People sick with rotavirus usually have many questions related to the course of the disease. For example, what is rotavirus infection, symptoms and treatment, how it proceeds, how long it lasts. Interested in the incubation period, how not to infect your family, diet during illness and after recovery, disease prevention. I will try to answer all questions in this article. Since the symptoms of rotavirus and therapy in adults differ from the course of the disease in children, today we are talking about the disease in the older generation.
What is rotavirus infection
Other names for this serious disease are rotavirus, rotavirus gastroenteritis, and intestinal flu. Affects adults and children. Interestingly, the disease is often seasonal, with outbreaks more often recorded in spring and summer.
The causative agent of the disease is the PHK-rotavirus microorganism, which is highly resistant to low temperatures, remains viable when treated with chlorine, ethers, formaldehyde, and is not afraid of ultrasound. Bacteria lose activity when exposed to alkali, acidic environment and prolonged boiling.
In the external environment, bacteria can remain viable for up to several months. Once in the gastrointestinal tract of an adult, viral agents begin to actively multiply in the stomach and mucous membranes of the small intestine. As a result, it becomes inflamed and the first symptoms of the disease appear.
How many days does the disease last?
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the duration of the acute period of the disease is 3-7 days, followed by a recovery period lasting 4-5 days.
Causes of rotavirus infection in adults
The causative agent of rotavirus infection in adults is a virus belonging to the family Reoviridae, and its name comes from the Latin “Rota - wheel” due to the similarity of the shape of the virion to a wheel. The virion that provokes the development of rotavirus infection in adults has small parameters (up to 75 nm), and its genotype is represented by double-stranded RNA. Rotavirus is most successfully cultivated in laboratory conditions in the cells of the renal parenchyma of monkeys. The diversity of the antigenic composition of rotavirus allows it to be divided into serological types, of which only six types are pathogenic to humans. A special feature of rotaviruses is their ability to retain signs of vital activity in the most unfavorable environmental conditions. The only factors that are detrimental to rotavirus infection are exposure to extremely high temperatures, as well as treatment with concentrated alkaline solutions.
The source and reservoir of rotavirus infection is exclusively a person of any age. The duration of release of rotaviruses into the environment through the feces of a sick person is on average three weeks. Due to the fact that pathomorphological changes in rotavirus infection are found both in the intestines and in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, we can assume an airborne and nutritional method of transmission of infection from a sick person to a healthy person.
In countries with tropical climates, rotavirus infection is recorded by epidemiologists year-round among adults and children, but in the cool season there is a tendency to increase the level of rotavirus infection. Among the adult category of patients, an inapparent course of clinical symptoms is much more often observed in comparison with children, in whom the clinical manifestations of the disease are clearly expressed. After the end of the clinical picture of rotavirus infection in adults, the formation of persistent type-specific immune mechanisms is observed, allowing the body to resist against this serotype of the pathogen.
The pathogenesis of the development of rotavirus infection in adults consists of the predominant reproduction and accumulation of the pathogen in the upper parts of the intestinal tract with the highest concentration in the epithelial cells of the duodenum. Subsequently, viral particles enter the lumen of the affected intestinal tract. The negative impact of rotaviruses is the massive death of mature enterocytes, which are replaced by immature absorptive cells that are not able to absorb carbohydrates, which inevitably ends in the development of active osmotic-type diarrheal syndrome in the patient. Restoration of the intestinal mucosa usually occurs after one and a half to two months.
After the end of the active clinical period of rotavirus infection, powerful active and passive protective immune mechanisms begin to develop in the adult body, supported by resistance factors, which prevents the possibility of re-infection with the same serotype of the pathogen.
Rotavirus infection - symptoms and treatment in adults
And again, answers to exciting questions about the onset of the disease, the appearance of the first symptoms, and subsequent treatment and prevention.
How many days does it take for the infection to appear?
The incubation period of the disease is quite short, ranging from 12-15 hours to a week. But usually it is 1-2 days. During this period, a person feels weakness, heartburn, slight nausea, and mild pain in the intestines. Sometimes the temperature rises slightly, a slight runny nose and sore throat appear, which is extremely rare, unlike the childhood manifestation of the disease. Therefore, the onset of rotavirus disease is often confused with a common ARVI.
After the incubation period, the disease manifests itself in an acute form, sharply, with characteristic symptoms.
How many days is a rotavirus patient contagious?
