Ultrasound of the gallbladder and many other organs is extremely common nowadays due to its ease of implementation and high information content. Due to its structure and location, the gallbladder is perfectly visualized using an ultrasound wave. This makes it possible to detect most pathological processes in the organ both in adults and in the younger generation. The painlessness of the method allows each patient not to be afraid of the examination and to carry out simple preparation before it.
Indications for ultrasound of the bile duct
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the gallbladder cavity in case of disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system. Often, along with the gall bladder, other organs are examined - the intestines, liver, pancreas. Symptoms that may indicate a problem with the organ include:
- heaviness or pain in the area where the organ is located (right);
- nausea;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- disorders in the blood composition (bilirubin content, AST, ALT).
When treating diseases such as cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, dyskinesia, bladder tumors, ultrasound is performed regularly to monitor dynamics. Periodic examinations are prescribed when taking oral contraceptives and certain other medications due to the increased risk of stone formation. Monitoring the state of the digestive tract is necessary when following a diet or obesity.
Functional diagnostics of the gallbladder is performed on infants, especially those born prematurely, during a comprehensive health examination. The procedure is performed for children if they have the same alarming symptoms as adults.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder
Ultrasound diagnostics is an informative, non-invasive method for studying the biliary system. This method determines the condition of the gallbladder along with the ducts.
They are usually scanned in conjunction with all organs of the abdominal cavity.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the gallbladder? What can and cannot be done before the procedure? How is a load-bearing ultrasound of the gallbladder performed? What is a disabled bubble? What does the scan show? Let's look into these issues
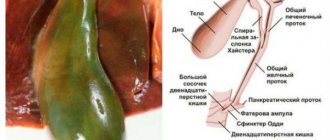
Anatomy of the hepatobiliary system
Indications for ultrasound
This study is prescribed by a gastroenterologist or therapist in the following cases:
- dull or paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium;
- suspicion of cancer;
- bitterness and dry mouth in the morning;
- cholelithiasis;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- icteric staining of the sclera and skin;
- dynamic monitoring of chronic diseases;
- changes in the level of bilirubin in the blood;
- obesity;
- chronic alcohol intoxication;
- abdominal injury;
- abuse of fatty foods;
- depleting diets;
- eating disorder.
Cholecystitis in women is a contraindication to taking hormonal drugs. When choosing contraceptives, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed.
How to prepare for research
Preparing for an ultrasound of the gallbladder involves following a diet and taking medications. It is recommended to follow a diet for 2 or 3 days before the session.
The recommended diet includes foods:
- buckwheat, oatmeal with water;
- low fat cottage cheese 2.5%;
- soft-boiled egg;
- a piece of boiled chicken or beef.
Foods that cause flatulence are excluded from the menu:
- yeast baked goods;
- legumes – lentils, beans, peas;
- fruits, vegetable salads, greens without heat treatment;
- coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks, milk.
Classic patient pose for pain in the gallbladder area
Medication preparation for the procedure for 2–3 days:
- It is recommended to take enzymes three times a day with meals - Festal, Creon, Pancreatin, Panzinorm;
- sorbents Enterosgel or Activated carbon 3 times a day between meals;
- Taking the carminative drug Espumisan three times eliminates flatulence.
Necessary actions before the ultrasound:
A light dinner at 7 p.m. is recommended. Before going to bed, you need to empty your bowels naturally. If there was no stool, put a glycerin suppository or make a Microlax microenema.
Actions on the morning of the examination:
- You only need to come to the procedure on an empty stomach. Can I drink liquid before the procedure? Drinking water is not recommended. Otherwise, a reflex release of bile will occur. A shortened gallbladder will give false results.
- What to do if the ultrasound is scheduled in the afternoon? In the morning, have a snack with crackers and tea. There should be 6 hours between breakfast and the session. If necessary, you can drink water 2-3 hours before the scan.
- Infants under 1 year of age are not given food and water 3–3.5 hours before the ultrasound.
- A child under 3 years of age is not given food or water 4 hours before the procedure. For children over 8 years old, the interval is 6 hours.
- Before the procedure, you should not smoke or use chewing gum.
Ultrasound technique
You must enter the scanning room without metal objects on your clothes or head. The person is asked to lie on his back and free the abdominal area from the shirt.
