Reasons for the development of pancreatitis
The main cause of the disease in men is alcohol abuse and smoking. These bad habits have the most negative effect on the cellular structure of the gland. Additional factors can provoke the pathological process, such as:
- errors in diet;
- urolithiasis and cholelithiasis;
- diseases of viral, fungal or infectious origin;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- frequent stress;
- genetic predisposition.
Any of these reasons or a combination of them can cause symptoms of the disease, which can be acute or chronic.
First symptoms of the disease
The clinical symptoms of the disease in adult men and women are not particularly different. The course of pancreatitis depends on the stage of the inflammatory process, its form, cause and degree of damage to the gland.
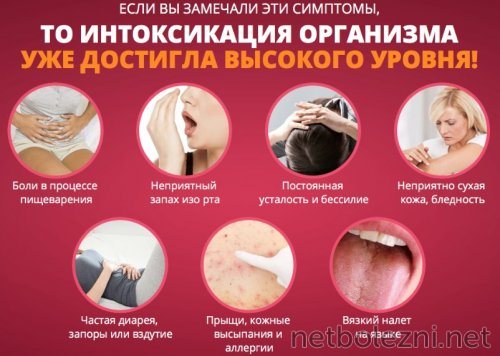
- abdominal pain
- their occurrence is associated with errors in diet, heavy physical labor or consumption of alcoholic beverages.
The localization of pain depends on the area of the gland affected. If the pathological process is located in the head of the organ, pain will be felt in the right hypochondrium, in the body of the gland - in the epigastric region, in the tail of the organ - in the left hypochondrium. Often the pain syndrome is girdling in nature, with pain radiating to the lower back: - stool disorder
- there is a change in the nature of the stool, which becomes liquid or mushy with a shiny surface from undigested fat;
- dyspepsia
- nausea, vomiting after eating; - phenomena of intoxication
- weakness, malaise, fever to subfebrile levels.
The appearance of the first symptoms of pancreatic disease in men due to alcohol consumption is often not a reason to visit a doctor. Lack of medical care leads to worsening inflammation and increased clinical symptoms with each attack.
Causes of pancreatic swelling
Swelling of the pancreas is evidence of the development of acute pancreatitis in a mild version of its course. Occurs in 80-85% of cases. Develops with excessive alcohol consumption, reflux of bile into the biliary ducts, injuries, autoimmune processes, acute infectious diseases, use of toxic drugs and chemicals. In some cases it occurs for no apparent reason.
The swelling is inflammatory in nature and is the result of damage to the pancreas tissue by its own enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin). It also develops with pancreatic necrosis, but here the first place is taken by deep damage to the glandular tissue with its death. The enzymes of the gland digest it itself. The accumulation of fluid during edema is diffuse, spreading over the entire area of the organ. Proliferation of liquid fractions occurs due to changes in vascular permeability against the background of the inflammatory process.

Separately, the peripancreatic infiltrate that occurs as a consequence of acute pancreatitis (in phase IB) should be considered. In this case, fluid accumulates both in the tissues of the gland itself and near it. The infiltrate does not have walls of fibrous tissue, is located freely, and can transform into a cyst or pseudocyst.
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by an inflammatory process and necrosis, which leads to diffuse and destructive changes in the pancreas. They provoke the occurrence of certain symptoms.
The most common cause of the development of an acute process in men is cholelithiasis, when the bile duct is blocked.
Gastric juice and bile begin to flow back into the pancreas, as a result of which the functioning of the organ stops and the gland begins to decompose its own tissues. A characteristic sign of acute pancreatitis is Mondor's triad, which manifests itself:
- bloating;
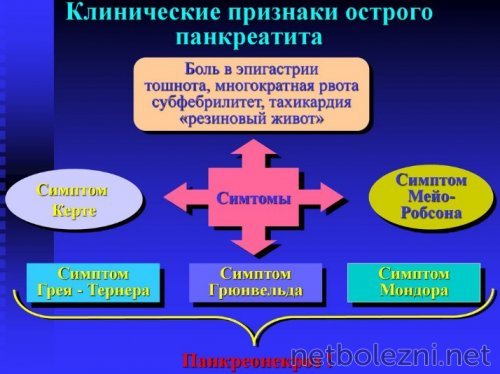
- pain;
- vomiting.
The pain occurs suddenly and is very intense, even to the point of loss of consciousness. During an attack, the patient rushes about, unable to find a position that would alleviate his condition. There is repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief, but causes dehydration.
During the attack, the bloating of the abdomen progresses and there is a feeling that it “will burst just a little longer.” The character of the stool changes. The stool becomes liquid and foamy with particles of undigested food. The condition quickly worsens, and the following symptoms of general intoxication and a drop in cardiac activity appear:
- tachycardia;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- profuse cold sweat;
- pale skin;
- decreased body temperature;
- lethargy;
- the appearance of hemorrhagic spots on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall in the projection of the pancreas (pancreatic necrosis or severe acute pancreatitis).
This condition requires emergency medical care in a surgical hospital. If assistance is not provided or is provided incompletely, death is possible.
Nature of pain in acute pancreatitis
Pain syndrome, in the acute course of the process, is often localized in the upper abdomen and has a girdling character. The pain is burning, sharp and scalding. But the pain syndrome can shift behind the sternum, to the area of the left hypochondrium, radiating to the left arm, scapula, and lower jaw.