Having fallen ill, a person becomes a carrier of the virus at the first symptoms of the disease. With proper and timely treatment, the infectious period lasts 2-7 days, until the sign of infection completely disappears.
How is rotavirus transmitted?
Animal rotaviruses do not pose a danger to humans; you can only catch the infection from other people. Many patients ask whether the virus is transmitted through airborne droplets. There are several ways to become infected with the virus:
- Through household objects - contact. These include transmission through shared personal hygiene items, in families where people are not accustomed to frequently washing their hands and observing other sanitary standards.
- With food – nutritional. A person becomes infected through food and drinking water. Prevention in this case is heat treatment of foods, washing vegetables and fruits, and boiling water.
- Airborne. Close contact with a sick person leads to the fact that infection occurs when a person sick with rotavirus sneezes and coughs.
Is it possible to become infected again?
Unfortunately, immunity after rotavirus infection does not last long. The transferred disease will not protect against re-infection later.

Symptoms of rotavirus infection in adults
Rotavirus infection in adults occurs more calmly than in children. There are no symptoms of severe intoxication. If a person has a strong, actively working immune system and high acidity of gastric juice, symptoms may be completely absent. Some patients mistake rotavirus infection for an intestinal disorder. Typically, adults experience the following symptoms:
- diarrhea appears;
- the person feels general malaise;
- nausea is present;
- there is a slight cough;
- a person feels pain in the epigastrium;
- there is low-grade fever and signs of rhinitis.
If a rotavirus infection occurs without symptoms in an adult, the person can still infect others. A carrier of infection who is in a group poses a danger to others. All the people he infected will take turns experiencing the infection within 5 days.
If a person has reached old age, suffers from chronic diseases or is faced with stress, rotavirus infection is quite severe. A number of other factors can also aggravate the disease.
The disease is dangerous for women carrying a child. Pathogenic organisms can cause dehydration. It has a negative effect on the fetus. Often the course of rotavirus infection is accompanied by bloating and contraction of the intestines. All this can cause a reflex spasm of the uterine muscles. This may lead to the risk of miscarriage or premature birth.
The most dangerous complication of rotavirus is dehydration. It occurs due to the loss of large amounts of water and salts during diarrhea and vomiting. The condition is characterized by the appearance of a headache, a decrease and then a complete cessation of urination, shortness of breath and tachycardia, dry mucous membranes and skin, lethargy, weakness and drowsiness. In severe cases, drooping eyes may occur. If at least one of the listed symptoms is present, the patient should be immediately taken to the hospital.
Rotavirus infection - symptoms in adults
Symptoms of intestinal flu in adults are somewhat less pronounced than in children. But it is better diagnosed, since in children the onset of rotavirus gastroenteritis is often confused with ARVI. Although in adults, the infection is often mistaken for simple food poisoning, since they have similar symptoms, read about them in another article.
There is no need to explain the importance of quickly recognizing the first signs of the disease; the main task is to begin treatment of the viral infection as soon as possible in order to avoid complications. Does rotavirus occur without diarrhea and vomiting? Know the signs of a virus infection.
Main symptoms:
- Severe vomiting.
- Non-stop diarrhea, frequent and severe. The color of the stool is cloudy yellow, with a sour odor, foaming.
- Pain and rumbling in the stomach.
- A noticeable decrease in appetite, even to the point of refusing food.
- Severe weakness, constant dry mouth.
- Signs of ARVI appear - runny nose.
- High temperature, dizziness.
- Redness of the eyes.
- There is a pronounced milky coating on the tongue.
- Reducing the frequency of urination.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- A urine test reveals elevated levels of protein, white blood cells, and red blood cells.
Signs of rotavirus infection in adults
The incubation period (asymptomatic) ranges from 3 to 7 days. In adults, the disease occurs as food poisoning and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- flatulence;
- hand tremors;
- smell of acetone from the mouth;
- tachycardia;
- copious secretion of saliva;
- dyspnea;
- chills;
- dizziness;
- bloating.
Under the influence of toxic agents, the process of fluid absorption is disrupted, acute diarrhea appears (up to 10-15 times a day), and repeated vomiting. All symptoms of rotavirus in adults increase the risk of decreased water and electrolyte balance.
With critical dehydration, hypovolemic shock, coma, and death are possible.
Symptoms of dehydration

Signs of decreased water-electrolyte balance in adults depend on the stage of its development. With mild dehydration, the following are observed:
- constant feeling of thirst;
- saliva viscosity;
- loss of appetite;
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- decrease in the amount of urine.