The doctor applies a gel to the transducer to eliminate the air cushion between the body and the sensor upon contact.
If the gallbladder is not visualized, the patient, at the doctor’s request, inhales deeply, holds his breath, or turns on his left side. To identify stones, a person must bend forward several times.
Preparing for Function Scanning
An ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of function is performed by a functional diagnostics doctor. The method reveals changes in the organ and its ducts after a choleretic breakfast. To determine contractility, monitoring is carried out with a functional test. But you won’t be able to do the research quickly. Preparation for the procedure is the same as for scanning the abdominal organs.
Diet before ultrasound a week before diagnosis:
- refusal to drink alcoholic beverages;
- exclude from the diet foods that cause flatulence - vegetables and fruits, whole milk, legumes and black bread;
- You are allowed to eat boiled fish and lean meat, water-based porridge, steamed cutlets, and dried bread.
Medication preparation 3 days earlier (you must coordinate the appointment with your doctor):
- Enzymatic agents - Pancreatin 10,000 units with each meal, washed down with a glass of water.
- For chronic constipation, it is recommended to take Lactulose daily at night.
- Drugs that stimulate the action of the intestines - Domperidone, Simethicone.
Actions the day before the procedure:
- Dinner no later than 8 pm consists of porridge with a minimum amount of sugar.
- In the evening, before going to bed, you should empty your bowels. If there was no stool, use a glycerin suppository. Attention! You can't do an enema.
Procedure on the day of the examination:
- Separate the yolks from the boiled eggs and bring them to the procedure. Instead, you can use 200 g of 20% sour cream as a choleretic agent. An alternative is also 20 g of sorbitol per 1 glass of warm water.
- If an ultrasound examination is performed in the middle of the day, you can have unsalted cheese, dried bread, and tea for breakfast at 7 a.m.
- You should not drink water before the session. Otherwise, the bile will be released before scanning. The results will be wrong.
When preparing a child, follow the same recommendations, only without the use of medications. Before the session, children under 3 years of age are not given food for 3 hours. The same interval before ultrasound of the gallbladder of a child up to one year old. Older children are not fed for 6 hours.
Carrying out a procedure with defining a function
Ultrasound of the gallbladder is done in stages at intervals:
- First, the norms of the organ parameters at rest are determined.
- A repeat scan is performed 5 minutes after breakfast.
- The next 2 sessions are done at intervals of 10 and 15 minutes.
The session takes place in the side and back position. Sometimes the patient is asked to get on all fours.
Interpretation of results
The interpretation of the ultrasound of the gallbladder is done 45 minutes from the start of the scan. During the scan, the doctor analyzes the following indicators: organ localization, bladder parameters, contractility, wall thickness, presence of sand or stones, diameter and patency of the ducts, whether there are neoplasms or polyps. The analysis takes into account the norms of organ parameters.
Dimensions of the gallbladder when examined by ultrasound:
- width 2–4 cm;
- length from isthmus to bottom from 4 to 10 cm;
- wall thickness does not exceed 3–4 mm;
- diameter of the common duct 6–8 mm;
- the internal diameter of the lobar ducts does not exceed 3 mm;
- The volume of the bladder in an adult is 35–70 cm3.
Qualified doctor's opinion
The normal size of this organ in children depends on height and body weight. The capacity of the bubble is calculated using the formula 0.5 x A x B x C. The value of A, B, C is length, width, thickness.
If the volume of the gallbladder is 60–80%, they speak of unimpaired function of the organ. A level above 80% indicates an increase in the contractility of the organ. In this case, based on ultrasound, a diagnosis of gallbladder dyskinesia of the hypertensive type is made. Volume less than 60% indicates dyskinesia with reduced motor function.
The results of the study are influenced by preparation for ultrasound of the gallbladder. Therefore, you need to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. Normally, an organ without pathology is pear-shaped, the cavity does not contain sand and stones. The walls are of normal thickness and contract after breakfast.
What diseases does ultrasound detect?
What does the examination show? Ultrasound detects diseases:
- The most common pathology is cholecystitis. The scan reveals an enlarged bladder with thickened walls. The cavity contains bubble inclusions and partitions. The contours of the light-colored walls are not clearly visible on the monitor screen. In a chronic process, the organ decreases in size and becomes deformed.