Such symptoms of acute pancreatitis can simulate an attack of angina. Taking heart medications does not relieve this pain, suggesting another etiology for the pain.
Clinic of the disease
The main symptom by which the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis of “pancreatic pseudocyst” is severe pain in the epigastric zone. Its manifestations are most intense in the initial period, when there is massive destruction of gland cells under the influence of pancreatic enzymes, and severe tissue swelling is observed.
Gradually, the intensity of the pain subsides, its format changes - instead of sharp attacks that cannot be eliminated by non-steroidal analgesics, it becomes dull and oppressive.
At the third stage, the pain syndrome is replaced by a constant feeling of discomfort, interspersed with periods of exacerbation during compression of the ducts by the cyst. There is a feeling of a lump in the throat.
A sharp attack of pain may indicate a rupture of the formation, the development of pyogenic microflora in it, as well as other complications.
Localization of pain helps to establish the location of the false cyst:
- if the head of the pancreas is affected - the right hypochondrium;
- if the body and tail are affected - the left hypochondrium or solar plexus area.
Pain may increase with physical activity, sudden bending or turning of the body, or squeezing the area with tight clothing or a belt. The symptom is eliminated by slightly tilting the body forward.
Important! Cases are recorded when cysts, the diameter of which does not exceed 5 cm, do not exert pressure on the adjacent internal organs and nerve fibers, thereby not showing their presence in any way. Ultrasound, MRI or computer diagnostics help to detect them.

Pain in the epigastric region and constant nausea are the main signs of false cysts in the pancreas
Other signs of the development of cystic formations include:
- nausea;
- persistent loss of appetite;
- diarrhea alternating with flatulence and constipation;
- vomit;
- severe weakness.
Important! A characteristic symptom of the disease is the lack of relief after an attack of vomiting.
An increase in general body temperature indicates infection of the cystic formation.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis
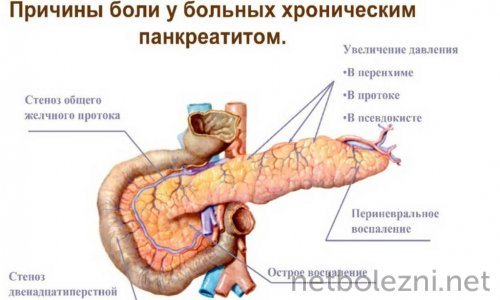
In the chronic course of the pathological process, the blood supply and nutrition of the cellular structures of the gland are disrupted, which entails their replacement with connective tissue. As a result, organ function is impaired, that is, enzymes and hormones are not produced by the pancreas in sufficient quantities.
Symptoms of pancreatitis of the pancreas in men in its chronic form appear as in the acute process, but not as intense. The pain syndrome is less pronounced and appears most often with errors in the diet.
Eating large amounts of fatty or fried foods, sweet carbonated water or alcohol provokes an attack of pancreatitis.
Periods of remission may be asymptomatic.
But if frequent exacerbations of the disease occur in men, then the following symptoms of chronic pancreatitis develop:
- discomfort, manifested by abdominal pain and mainly after eating;
- bloating;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of intermittent constipation and diarrhea with changes in the color and consistency of stool;
- the appearance of yellowness of the sclera and skin;
- weight loss due to impaired digestive function of the pancreas;
- decreased appetite;
- the appearance of pale and dry skin, brittle nails, hair loss due to vitamin deficiency;

