and takes the required body position. The reason for prescribing the diagnostic procedure is severe girdling pain. A clear image of the organ gives the patient an immobilized state.
Despite the fact that MRI gives a clear picture of the internal organs, to check the condition of the pancreas, all tests are taken, since together there is a more pronounced understanding of the disease and the prescription of the correct treatment.
Source: https://mr-gergebil.ru/kakoj-analiz-sdat-chtoby-proverit-podzheludochnuju-zhelezu/
Laboratory diagnostics
How to check the pancreas, what tests need to be done for this? Diagnosis of the pancreas is carried out by many methods and techniques. Among them there are diagnostic methods, these are laboratory tests and instrumental methods for diagnosing the pancreas.
Laboratory diagnosis of the pancreas is the control of enzymes and hormonal activity of the organ. When suffering from pancreatitis, the outflow of digestive (pancreatic) juice from the organ into the duodenum is disrupted, which disrupts the activity of the gland. Therefore, during inflammation, the accumulating juice reacts and enters the blood and lymphatic system of the body, which makes it possible to determine by analysis the complete picture of damage to the organ and the body as a whole.
At the time of inflammation, the gland becomes damaged and disrupts the production of hormones and enzymes. A disruption in the production of enzymes and hormones provokes the occurrence of such pathologies that accompany this type of disease:
- diabetes;
- renal and liver failure;
- damage to the human lymphatic defense system;
- necrosis of tissues and organs;
- spleen damage.
If you define a disease by its symptoms, then an accurate diagnosis based on these symptoms is not possible and is subject to errors. This is due to the fact that pancreatitis can be a secondary disease of other complex and no less serious diseases. Therefore, diagnosing the disease with inflammation of the pancreas requires complete tests of blood, feces, and urine using instrumental methods.
The gland is an organ that produces enzymes and hormones that participate in the body's metabolism. Therefore, inflammatory processes in the pancreas lead to a malfunction of the digestive system and changes in the composition of blood, urine, and feces.
Blood tests
For pancreatitis, two types of blood tests are performed:
Clinical general, serves as an auxiliary to confirm other types of tests and is important in determining the disease.
- Firstly, the level and quantity of hemoglobin and red blood cells. If red blood cells are present in smaller quantities, this indicates blood loss, which confirms the progression of complications that caused inflammation of the organ.
- And also, if the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased, this is a sure sign of an inflammatory state in the body.
- Increase in leukocytes in the blood. This also serves as confirmation of the inflammatory process and possibly necrosis of the tissue of the gland organ.
- Increased hematocrit. This is an imbalance of blood and fluid (electrolytes).
A general blood test helps determine and confirm the presence of inflammatory processes in the pancreas.
A biochemical blood test shows a complete picture of the course of the disease and damage to the gland.
This analysis itself for pancreatic enzymes and hormones will show the following data:
- The amount of amylase is an enzyme for dissolving starch. It is the main pancreatic enzyme in the pancreas.
- The amount of glucose - in this case, the analysis shows that the production of insulin in the pancreas is insufficient.
- Elastase, lipase, phospholipase - the amount of these substances indicates a dysfunction of the pancreas.
- Transaminases - if an increased amount is detected, it indicates a change in the gland itself.
- Bilirubin is increased, indicating inflammation of the gland itself and blockage of the bile ducts.
- A reduced protein content will tell about the body’s starvation not only for protein foods, but also for energy shortage.
A biochemical blood test is detailed and according to it, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment and diagnosis of the disease and what type of developing pancreatitis is, chronic or acute.
An inflamed pancreas requires two types of blood tests to determine the form of the disease - this gives a complete picture of the disease and an understanding of the progression of pancreatitis.
Analysis of urine
If inflammation of the pancreas is suspected, a urine test is prescribed. With pancreatitis, the patient's urine has an increased level of amylase. Diagnosis is carried out according to a general criterion:
- detection of leukocyte levels;
- squirrel;
- bilirubin;
- glucose;
- ESR.
They also look at the color and smell, the acidity of urea, which also serves as confirmation of the inflammatory process. Morning urine on an empty stomach is taken for analysis. Urine is placed in a special container. The procedure is carried out in compliance with hygienic rules, which will eliminate the risk of contamination of this diagnostic sample.
If necessary, monitoring of the amount of diastase is prescribed, so the analysis is carried out throughout the day with an interval of up to 2 hours.
Accordingly, urine analysis is also done biochemically. This will give a complete study of urine, determination of diastase in the urine, which indicates an inflammatory process.