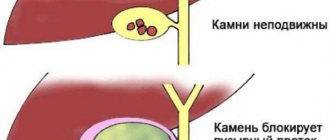
- Cholelithiasis is a gallstone disease. Ultrasound identifies stones in the bladder and ducts. When the body position changes, they shift. The walls of the organ are thickened with uneven edges. A sign of small stones on ultrasound is an expansion of the duct above the blockage. Stones are more often found in women than in men.
- Dyskinesia of the biliary tract is manifested during scanning by increased tone and thickening of the walls of the bladder. A bend in the neck is detected.
- The tumor is visualized as a mass. The walls of the deformed bladder are thickened.
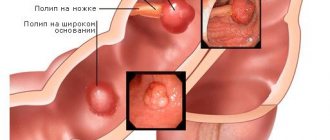
- Polyps appear on the monitor as round formations. A size greater than 1 cm requires dynamic monitoring, as there is a risk of a malignant process.
- Congenital pathology – double gallbladder or diverticulum.
The study of this part of the liver is carried out at the gastroenterology center. It is better to combine the procedure in combination with all digestive organs.
Ultrasound of a nonfunctional bladder
The functions of the gallbladder are the accumulation of bile and its release, if necessary, into the digestive system. The fluid is regularly produced in the liver lobules and flows through the duct into the bladder, which is a reservoir for its storage.
Important! Only during eating do its walls contract reflexively, and bile exits through the ducts into the duodenum. It is necessary for complete digestion and absorption of food in the small intestine, stimulating peristalsis.
A disabled gallbladder (GBB) is a non-functioning organ. The deformed bladder is filled with calculi (small stones), its walls are thickened, and consist of scars.
The organ does not accumulate bile and cannot release it into the intestines. The disease is caused by cholelithiasis, biliary dyskinesia, and chronic cholecystitis.
A rare meal contributes to the disease, when the liquid stagnates, thickens, and stones form from it, clogging the ducts.
A disabled gallbladder in the initial stage is manifested by signs of cholecystitis:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- heartburn;
- flatulence;
- temperature increase;
- dryness and bitterness in the mouth in the morning;
- icteric discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes;
- dyspeptic disorders - diarrhea or constipation.
Lime is deposited on the walls of the modified tank. They become dense, and the organ itself is called “porcelain”. Important! A disconnected bladder leads to the accumulation of pus. Breaking through the wall of the organ, it enters the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis.
The main study for suspected CBD is ultrasound. Ultrasound reveals 3 conditions:
- A disabled gallbladder that doesn't work. The reservoir does not respond with a reduction in breakfast. There is no bile in it, but pebbles may be found. The scan does not detect an organ cavity.
- The bubble is temporarily not functioning. Although it contains bile, the walls do not contract after breakfast. The fluid does not pass into the duodenum. In this case, ultrasound determines a small cavity with thickened walls. The bubble shape is deformed. This condition causes acute cholecystitis, cholelithiasis or hypotonic dyskinesia.
- Fully preserved contractile properties. In this case, there are no deviations from normal parameters.
If an ultrasound detects a blockage of a duct with a stone, the problem is solved with the help of a catheter. In other cases, surgery is required.
Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder is the main informative and painless diagnostic method. It is used at any age, including pregnant women, and has no contraindications. To determine the function of the bladder, an ultrasound is performed after a choleretic breakfast. To ensure an accurate examination, it is recommended to follow a diet in the preparatory period.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder Link to main publication
Source: https://CheckUpAdviser.ru/uzi/abdomen/uzi-zhelchnogo-puzyrya
What can a gallbladder ultrasound reveal?
Ultrasound diagnostics shows all abnormalities in the functioning of the organ, including at the initial stage, when it is possible to effectively treat them. It can reveal:
- inflammation (cholecystitis) in both acute and chronic forms;
- the presence of sand and hard stones in the gallbladder and ducts;
- tumors, polyps and other neoplasms;
- cessation of organ function as a result of blockage of the bile ducts and other reasons (disconnected gallbladder);
- congenital abnormal location and size of the organ;
- violation of contractile function - during dynamic studies.