- general weakness, loss of strength;
- development of asthenia with sleep disturbances, periodic headaches, irritability;
- the appearance of diabetes mellitus due to disruption of the hormonal function of the pancreas.
An increase in the symptoms of the disease forces a man to see a doctor and undergo examination by a gastroenterologist.
The nature of pain in chronic pancreatitis
In chronic pancreatitis, the nature of the pain can vary and be felt as:
- aching;
- Pulling;
- piercing;
- drilling;
- stupid.
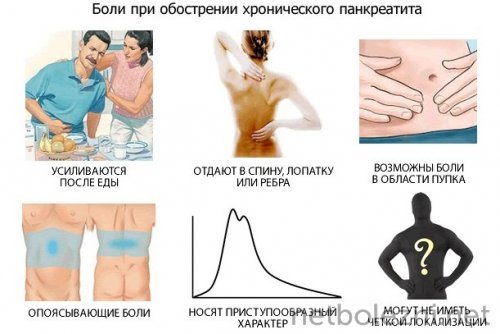
This pain can last for several hours. If it is not stopped and therapy to relieve inflammation is not started, the pathological process can cause serious complications that can lead to irreversible processes in the pancreas and the practical cessation of its functioning.
What is fluid in the pancreas?
The accumulation of fluid in the pancreas indicates the development of an organ cyst. Development occurs against the background of tumors, parasitic infestations, and traumatic injuries. The cyst itself is a limited cavity filled with serous or hemorrhagic contents. On ultrasound it is defined as an anechoic formation with clear edges. There are true and pseudocysts. The inner surface of a true type cyst is lined with epithelium from the inside, while a false one is represented by a dense fibrous capsule.
According to the duration of their course, cysts are divided into acute (up to 3 months from the moment of formation), subacute (3-6 months) and chronic (more than six months). According to the flow they can be simple and complicated. In the latter case, there is suppuration of the contents, perforation of the cystic wall or its degeneration with the acquisition of the properties of a malignant tumor.
Clinically, the disease is manifested by dull pain in the epigastric region and dyspeptic symptoms. It is difficult to detect by palpation, since the pancreas is covered by the stomach. The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, existing predisposing diseases, ultrasound data, computed tomography, and radiographic examination. Treatment is surgical, carried out by opening or total removal of the cyst. In case of malignancy of the lesion, subtotal resection of the pancreas is performed in accordance with the principles of oncological therapy.
Complications of pancreatic inflammation
Late seeking medical help when symptoms of pancreatitis appear can lead to serious consequences and a threat to life. An untreated process provokes complications of the disease in the form of:
- pancreatic necrosis;
- formation of abscesses;
- peritonitis, with subsequent development of sepsis;
- internal bleeding;
- gland cancer.
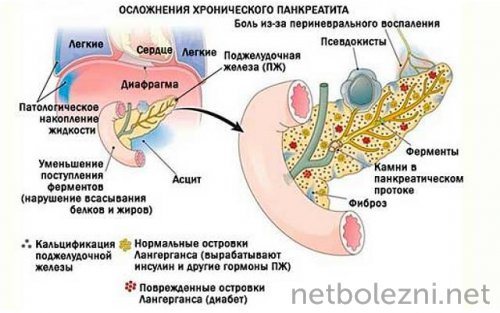
The development of any of these conditions requires surgical intervention, in the form of removal of part of the organ or the entire pancreas.
Causes and process of formation of cystic lesions
One of the main reasons contributing to the development of cystic lesions of the pancreas is the presence of acute or chronic pancreatic pathology. In acute pancreatic inflammation of a parenchymal organ, the development of a cyst occurs in approximately 18-20% of cases, and in the chronic form of pancreatitis, a complication in the form of cyst development occurs in 45-75%. The main etiological factor, in most cases, is pancreatitis due to alcohol intoxication of the body.
In more rare cases, cyst formation may occur due to the following factors:
- receiving trauma to the epigastric region of the abdomen,
- development of pathological dysfunction of the gallbladder and bile ducts,
- exacerbation of a chronic form of obstructive pancreatic pathology with impaired patency of the Wirsung duct,
- tumor in the area of localization of the duodenal nipple and sphincter of Oddi,
- infestation by individual representatives of helminths.
The modern society of leading surgical specialists has identified 5 main reasons contributing to the development of cystic lesions of a parenchymal organ:
- Excessive consumption of high-strength alcohol-containing products accounts for 63% of all cases with damage to the pancreas, leading to the development of cystic formation.
- The development of diabetes mellitus, which has the second type of progression, was 14%.
- Pathological changes in metabolic processes in the body, in combination with the predominance of a large number of extra pounds - 32%.
- Consequences of surgical interventions on any part of the pancreas.
Let us consider in more detail the process of formation of cystic lesions of a parenchymal organ in the presence of pancreatic pathology. When the tissue structures of the gland are damaged, a local accumulation of lymphocytes and neutrophils occurs along with the development of a destructive and inflammatory process. But, the affected area of the gland is separated from the entire parenchyma located around it. There is an intensive spread of connective tissues and the formation of granulations, through which the gradual destruction of tissue elements in the center of the lesion by cells of the immune defense system occurs, which leads to the formation of a cyst cavity.
When a cystic lesion of the pancreas communicates with its ductal system, an accumulation of pancreatic juice, inflammatory exudates, as well as necrotic elements of tissue structures can occur in the formed cystic cavity. If the blood vessels are damaged, then fluid in the form of blood accumulates in the cavity of the developing cyst.
If the passage of the common pancreatic duct of a parenchymal organ is disrupted, a cystic formation with an epithelial lining occurs, in the cavity of which there is an accumulation of pancreatic juice. Their pathogenetic mechanism of formation is based on the process of intraductal hypertension. There is scientific evidence that the internal pressure of the cystic cavity is three times higher than the natural level of internal pressure in the ducts of the gland.
Diagnosis of pancreatitis
A doctor can help diagnose pancreatitis not only by collecting an anamnesis, the man’s complaints and objective data. Additionally, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out, including:
- blood for general analysis, amylase;
- urine for amylase (diastase);
- biochemical blood test to determine enzymes;
- Ultrasound, MRI.