The Nechiporenko method is often used. Urine is passed through a special centrifuge, and the resulting sediment is carefully studied and a conclusion is made about the pathology of the kidneys, liver, and ureters, which are concomitant diseases of pancreatitis. A urine test for pancreatic enzymes is important and provides additional insight into the problem of the pancreas and associated diseases.
Hormone analysis
The production of hormones in the pancreas occurs in the pancreatic islets. These are cells that have capillary networks. The hormones produced by these islets improve the functioning of the digestive system. Hormones include:
The presence of hormones in the urine or blood indicates a strong inflammatory process in the body and pancreas. Therefore, an analysis of hormones for pancreatitis of the pancreas is important and shows the presence of concomitant diseases:
- diabetes;
- liver failure.
All these diseases, without their treatment, will not provide a successful fight against inflammation of the pancreas.
Coprogram
The appearance of pancreatic enzymes in the coprogram analysis indicates a severe malfunction of the pancreas. The pancreas and how to check its function? To do this, the doctor prescribes a coprogram diagnosis. When diagnosing stool using this method, pay attention to the appearance and microscopic characteristic components. And also special attention is paid to color, shape, smell, possible blood discharge or undigested food.
What a coprogram helps to identify:
- Disruption of the enzymatic functions of the pancreas.
- Malfunction of the intestines.
- Insufficient production of acid-forming substances in the stomach.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Malabsorption in the duodenum.
- Detects rapid evacuation of food from the stomach and intestines.
- Chronic diseases of all gastrointestinal organs.
Detailed laboratory examination of the pancreas
[40-485] Detailed laboratory examination of the pancreas RUB 2,230.
A comprehensive blood test that allows you to identify the main disorders of various etiologies in the functional state of the pancreas.
The research results are provided with a free doctor’s commentary.
English synonyms
Pancreatic panel.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet for 24 hours before the test.
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test; you can drink clean still water.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress for 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 3 hours before the test.
General information about the study
The pancreas is an organ of the gastrointestinal tract located behind the stomach and performs important exocrine and endocrine functions. Digestion of proteins and fats in the small intestine is carried out due to the synthesis and secretion of digestive enzymes by the exocrine part of the gland.
In addition to proteo- and lipolytic enzymes, it releases bicarbonates, neutralizing the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice in the duodenum.
The endocrine function of the pancreas is provided by islet tissue, in which the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide are synthesized and then secreted into the blood. Insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose levels and its transport in tissues.
Pathology of the pancreas primarily leads to digestive disorders, and in chronic diseases contributes to the development of endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus).
The causes of pancreatic diseases are different: genetic and autoimmune disorders, infections (usually viral), injuries, toxic lesions, taking certain medications (estrogens, furosemide, azathioprine, etc.), neoplasms.
Most often, pathology of the pancreas occurs against the background of liver dysfunction, diseases of the biliary tract (cholelithiasis with choledocholithiasis), due to impaired outflow of bile and pancreatic juice.
Another common cause of pancreatic diseases is alcohol abuse.
Clinical manifestations of pancreatic diseases depend on the etiology, degree of dysfunction and activity of the process.
Acute inflammatory changes, trauma to the gland, as well as chronic diseases during exacerbation in most cases are accompanied by pain and burning in the epigastric region with irradiation to the back, nausea, vomiting, and increased body temperature.
Chronic diseases of the pancreas lead to pancreatic insufficiency, weight loss, and the development of ascites due to impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients from the intestine.
An increase in the activity of pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase) and the level of C-reactive protein in the blood are signs of active inflammation of the organ - acute pancreatitis.
Changes in the level of glucose and C-peptide indicate a violation of the endocrine function of the pancreas and are an indirect sign of damage to pancreatic islet tissue, which can occur with chronic pancreatitis.
A sharp increase in the tumor marker CA 19-9 against the background of changes in biochemical indicators of gland function most often indicates pancreatic cancer.
An increase in the concentration of amylase and lipase enzymes indicates the simultaneous involvement of the liver and pancreas in the pathological process, which usually occurs with a common bile duct stone and reactive pancreatitis.
If the indicators of this complex analysis change, it is necessary to perform additional laboratory and instrumental studies to clarify the causes and mechanisms of the development of the disease and select therapy.
What is the research used for?
- To assess the functional state of the pancreas and the severity of damage;
- for differential diagnosis of pancreatic diseases;
- to monitor a patient with chronic diseases of the hepatopancreabiliary zone (cholelithiasis, cholelithiasis, chronic pancreatitis);
- to monitor the effectiveness of treatment of pancreatic diseases.