The most frequently detected are cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. These diseases usually arise due to poor nutrition and accompanying digestive disorders.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the gallbladder
The manipulation is performed when the organ is filled and stretched. In this case, there should be no gases or food debris in the intestines that would interfere with viewing the gallbladder. To accumulate bile before the procedure, a short fast is necessary. When food enters the intestines, the bladder contracts and begins to secrete bile, which makes it difficult to consider all the parameters.
The last meal is allowed at least 6 hours before the procedure, and you should stop drinking water 2-3 hours before the gallstone ultrasound. This promotes the accumulation of a sufficient amount of bile in the bladder. You should also not chew gum or smoke to prevent air from entering the digestive tract. If the examination is scheduled for the morning, you can have porridge for dinner, but you cannot have breakfast.
When performing the procedure in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed 6 or more hours before the examination. Before the ultrasound, you need to empty your bowels yourself, using a laxative or an enema.
What can you drink and eat - diet before ultrasound
The principle of nutrition before the procedure should be aimed at reducing gas formation. To properly prepare for an ultrasound, you need to start a diet a week before the examination. Before an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder, you should not eat foods that increase gas formation in the intestines and stress on the liver:
- legumes;
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- flour products, yeast bread;
- fermented milk products (cottage cheese is allowed);
- dried fruits;
- fatty meat, milk;
- fried, sour, spicy foods;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
The main menu should consist of low-fat soups, boiled vegetables, cereals, cottage cheese, and compotes. Before an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder, you are allowed to eat 1 chicken egg per day. It is better to eat food often and in small portions so that it is completely digested. It is recommended to drink plenty of water (still). To improve digestion, some patients are prescribed medications based on pancreatic enzymes 2-3 days before the procedure.
Before an ultrasound, you can take adsorbents like activated carbon or special medications (Smecta, Enterosgel). Chamomile decoction is useful in preparing for research. If you are prone to gas formation, Espumisan or another drug that eliminates air bubbles in the intestines is prescribed before the procedure. Detailed recommendations about what you can eat and what medications to take are given by your doctor individually.
Preparatory measures
The doctor’s assumption about the presence of a pathological process in the gallbladder is an indication for prescribing an ultrasound. When making an appointment with an ultrasound diagnostic doctor or endoscopist, the patient receives recommendations regarding the preparatory period for the study:
- Three days before the diagnostic procedure, it is necessary to remove from the diet all foods that directly affect the formation of gases in the intestines. This applies to vegetables from the legume family, baked goods and other products produced using yeast. It is also worth excluding products of individual intolerance, for example, milk, intolerance of which is often observed in adults; children suffer less from this.
- Preparation for the procedure may also include the use of medications to reduce gas formation if this cannot be achieved through diet. It is possible to use herbal complexes, for example, a decoction of chamomile or mint. As prescribed by a doctor, enterosorbents or enzymatic agents are used to eliminate the problem, respectively, activated carbon and pancreatin (Creon, Mezim Forte).
- Some recommendations also relate to the examination plan for patients with diseases of the digestive tract. Thus, the gallbladder should be examined by ultrasound at least 3 days after fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This time is necessary to restore the gastrointestinal mucosa, probably damaged by the mechanical action of invasive devices, which affects the microflora of organs and their acidic environment. Restoring the normal state of the duodenum maximally reflects the work of the gallbladder in everyday life.
Naturally, if you need to do an ultrasound of the gallbladder urgently, there is no preparatory stage at all. Immediate treatment requires stone obstruction of the organ ducts, which is easily diagnosed by ultrasound.
Methodology
An ultrasound examination is performed in a supine position on a couch. A functional diagnostics specialist applies cream to the right side of the abdomen to improve the passage of waves. Then a scanner is applied to the area of the gallbladder and an image of the internal organs is visualized on the screen. No special interpretation of the results is required - the doctor evaluates and records the echographic image of the organs and parameters during the procedure. The examination does not cause any discomfort or pain for the patient.
To give the doctor a better look at the organ, you may need to take a deep breath or lie on your side. If you suspect the presence of stones, you need to bend over and change your body position. This will help distinguish stones from other opacities.