Articles on the topic
- Vomiting and diarrhea in an adult - treatment with drugs and folk remedies
- Rotavirus in children - signs and manifestations, treatment methods, consequences
- Pepidol - instructions for use, indications, mechanism of action and analogues
As the infection progresses, back pain, leg muscle spasms, headaches, and heartburn appear. In severe cases of dehydration, the symptoms of rotavirus infection in adults increase. Appears:
- excessive dry skin;
- repeated vomiting;
- lethargy;
- sunken eyes;
- delirium, up to loss of consciousness.
Treatment of rotavirus infection in adults
Having recognized the symptoms of rotavirus and consulted a doctor, it is important to follow all recommendations for treating the disease in order to avoid complications. Your doctor will tell you how to treat intestinal flu at home. Common recommendations include bed rest, avoiding contact with loved ones, drinking plenty of fluids and eating the right diet.
There are no specific drugs for the treatment and suppression of rotavirus itself. Treatment is aimed at eliminating symptoms - diarrhea and vomiting.
Medications
Frequently asked question: can I take antibiotics? No, they are usually not appointed, they have a different area of activity. Doctors prescribe medications that can replenish fluid and stop intoxication of the body.
- Spasms in the intestines are relieved with ordinary No-shpa.
- Reduce the temperature no earlier than the readings reach 38 degrees, let the body cope with the virus on its own, since most die at high temperatures. If the need arises, knock it down by taking Paracetamol, Nurofen, Coldrex, Rinza.
- To alleviate the state of intoxication, it is recommended to use sorbents that absorb and remove toxins from the body. These are activated carbon tablets, Polysorb, Smecta, Enterosgel, Liferan.
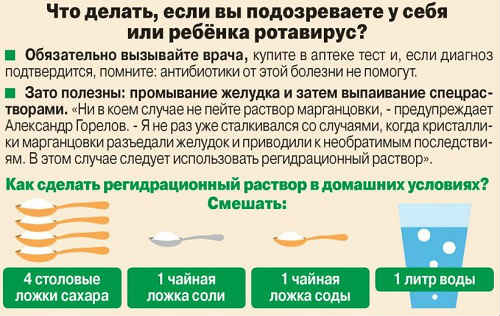
- If there is a large loss of fluid, the drug Regidron is prescribed, which retains fluid in the body. In its absence, make a simple saline solution at home.
Rotavirus infection during pregnancy
The symptoms of intestinal flu in pregnant women are the same as in other adults. Doctors say that this disease is not dangerous for the fetus.
When treating a pregnant woman, the main task is to prevent dehydration. Lack of fluid leads to the threat of miscarriage and premature birth, as it causes oxygen starvation in the fetus. Hence the doctor's recommendation - drink plenty of fluids.
What can you drink? Large quantities of fruit drink, still water, and compote are allowed.
Medicines prescribed include Polysorb, Smecta, and activated carbon tablets. It is allowed to bring down the high temperature. After the end of the acute period, it is recommended to restore the intestinal microflora with Lactobacillus preparations.
Restoration of microflora
With proper treatment, the symptoms of rotavirus soon disappear, and the time comes to restore the microflora in the intestines. In addition to diet, probiotics, for example Linex, are prescribed to those recovering.
Treatment of rotavirus infection
There are no special medications that will help cure rotavirus. Treatment is symptomatic. That is, if the patient is overcome by a gag reflex, then it should be suppressed; in case of high temperature, an antipyretic is given; in case of diarrhea, stool fixatives are needed.
It is very important to provide the patient with first aid to reduce the symptoms so that the disease proceeds as mildly as possible.
In the first days of the onset of the disease, you should not force the patient to eat if he has no appetite. It is necessary to eat something light and in small portions so as not to provoke vomiting. Under no circumstances should you eat dairy products, as they are a suitable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
During illness, it is very important to prevent dehydration; this is one of the most dangerous complications of the disease. It is necessary to constantly replenish the water-salt balance. An adult can regulate the amount of drink himself, but a child should be monitored and given 1 tsp every 5-10 minutes. water, or even better saline solution (rehydron). In case of severe intoxication, the patient is given intravenous fluids.
To remove toxic substances from the intestines, it is necessary to use sorbents during treatment: Enterosgel, Phosphalugel, Smecta, Activated Carbon, Polysorb, etc.