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of possible damage to the pancreas (girdling pain and/or burning in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, change in color, quantity and consistency of stool);
- when the structure and size of the pancreas changes according to instrumental research methods;
- when examining persons who abuse alcohol;
- if there is a family history of pancreatic diseases;
- when monitoring patients with chronic diseases of the liver, pancreas and biliary tract;
- during a preventive examination.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
C-peptide: 0.9 – 7.1 ng/ml.
Plasma glucose
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 3 years | 3.3 – 5.5 mmol/l |
| 3 – 16 years | 3.3 – 5.5 mmol/l |
| More than 16 years | 4.1 – 5.9 mmol/l |
Lipase
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 year | 0 – 8 IU/l |
| 1 – 10 years | 5 – 31 IU/l |
| 10 – 18 years | 7 – 39 IU/l |
| Over 18 years old | 21 – 67 IU/l |
Total amylase in serum: 28 – 100 U/l.
CA 19-9: 0 – 35 U/ml.
Serum total amylase
Reasons for the increase:
- Acute or reactive pancreatitis
- Pancreas cancer
- Alcoholism
- Biliary obstruction (cholelithiasis)
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Inflammation of the salivary glands
- Parotitis
- Perforation of a stomach or intestinal ulcer
- Peritonitis
- Pregnancy
Reasons for the downgrade:
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Hepatitis
- Cystic fibrosis
- Severe burns
- Severe thyrotoxicosis
Lipase
Reasons for the increase:
- Acute pancreatitis
- Chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic trauma or cancer, pancreatic duct obstruction
- Cholecystitis
- Hemodialysis
- Peritonitis
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Strangulated intestinal obstruction, intestinal infarction
- Chronic renal failure
Reasons for the downgrade:
- Decreased thyroid function
- Cystic fibrosis
Plasma glucose
Reasons for the increase:
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, Cushing's syndrome, hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, pheochromocytoma, pituitary adenoma, glucagonoma)
- Acute emotional or physical stress
- Obesity
- Hemochromatosis
- Acute or chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer
- Chronic kidney disease
- Pregnancy
Reasons for the downgrade:
- Alcoholic liver disease, liver toxicity, liver necrosis, cirrhosis, liver failure
- Insulinoma
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Malabsorption
- Starvation
- Overdose of insulin drugs
- Physical stress, intense physical activity
C-peptide
Reasons for the increase:
Reasons for the downgrade:
CA 19-9
Reasons for the increase:
- Pancreatic cancer (significant increase)
- Lung cancer (significant increase)
- Gallbladder cancer (significant increase)
- Colorectal cancer (moderate increase)
- Stomach cancer (moderate increase)
- Cholecystitis (slight increase)
- Cholelithiasis
- Liver pathology, cirrhosis
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis)
- Pancreatitis
What can influence the result?
Factors distorting the result:
- study with intravenous administration of a contrast agent 24 hours before the study;
- pregnancy;
- concomitant pathology (diseases of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, malignant neoplasms or acute inflammation of other localizations, endocrine pathology, blood diseases);
- infectious mononucleosis, adenovirus infection, mumps and other acute infections affecting the pancreas;
- taking medications that affect certain test indicators.
Important Notes
- Considering the fact that each individual biochemical indicator of the study is not a strictly specific marker of pancreatic function, changes identified by the analysis require the exclusion of possible pathology of other organs and systems, as well as clarification of the etiology of the pathological process.
- Test results should be analyzed taking into account clinical symptoms, disease duration and comorbidities. When interpreting them, a careful differential diagnosis is necessary, which is carried out by a qualified physician. Sometimes instrumental studies (ultrasound, CT scan of the abdominal cavity) can be used.
Also recommended
Who orders the study?
Gastroenterologist, therapist, general practitioner.
Literature
- Nazarenko G.I., Kishkun A. Clinical assessment of laboratory research results. – M.: Medicine, 2000. – 533 p.
- Fischbach FT, Dunning MB A Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests, 8th Ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2008: 1344 p.
- Wilson D. McGraw-Hill Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests 1st Ed. Normal, Illinois, 2007: 666 p.
Source: https://helix.ru/kb/item/40-485
MRI of the pancreas
Magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic method for visually identifying the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, liver, and spleen. With pancreatitis, the disease is difficult to detect, so this diagnostic method is of the highest quality, where the doctor can see with his own eyes the inflammation or enlargement of organs. MRI will allow you to quickly identify problems in the gastrointestinal tract and begin urgent treatment of the disease.
To begin the procedure, the victim removes metal objects and takes the required body position. The reason for prescribing the diagnostic procedure is severe girdling pain. A clear image of the organ gives the patient an immobilized state.
Despite the fact that MRI gives a clear picture of the internal organs, to check the condition of the pancreas, all tests are taken, since together there is a more pronounced understanding of the disease and the prescription of the correct treatment.
source