After the diagnosis is made, treatment for pancreatitis is prescribed, which, depending on the form of the disease, has distinctive features.
Symptomatic manifestations
Symptoms of progression of cystic lesions of the pancreas can be completely different depending on the provoking factor, the area of localization, as well as the external parameters and size of the cyst.
Very often there are cases when the development of a pancreatic cyst does not contribute to the manifestation of any symptomatic sign, since formations having a diameter not exceeding 5.5 centimeters do not come into contact with nearby internal organs and do not put pressure on nerve fibers, so no discomfort in the patient.
When a cyst acquires a large size, the main sign of its presence is intense pain in the epigastric area.
The greatest intensity of the painful manifestation is the symptomatic sign of the development of a false cyst against the background of an acute pancreatic disease or an acute stage of a chronic pathology of an inflammatory nature, as destructive changes occur in the parenchymal organ. Over time, the activity of painful manifestations subsides, the pain syndrome acquires a dull character of manifestation, and only a feeling of slight discomfort may remain.
In some cases, against the background of mild symptomatic manifestations, attacks of pain caused by intraductal hypertension may develop. The appearance of sharp, severe pain may indicate a breakthrough of the cystic formation. The gradual nature of the increase in pain against the background of elevated body temperature and signs of intoxication of the body may indicate suppuration of the cyst.
Significant differences in the symptomatic signs of cystic lesions of a parenchymal organ appear in cases of compression of the solar plexus. There is a manifestation of severe burning pain with gradual irradiation to the back area, with an increase in the intensity of the manifestation even from tight clothing. The knee-elbow position will help alleviate the patient’s condition, and pain manifestations are treated with narcotic analgesics.
Symptomatic signs of this pathology may include the following:
- feeling of nausea,
- discharge of vomit,
- weakness throughout the body
- loss of consciousness
- dryness of the mucous surfaces of the oral cavity
- increased urge to urinate and number of bladder bowel movements,
- possible loss of consciousness,
- development of diarrhea or constipation.