For diarrhea - Enterofuril and its analogues.
Intestinal viruses die on their own at high temperatures, so if the patient can easily tolerate the fever, then it is better not to lower the temperature. Children are given an antipyretic when their body temperature is above 38 ⁰ C - suppositories Tsefekon, Nurofen, liquid Paracetamol, Panadol, etc.
Read also Acute intestinal infection: routes of transmission, diagnosis, treatment
If you have digestive problems, it is recommended to take Mezim or Pancreatin.
In case of oral infection, it is necessary to restore the damaged intestinal microflora, otherwise dysbacteriosis may occur. For this, the doctor may prescribe Linex, Acipol, Baktisubtil, Bifiform.
When treating the disease, it is recommended to use antiviral drugs. For rotavirus in children, the following medications are used:
- Ingavirin.
- Viferon.
- Cycloferon.
- Lipoferon.
Antibiotics are not needed to treat mouth infections. The disease is caused by viruses, so antibacterial drugs are ineffective here.
Diet for illness
Among the main methods of treating intestinal flu is proper nutrition. In the acute period, and during recovery, you should definitely follow a diet. Most patients refuse food, do not force them to eat, it is better to drink more.
What can you eat
- Jelly, fruit drinks, decoctions of blueberries, currants, and raspberries are perfect.
- If the patient asks for food, at the beginning of the illness, cook chicken broth, liquid porridge in water, preferably rice.
- It is not forbidden to eat boiled meat, fish, and stale crackers.
- During the recovery stage, add dried bread, vegetable soups, mashed potatoes, cauliflower, jam, semolina, and buckwheat to your diet.
- Can you eat eggs? Yes, it is acceptable, but no more than 1 per day.
- The question about bananas is often asked. It is not prohibited, but in limited quantities, no more than one.

The diet implies dietary restrictions, so you absolutely cannot:
- Canned food, sausages, smoked meats.
- Baked goods and fresh bread.
- Dairy products, since the fermented milk environment is especially loved by viruses.
- Pasta, wheat cereals.
- Among vegetables, cabbage, garlic, radish, and onions are not allowed.
- Carbonated drinks, sweets, chocolate.
How to treat rotavirus infection in adults
The prognosis of therapy depends on the severity of clinical symptoms. With mild to moderate dehydration, the outcome is favorable. Long-term disturbance of water and electrolyte balance leads to the development of heart and kidney failure.
Treatment of rotavirus infections in adults with obvious signs is carried out in a hospital. The patient is prescribed:
- bed rest;
- drug therapy;
- rehydration treatment;
- a gentle diet.

Medicines for intestinal infections in adults
The basis of treatment is the intake of sorbents, antiemetics and probiotics. Antiviral drugs for rotavirus are additional. They improve immunity and speed up recovery. Antibiotics are not used for treatment.
Drug therapy includes taking the following medications or their analogues:
- Imodium is an antidiarrheal agent. Increases sphincter tone. Prescribed at the acute stage of rotavirus infection, 2 capsules. The tablet is placed on the tongue and dissolved.
- Polysorb is an enterosorbent. Removes toxins from the body. Adults are prescribed 100-200 mg of the drug per 1 kg of weight. Frequency of administration – 3 times/day.
- Arbidol is an immunostimulant. Strengthens antiviral protection. It is prescribed at a dosage of 200 mg every 6 hours. The course of admission is 5 days.
- Motilium is an antiemetic drug. Improves intestinal motility, accelerates the movement of food through the digestive tract, suppresses the gag reflex. Take 10 mg 3 times/day.
- Linex is a probiotic. Normalizes intestinal microflora. Take 2 capsules 3 times/day. The duration of treatment is determined individually.
Rehydration therapy
To avoid complications, saline solutions for oral rehydration are included in the treatment regimen. They replenish the balance of electrolytes and macroelements. Prescribed drugs:
- Regidron;
- Hydrovit;
- Trihydron;
- Humana electrolyte.
These medications come in the form of a powder. They are dissolved in liquid according to the instructions and taken orally. The course of treatment is selected individually. Sometimes intravenous administration of solutions of glucose, sodium chloride, and vitamins is carried out.
Article on the topic: Which is better Essentiale Forte or Karsil?
Diet for rotavirus in adults
Maintaining proper nutrition is an integral part of treating rotavirus infection. In the acute period, food should be easily digestible and provide the body with a set of essential nutrients. During the recovery stage, the diet helps normalize the intestinal microflora.