Conventional echo scanning
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. The bladder should be filled with bile and be in a calm state (without contractions). Bile helps determine the exact size of the organ, wall thickness, and the presence of stones or tumors. The doctor can see the approximate structure of the bile - thickness, presence of sand.
Echo scanning in dynamics
This is a procedure to study the contractile function of the gallbladder. Before an ultrasound of the gallbladder in dynamics - with a load - a routine examination is carried out, and then with the help of food or a sorbitol solution, contractions of the bladder and the separation of bile are caused.
Cottage cheese, sour cream, and egg yolks are used as choleretic foods. A functional test is carried out after a regular ultrasound to compare the results - three times at intervals of 10-15 minutes. This makes it possible to identify abnormalities that were not noticeable on ultrasound.
Dynamic echo-choledochography
The study is carried out in people who have had their gallbladder removed. The function of bile secretion is determined, its movement along the ducts in the absence of a “reservoir” for accumulation. The first stage of ultrasound of the gallbladder in dynamics with determination of function is carried out before meals, the second - after it (after 30-60 minutes).
Progress of the diagnostic procedure
Preparation for an ultrasound of the gallbladder precedes the actual examination. During the procedure, simple steps are performed; the examination is performed abdominally:
- The patient is asked to remove clothing from his stomach and lie on his back on a couch located in an equipped office.
- To perform an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the anatomical area of the right hypochondrium is examined. This surface is coated with a gel-like substance for better transmission of the ultrasonic wave and a small sensor is placed here.
- With a standard physique and optimal body mass index of the patient, the gallbladder is perfectly visualized. Some discomfort may be felt by patients with a developed layer of fatty tissue, on which the doctor will have to press in order to obtain a reliable ultrasound picture. If there is cholecystitis in the acute phase of its development, a diagnostic examination may also provoke some pain.
- The study includes measuring the size of the gallbladder, assessing its shape and mobility. The condition of the walls of the bladder, the presence of sand, stones, constrictions and other pathological formations in it are of diagnostic importance.
Features of ultrasound examination allow on-site interpretation of the results obtained on the screen of specialized equipment.
Decoding the results
Ultrasound allows you to see deviations in the size and volume of the gallbladder and ducts, thickening of its walls, stagnation of bile, the presence of stones and neoplasms, and assess contractility.
Normal for adults
Normal indicators detected during ultrasound of the gallbladder in adults are shown in the table.
| Index | Meaning |
| Volume of the bile filled bladder | from 30 to 70 cm3 |
| Organ shape | pear-shaped or oval |
| Location | under the liver or with a protrusion of 1-1.5 cm from its edge |
| Length | from 4 to 10 cm |
| Width | From 3 to 5 cm |
| Wall boundaries | clear boundaries |
| Wall thickness | up to 4 mm |
| Contractility after eating | up to 70% |
| Duct diameter | 6-8 mm |
| Diameter of lobar ducts | up to 3 mm |
| Stones | none |
| Polyps | none |
| Tumors | none |
| Thickening of bile | absence of stagnation |
Deviation from the norm
First of all, the presence of pathology is indicated by a change in the normal size of the gallbladder. If the function is impaired, the volume decreases and swelling of the mucous membrane occurs. Pus, thickening or stagnation of bile (looks like “flakes” in the liquid) are sometimes found in the organ. If there is a metabolic disorder, the walls may be covered with cholesterol or calcareous deposits.
Impaired contractility indicates dyskinesia. The normal figure according to the table is 70%. The tone of the organ can be either increased (more than 80% - hypertonicity of the gallbladder) or decreased (up to 60% - hypotonic dyskinesia).
Thickening of the walls (swelling of the mucous membrane) most often occurs during the inflammatory process. In this case, stones are usually present in the bladder. Dilation of the bile ducts also indicates a malfunction of the organ or the presence of stones. Ultrasound helps determine the exact location of stones and assess the possibility of their medical and surgical treatment.
Sometimes during the examination it is discovered that the organ is excluded from the digestive process. The gallbladder is visualized on ultrasound as a wrinkled, empty sac. The reason for this may be blockage of the ducts with stones or adhesions (which is also detected on ultrasound), weakening and deformation of the organ due to chronic inflammation over a long time, or a tumor disease.