The progressive stage of the cyst can contribute to the occurrence of compression syndrome of nearby organs.
Treatment of pancreatitis
Therapeutic measures for the disease depend on its form. Therapy of acute pancreatitis and its chronic form in the acute stage is carried out in a hospital setting.
The main task of the doctor is to relieve acute pain and provide drug treatment to relieve inflammation.
Acute symptoms of the disease include hunger, rest and cold in the abdominal area for several days. For severe complications of pancreatitis, surgical treatment is indicated.

Drug therapy
To stop the pathological process, the following groups of medications are prescribed:
- antispasmodics - to relieve pain;
- drugs containing enzymes - only during remission;
- H2 receptor blockers - to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid in order to ensure rest of the pancreas;
- antacids - to lower the pH of gastric juice and form a protective film on the gastric mucosa;
- broad-spectrum antibiotics - to relieve inflammation and further progression of the pathological process;
- antiemetic drugs - to prevent fluid loss from the body and relieve discomfort to the patient;

- choleretic drugs - for better outflow of bile and only during remission;
- anticholinergics - to reduce the enzymatic activity of the gland and relieve pain.
Medicines are taken strictly on the recommendation of a gastroenterologist, taking into account the form, activity of the pathological process and the general well-being of the man. Self-administration of antispasmodics and other medications is not allowed due to the seriousness of the disease and the danger of its progression.
Folk remedies for treating pancreatitis
During the period of remission of pancreatitis, treatment with traditional medicine, which includes decoctions and infusions of various herbs, has a good effect. These natural medicines have a positive effect on the digestive system, relieving flatulence, heaviness and pain in the abdomen, and stool upset.
Herbal preparations for the treatment of the pancreas can be purchased at the pharmacy or prepared at home. A positive effect is observed when consuming the following herbal infusions:
- A mixture of peppermint leaves, motherwort and St. John's wort is prepared in a 1:1:1 ratio. Herbal raw materials in the amount of 1 tbsp. l. placed in a thermos and poured 200 ml of boiling water, followed by infusion for 2 hours. After straining, take ¼ cup 3 times a day;

- A mixture of calendula flowers, marsh cudweed leaves, yarrow and peppermint in equal proportions is prepared. 1 tbsp. l. The mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and infused for 2 hours. Take ½ glass 2 times a day before meals.
A good effect in the treatment of pancreatitis is observed when consuming oat jelly or freshly squeezed potato juice. They are prepared according to the following recipe:
- washed oats are poured with water and left for 24 hours, after which they are dried and ground in a blender to form flour, which is then diluted with water. Next, the mixture is boiled for 5 minutes, after which it is infused for another 30 minutes. After cooling and straining, the jelly is ready for use, treatment of which is carried out only in freshly prepared form;
- 2-3 tubers of peeled potatoes are grated on a fine grater. The resulting pulp is squeezed through gauze. You can also extract juice using a juicer. Take half a glass of juice 3 times a day. Each portion of it is consumed only fresh. Storing juice in the refrigerator is not allowed.

Propolis, which is rich in microelements, vitamins, and flavonoids, has a positive effect on the pancreas. Its use stimulates tissue regeneration and leads to the restoration of damaged cellular structure.
Propolis is used in its natural form in small pieces by resorption.
Treatment of pancreatitis in men with folk remedies should only be carried out as prescribed by a doctor. The gastroenterologist will give recommendations on the selection of the type of herbs, their dosage, and the duration of the course of treatment.
Diagnosis of ascites
The presence of pancreatogenic ascites in patients is determined by a number of studies. These include:
- Taking an anamnesis based on the patient’s complaints and the presence of any diseases;
- X-ray and ultrasound of the pancreas;
- Examination of the patient.
Examinations help determine the volume of accumulated fluid and determine the cause of the current situation. Also, with local anesthesia, laparocentesis is performed.
A special instrument is used to pierce the patient's abdominal wall and remove part of the fluid. It is sent to the laboratory, where the percentage of leukocytes, neutrophils, protein levels, glucose, and certain enzymes are determined. In addition, the liquid is examined for the presence of microorganisms, tumor cells, and tubercle bacilli.
Expert opinion
Guseva Yulia Alexandrova
Specialized endocrinologist
Laparocentesis is performed quickly and significantly alleviates the condition of people suffering from ascites.
Diet for pancreatitis
Dietary nutrition for pancreatitis is the basis for restoring pancreatic function. Treatment table No. 5p according to Pevzner is recommended after acute pain subsides and fasting for 3 days. With the help of dietary nutrition, goals are determined that can be achieved by:
- normalize the secretory function of the pancreas;
- reduce congestion in the duodenum;