For rotaviruses, table No. 4 is prescribed. Its goal is maximum sparing of the gastric and intestinal mucosa. Basic principles of nutrition:
- Eating only warm food, in small portions (5-6 times/day).
- Refusal of cold and hot dishes, spices, preserves, hot spices.
- The consistency of the dishes is liquid or semi-liquid.
- Products must undergo heat treatment. Preferred cooking methods are boiling, stewing, and steaming.
- Refusal of milk and fatty dairy products (only for the acute period).
- Compliance with drinking regime. The optimal volume of liquid is 1.5-2.5 liters.

For the first 2-3 days, therapeutic fasting is recommended. Rusks, non-acidic compotes, jelly, and sweet tea are allowed. Then the diet consists of the following products:
- turkey;
- skinless chicken;
- buckwheat and semolina porridge;
- rice water;
- chicken or fish broth;
- crackers;
- yogurt;
- strong black tea;
- jelly;
- rosehip decoction;
- compote;
- soft-boiled eggs (no more than two per day);
- fresh cottage cheese.
Coffee, green tea, sour juices, whole milk, and alcohol are not recommended. Products prohibited:
- vegetable dishes;
- fatty fish/meat;
- smoked meats;
- bakery;
- fresh bread;
- hot spices;
- chocolate, sweets;
- ice cream;
- semi-finished products;
- pasta;
- fried eggs;
- wheat porridge.
Disease prevention
On vacation, in particular, in nature, by the sea and in the country, use boiled water. Not possible, buy bottled.
- Wash fruits and vegetables in running water.
- Eat quality foods.
- Remember to wash your hands, especially after visiting a public toilet, and keep alcohol-based hand gel in your purse.
- An excellent means of preventing intestinal infection is vaccination, which must be done in advance, before the onset of the spring-summer epidemic.
How not to infect your family
If there is a patient with rotavirus in the house, the following preventive measures will help protect against the disease:
- Eliminate contacts, allocate a separate room. Ventilate it often and do wet cleaning.
- If you are caring for a sick person and contact cannot be avoided, wear a mask covering the lower part of your face.
- The patient should have specially designated eating utensils; it is advisable to wash them separately from the rest of the utensils.
- To avoid infection, provide the patient with his own towel and bed linen.
Prevention of rotavirus infection in adults
If an adult has been in contact with a patient with rotavirus infection, then he needs to take the following preventive measures to avoid infection:
- Wash your hands and face using soap. Viruses could settle on the skin, from which they can easily enter the mouth.
- Change things. Clothes should be washed at high temperatures using washing powder. All items (ballpoint pens, mobile phone, bag, etc.) must be wiped with disinfectant solutions, such as alcohol or bleach.
- For preventive purposes, you can take an immunomodulator drug, for example, Kagocel. This will activate the body’s immune forces and prevent the virus from gaining a foothold in the mucous membrane of the intestinal wall.
- You need to pay special attention to your own health. It is necessary to control stool, body temperature, and monitor your own well-being. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor and inform him about the possibility of infection with rotaviruses.
- Perform a rota test. You can purchase a rapid test for detecting rotavirus infection at the pharmacy. It's easy to make at home. If the result is positive, you should consult a doctor.
As for immunity, it is developed after a single infection, but it is very weak and short-lived. Therefore, the likelihood that a person may become infected again with the same strain of the virus in the near future remains high. Moreover, immunity is formed only in relation to one type of virus, and there are seven of them (those that are capable of infecting humans). Therefore, infection can be avoided only if sanitary and hygienic standards are carefully observed.
Since adults most often become infected from sick children, they need to know and follow the rules of child care. First of all, this is high-quality disinfection. Wet cleaning in the room where the patient is located should be done 2-3 times a day. Moreover, the bathroom and toilet that are visited by a child or an infected adult are subject to disinfection. The patient's belongings and bedding should be washed at high temperatures and ironed. All items used must be treated with boiling water or disinfectant solutions. Every few hours you need to ventilate the room in which the patient is located, and after any contact with him, you need to wash your hands.
An adult with a rotavirus infection is given a sick leave certificate for a period of one week to 10 days. At this time, he is a source of spread of infection, so he must remain isolated from the team. In case of a complicated course of the disease, sick leave can be extended to 3 weeks or more, depending on the patient’s condition.