Sometimes deviations from the norm in the size and shape of the gallbladder in adults and children indicate a congenital deformity. There is such an anomaly as a double organ (diverticulum).
Ultrasound is the main method for studying gallbladder diseases. It provides accurate information about the condition of the organ, helps to detect pathologies, begin their treatment on time and avoid its removal.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder - preparation, functions and interpretation
Ultrasound diagnostics is an effective and harmless method for identifying pathologies of various organs. An examination of the gallbladder is carried out both when a disease is suspected and during a general diagnosis of the body. Ultrasound results are influenced by quality preparation, so before performing the procedure you must follow a diet according to your doctor’s recommendations.
Indications for ultrasound of the bile duct
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the gallbladder cavity in case of disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system. Often, along with the gall bladder, other organs are examined - the intestines, liver, pancreas. Symptoms that may indicate a problem with the organ include:
- heaviness or pain in the area where the organ is located (right);
- nausea;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- disorders in the blood composition (bilirubin content, AST, ALT).
When treating diseases such as cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, dyskinesia, bladder tumors, ultrasound is performed regularly to monitor dynamics. Periodic examinations are prescribed when taking oral contraceptives and certain other medications due to the increased risk of stone formation. Monitoring the state of the digestive tract is necessary when following a diet or obesity.
Functional diagnostics of the gallbladder is performed on infants, especially those born prematurely, during a comprehensive health examination. The procedure is performed for children if they have the same alarming symptoms as adults.
Contraindications
The method of ultrasound examination of the parameters of the gallbladder is harmless to everyone and can be used for diagnosis at any age. The procedure is also performed on children and pregnant women. The diagnosis should be postponed only if there is a wound or burn on the skin at the scan site.
What can a gallbladder ultrasound reveal?
Ultrasound diagnostics shows all abnormalities in the functioning of the organ, including at the initial stage, when it is possible to effectively treat them. It can reveal:
- inflammation (cholecystitis) in both acute and chronic forms;
- the presence of sand and hard stones in the gallbladder and ducts;
- tumors, polyps and other neoplasms;
- cessation of organ function as a result of blockage of the bile ducts and other reasons (disconnected gallbladder);
- congenital abnormal location and size of the organ;
- violation of contractile function - during dynamic studies.
The most frequently detected are cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. These diseases usually arise due to poor nutrition and accompanying digestive disorders.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the gallbladder
The manipulation is performed when the organ is filled and stretched. In this case, there should be no gases or food debris in the intestines that would interfere with viewing the gallbladder. To accumulate bile before the procedure, a short fast is necessary. When food enters the intestines, the bladder contracts and begins to secrete bile, which makes it difficult to consider all the parameters.
The last meal is allowed at least 6 hours before the procedure, and you should stop drinking water 2-3 hours before the gallstone ultrasound. This promotes the accumulation of a sufficient amount of bile in the bladder. You should also not chew gum or smoke to prevent air from entering the digestive tract. If the examination is scheduled for the morning, you can have porridge for dinner, but you cannot have breakfast.
When performing the procedure in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed 6 or more hours before the examination. Before the ultrasound, you need to empty your bowels yourself, using a laxative or an enema.
What can you drink and eat - diet before ultrasound
The principle of nutrition before the procedure should be aimed at reducing gas formation. To properly prepare for an ultrasound, you need to start a diet a week before the examination. Before an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder, you should not eat foods that increase gas formation in the intestines and stress on the liver:
- legumes;
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- flour products, yeast bread;
- fermented milk products (cottage cheese is allowed);
- dried fruits;
- fatty meat, milk;
- fried, sour, spicy foods;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
The main menu should consist of low-fat soups, boiled vegetables, cereals, cottage cheese, and compotes. Before an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder, you are allowed to eat 1 chicken egg per day.
It is better to eat food often and in small portions so that it is completely digested. It is recommended to drink plenty of water (still).
To improve digestion, some patients are prescribed medications based on pancreatic enzymes 2-3 days before the procedure.
Before an ultrasound, you can take adsorbents like activated carbon or special medications (Smecta, Enterosgel). Chamomile decoction is useful in preparing for research.
If you are prone to gas formation, Espumisan or another drug that eliminates air bubbles in the intestines is prescribed before the procedure.
Detailed recommendations about what you can eat and what medications to take are given by your doctor individually.