- reduce excitability of the gallbladder;
- reduce the load on the intestines;
- prevent pathological degeneration of the cellular structures of the pancreas.
Diet is an integral part of the treatment process for pancreatitis. Dietary nutrition requires strict adherence to certain food rules, such as:
- meals should be fractional, every 2-3 hours in small portions;
- the volume of 1 serving of food per meal should not exceed 250 g;
- food is consumed warm;
- Food is steamed without salt and taken pureed.

Compliance with nutritional rules must be constant. How a man adheres to them determines his recovery after an exacerbation of the disease and the duration of remission. Table No. 5p suggests a list of foods that can be consumed by a man with pancreatitis:
- “yesterday’s” white bread made from premium flour;
- rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, semolina porridge, cooked in water;
- vegetable puree soups with pureed cereals;
- dietary varieties of chicken, turkey, rabbit;
- low-fat varieties of sea fish;
- soft-boiled or steamed eggs;
- low-fat dairy products (kefir, fermented baked milk, sour cream, cottage cheese);
- pureed boiled vegetables;
- fruit jelly, compotes, mousses;
- weak black or green tea, rosehip infusion, chamomile infusion, freshly squeezed juices diluted half with water.

The following products are prohibited for pancreatitis:
- fresh white and rye bread;
- confectionery and flour products;
- legumes;
- rich meat broths;
- fatty beef, lamb, pork;
- animal fats;
- cabbage, eggplant, onion, garlic;
- fresh fruits in their natural form;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- chocolate, coffee, cocoa, ice cream, any jam.

Such restrictions in the choice of foods in the diet prevent stress on the pancreas and its irritation. The diet must be followed by a man constantly. Its gradual expansion is possible only on the recommendation of a doctor and in stable remission of the disease, confirmed by laboratory tests.
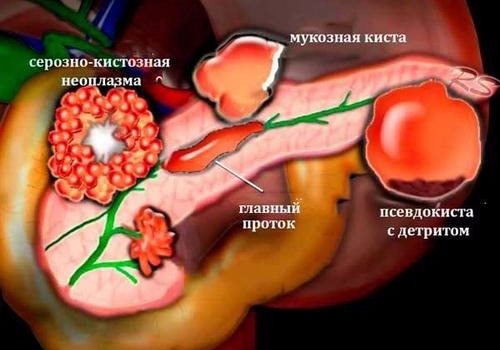
Classification of cystic lesions of a parenchymal organ
According to morphological indicators, all types of cystic lesions of the pancreas are divided into two main typologies:
- Formed during complications, formed during the development of an inflammatory disease of a parenchymal organ, without an epithelial lining, referred to as pseudocysts.
- Formed during obstructive processes in the cavity of the ducts, glands with a characteristic epithelial lining are called true cysts, or retention cysts.
In most cases, to assess cystic lesions of the pancreas, which has formed as an aggravation of the development of acute pancreatic pathology, the Atlanta classification is used, according to which the following varieties of this pathology are distinguished:
- acute fluid injury,
- subacute form with accumulated fluid,
- development of gland abscess.
Rapidly developing cysts with an acute course have incompletely formed walls of their cavity, which may include parapancreatic tissue, pancreatic ducts and the pancreatic parenchyma itself. But cystic formations formed during the chronic course of pancreatic pathology have walls made of fibrous and granulation tissue structures.
An abscess is a cavity filled with purulent contents formed during the development of pancreatic necrosis or suppuration of a cystic lesion.
Cysts can be localized both in the area of the head of the gland, its body, and in the tail area. Among other things, there is also an uncomplicated development of a pancreatic cyst and a complicated one. Cystic lesions can be complicated by the development of processes such as:
- perforation,
- suppuration,
- fistula formation,
- hemorrhage,
- progression of peritonitis,
- malignancy.