Methodology
An ultrasound examination is performed in a supine position on a couch. A functional diagnostics specialist applies cream to the right side of the abdomen to improve the passage of waves.
Then a scanner is applied to the area of the gallbladder and an image of the internal organs is visualized on the screen. No special interpretation of the results is required - the doctor evaluates and records the echographic image of the organs and parameters during the procedure.
The examination does not cause any discomfort or pain for the patient.
To give the doctor a better look at the organ, you may need to take a deep breath or lie on your side. If you suspect the presence of stones, you need to bend over and change your body position. This will help distinguish stones from other opacities.
Conventional echo scanning
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. The bladder should be filled with bile and be in a calm state (without contractions). Bile helps determine the exact size of the organ, wall thickness, and the presence of stones or tumors. The doctor can see the approximate structure of the bile - thickness, presence of sand.
Echo scanning in dynamics
This is a procedure to study the contractile function of the gallbladder. Before an ultrasound of the gallbladder in dynamics - with a load - a routine examination is carried out, and then with the help of food or a sorbitol solution, contractions of the bladder and the separation of bile are caused.
Cottage cheese, sour cream, and egg yolks are used as choleretic foods. A functional test is carried out after a regular ultrasound to compare the results - three times at intervals of 10-15 minutes. This makes it possible to identify abnormalities that were not noticeable on ultrasound.
Dynamic echo-choledochography
The study is carried out in people who have had their gallbladder removed. The function of bile secretion is determined, its movement along the ducts in the absence of a “reservoir” for accumulation. The first stage of ultrasound of the gallbladder in dynamics with determination of function is carried out before meals, the second - after it (after 30-60 minutes).
Decoding the results
Ultrasound allows you to see deviations in the size and volume of the gallbladder and ducts, thickening of its walls, stagnation of bile, the presence of stones and neoplasms, and assess contractility.
Normal for adults
Normal indicators detected during ultrasound of the gallbladder in adults are shown in the table.
| Index | Meaning |
| Volume of the bile filled bladder | from 30 to 70 cm3 |
| Organ shape | pear-shaped or oval |
| Location | under the liver or with a protrusion of 1-1.5 cm from its edge |
| Length | from 4 to 10 cm |
| Width | From 3 to 5 cm |
| Wall boundaries | clear boundaries |
| Wall thickness | up to 4 mm |
| Contractility after eating | up to 70% |
| Duct diameter | 6-8 mm |
| Diameter of lobar ducts | up to 3 mm |
| Stones | none |
| Polyps | none |
| Tumors | none |
| Thickening of bile | absence of stagnation |
Deviation from the norm
First of all, the presence of pathology is indicated by a change in the normal size of the gallbladder. If the function is impaired, the volume decreases and swelling of the mucous membrane occurs. Pus, thickening or stagnation of bile (looks like “flakes” in the liquid) are sometimes found in the organ. If there is a metabolic disorder, the walls may be covered with cholesterol or calcareous deposits.
Impaired contractility indicates dyskinesia. The normal figure according to the table is 70%. The tone of the organ can be either increased (more than 80% - hypertonicity of the gallbladder) or decreased (up to 60% - hypotonic dyskinesia).
Thickening of the walls (swelling of the mucous membrane) most often occurs during the inflammatory process. In this case, stones are usually present in the bladder. Dilation of the bile ducts also indicates a malfunction of the organ or the presence of stones. Ultrasound helps determine the exact location of stones and assess the possibility of their medical and surgical treatment.
Sometimes during the examination it is discovered that the organ is excluded from the digestive process. The gallbladder is visualized on ultrasound as a wrinkled, empty sac. The reason for this may be blockage of the ducts with stones or adhesions (which is also detected on ultrasound), weakening and deformation of the organ due to chronic inflammation over a long time, or a tumor disease.
Sometimes deviations from the norm in the size and shape of the gallbladder in adults and children indicate a congenital deformity. There is such an anomaly as a double organ (diverticulum).
Ultrasound is the main method for studying gallbladder diseases. It provides accurate information about the condition of the organ, helps to detect pathologies, begin their treatment on time and avoid its removal.
Source: https://puzyr.info/uzi-zhelchnogo-puzyrya/